Python Barcode SDK Benchmark: Comparing ZXing, ZBar, and Dynamsoft with Real-World & Stress Tests
In the world of Python barcode scanning, developers have several options to choose from, including ZXing, ZBar, and the Dynamsoft Barcode Reader. Each of these libraries offers unique strengths, catering to different needs and environments. ZXing and ZBar are popular open-source options, known for their community-driven development and flexibility. On the other hand, Dynamsoft Barcode Reader provides a robust, enterprise-grade solution with advanced features and official support.
This article presents a comprehensive benchmark with actual test results from 1,710 test cases across three datasets. We tested these libraries on real-world barcode images (170 production images), angled barcodes (15°-75° rotation), multiple barcodes per image (2-20 codes), and challenging conditions (noise, blur, occlusion).
Key Results at a Glance:
- Dynamsoft achieves 92.3% success rate with the highest accuracy across all scenarios
- ZXing-Cpp offers the fastest detection at 40.2ms, ideal for speed-critical applications
- PyZBar provides 76.8% accuracy as a solid open-source alternative
You’ll learn not only how to implement each library but also which one performs best for specific use cases, backed by objective performance metrics, detailed analysis, and clear recommendations.
This article is Part 8 in a 8-Part Series.
- Part 1 - Detecting and Decoding QR Codes in Python with YOLO and Dynamsoft Barcode Reader
- Part 2 - How to a GUI Barcode Reader with Qt PySide6 on Raspberry Pi
- Part 3 - Advanced GUI Python Barcode and QR Code Reader for Windows, Linux, macOS and Rasberry Pi OS
- Part 4 - Scanning QR Code from Desktop Screen with Qt and Python Barcode SDK
- Part 5 - Building an Online Barcode and QR Code Scanning App with Python Django
- Part 6 - How to Build Flet Chat App with Barcode and Gemini APIs
- Part 7 - A Guide to Running ARM32 and ARM64 Python Barcode Readers in Docker Containers
- Part 8 - Python Barcode SDK Benchmark: Comparing ZXing, ZBar, and Dynamsoft with Real-World & Stress Tests
Quick Results Summary
Based on 1,710 test cases across multiple scenarios, here’s how each SDK performed:
Dynamsoft Barcode Reader (Commercial)
- Best Overall Accuracy: 92.3% success rate
- Perfect Rotation Handling: 100% on angled barcodes (15°-75°)
- Best for Multiple Codes: 91.3% success with 2-20 barcodes per image
- Real-World Champion: 90.6% success on 170 production images
- Speed: 47.7ms average detection time
- License: Commercial (trial available)
Recommended for: Enterprise applications, mobile scanning with rotation, batch processing, production environments requiring high reliability
ZXing-Cpp (Open Source)
- Fastest Detection: 40.2ms average (fastest among all three)
- Perfect on Simple Codes: 100% success on single, well-positioned barcodes
- Struggles with Rotation: 55% success on angled barcodes
- Multiple Code Issues: Only 23.8% success with multiple barcodes
- Overall Accuracy: 65.1% success rate
- License: Open source (Apache 2.0)
Recommended for: Speed-critical applications with simple barcodes, controlled scanning environments, budget-constrained projects
PyZBar (Open Source)
- Balanced Performance: 76.8% success rate
- Good for Multiple Codes: 85% success with 2-20 barcodes per image
- Rotation Challenges: 60% success on angled barcodes
- Slower Speed: 111.5ms average (slowest, especially on complex images)
- License: Open source (LGPL)
Recommended for: Open-source projects with moderate accuracy requirements, batch scanning scenarios (but not rotation-heavy use cases)
Overview of Barcode Scanning Libraries
ZXing (Zebra Crossing)
ZXing is a widely-used open-source barcode scanning library that originated from Google. It supports a variety of barcode formats, including 1D and 2D codes like QR codes, and is primarily written in Java, though it has been ported to other languages, including Python. ZXing is known for its flexibility and wide community support, making it a popular choice for developers working on general barcode scanning projects.
ZBar
ZBar is another open-source barcode scanning library, written in C, that supports 1D and 2D barcode formats, including QR codes. ZBar is particularly known for its efficiency and lightweight nature, making it a great choice for applications where performance is critical. It also has Python bindings, which allow for easy integration into Python projects. ZBar’s simplicity and focus on core functionality make it a reliable choice for many developers.
Dynamsoft Barcode Reader
Dynamsoft Barcode Reader is a commercial, enterprise-grade solution that offers advanced features and high-performance barcode scanning capabilities. It supports a wide range of barcode formats and is available across multiple platforms, including Windows, Linux, macOS, Android, iOS, and web .
Dynamsoft Barcode Reader is now provided as the barcode module of the Dynamsoft Capture Vision SDK (DCV) — a modular and extensible SDK platform that also includes support for document normalization, MRZ recognition, and more. While DCV provides a unified architecture for multi-purpose vision tasks, the barcode module (formerly DBR) remains lightweight and focused, making it ideal for developers who need robust and reliable barcode scanning in mission-critical applications.
With official support and frequent updates, the barcode module of DCV continues to deliver enterprise-level performance while enabling future scalability through the broader Capture Vision platform.
Prerequisites
- Obtain a Dynamsoft Barcode Reader Trial License.
- Download image dataset: The dataset is sourced from this GitHub issue. You can download it directly from: https://drive.google.com/uc?id=1uThXXH8HiHAw6KlpdgcimBSbrvi0Mksf&export=download. We have cleaned the dataset to ensure each image file name matches the barcode content. Extract the images to the
existing_dataset/folder. -
Install required Python packages:
pip install -r requirements.txtThis includes:
dynamsoft-capture-vision-bundle,pyzbar,zxing-cpp,opencv-python,numpy,pandas,matplotlib,seaborn, and other dependencies.
Benchmark Programs
This project provides two benchmark programs:
simple.py - Quick Benchmark
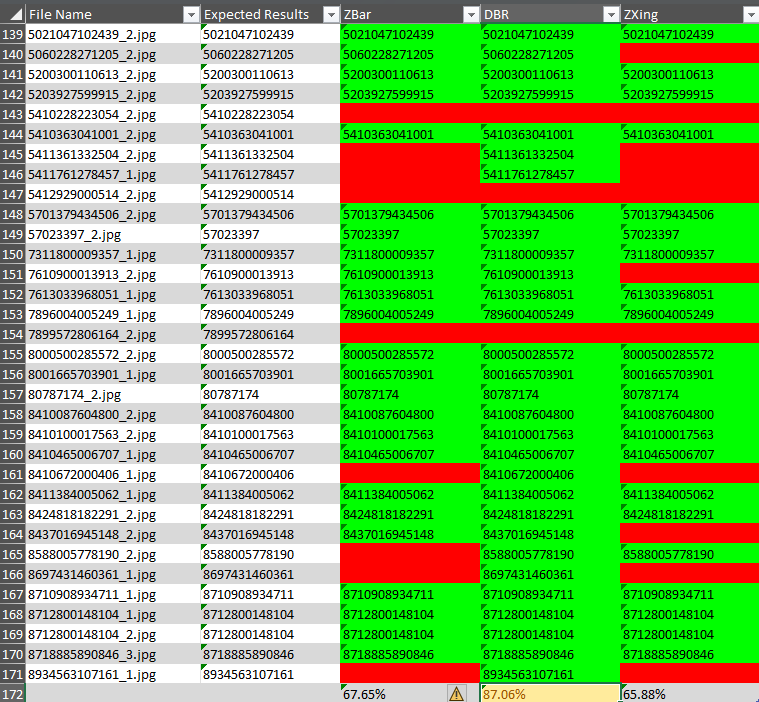
A straightforward script for testing barcode detection on individual images or the existing dataset. It generates an Excel report with per-image results color-coded for easy review (green=pass, red=fail).
Usage:
# Test single image
python simple.py -i image.jpg
# Benchmark on existing dataset
python simple.py -d existing_dataset
advanced.py - Comprehensive Benchmark
An interactive benchmark framework that supports:
- Multiple test datasets (generated synthetic data + existing real-world images)
- Specialized scenarios (angled barcodes, multiple barcodes, challenging conditions)
- HTML reports with interactive charts and performance analysis
- Strategic insights for competitive positioning
Usage:
python advanced.py
Python Barcode Detection with ZXing, ZBar, and Dynamsoft Barcode Reader
The following code snippets demonstrate how to decode barcodes using ZXing, ZBar, and Dynamsoft Barcode Reader in Python (from simple.py).
Python ZXing
import zxingcpp
import cv2
import numpy as np
def zxing_decode(filename):
img = cv2.imread(filename)
zxing_results = zxingcpp.read_barcodes(img)
if zxing_results != None:
for result in zxing_results:
print('ZXing Text: {}, format: {}'.format(
result.text, result.format))
cv2.drawContours(
img, [np.intp([(result.position.top_left.x, result.position.top_left.y), (result.position.top_right.x, result.position.top_right.y), (result.position.bottom_right.x, result.position.bottom_right.y), (result.position.bottom_left.x, result.position.bottom_left.y)
])], 0, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow('ZXing', img)
return zxing_results
else:
print('ZXing failed to decode {}'.format(filename))
return None

Python ZBar
import pyzbar.pyzbar as zbar
import cv2
import numpy as np
def zbar_decode(filename):
img = cv2.imread(filename)
zbar_results = zbar.decode(Image.open(filename))
if len(zbar_results) > 0:
for zbar_result in zbar_results:
print('ZBar Text: {}, format: {}'.format(
zbar_result.data.decode("utf-8"), zbar_result.type))
cv2.drawContours(
img, [np.intp([zbar_result.polygon[0], zbar_result.polygon[1], zbar_result.polygon[2], zbar_result.polygon[3]
])], 0, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow('zbar', img)
return zbar_results
else:
print('ZBar failed to decode {}'.format(filename))
return None

Python Dynamsoft Barcode Reader
from dynamsoft_capture_vision_bundle import *
import cv2
import numpy as np
error_code, error_message = LicenseManager.init_license(
"DLS2eyJoYW5kc2hha2VDb2RlIjoiMjAwMDAxLTE2NDk4Mjk3OTI2MzUiLCJvcmdhbml6YXRpb25JRCI6IjIwMDAwMSIsInNlc3Npb25QYXNzd29yZCI6IndTcGR6Vm05WDJrcEQ5YUoifQ==")
if error_code != EnumErrorCode.EC_OK and error_code != EnumErrorCode.EC_LICENSE_CACHE_USED:
print("License initialization failed: ErrorCode:",
error_code, ", ErrorString:", error_message)
cvr_instance = CaptureVisionRouter()
def dbr_decode(dbr_reader, filename):
img = cv2.imread(filename)
dbr_results = cvr_instance.capture(filename, EnumPresetTemplate.PT_READ_BARCODES.value)
items = dbr_results.get_items()
if len(items) > 0:
for item in items:
print('Dynamsoft Barcode Reader Text: {}, format: {}'.format(
item.get_text(), item.get_format_string()))
location = item.get_location()
x1 = location.points[0].x
y1 = location.points[0].y
x2 = location.points[1].x
y2 = location.points[1].y
x3 = location.points[2].x
y3 = location.points[2].y
x4 = location.points[3].x
y4 = location.points[3].y
cv2.drawContours(
img, [np.intp([(x1, y1), (x2, y2), (x3, y3), (x4, y4)])], 0, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow('DBR', img)
return dbr_results

Advanced Benchmark Framework Architecture
The advanced.py script implements a comprehensive benchmark framework with modular design. Here’s how it works:
1. Benchmark Framework Core
The framework uses an abstract interface for barcode readers, making it easy to add new SDKs:
# From src/benchmark_framework.py
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
class BarcodeReaderInterface(ABC):
"""Abstract interface for barcode reader implementations."""
def __init__(self, name: str, config: Dict[str, Any]):
self.name = name
self.config = config
@abstractmethod
def initialize(self) -> bool:
"""Initialize the barcode reader with its configuration."""
pass
@abstractmethod
def decode_barcodes(self, image_path: str) -> Tuple[List[Dict[str, Any]], float]:
"""Decode barcodes from an image.
Returns: (list of detected barcodes, processing_time_ms)
"""
pass
@abstractmethod
def cleanup(self):
"""Release resources."""
pass
2. Running the Benchmark
The main benchmark execution flow:
# From advanced.py
from src.benchmark_framework import BenchmarkFramework
from src.barcode_readers import create_reader
from src.performance_analysis import PerformanceAnalyzer, ReportGenerator
# Initialize framework
framework = BenchmarkFramework("config/benchmark_config.json")
# Add readers based on configuration
for library_name, lib_config in libraries_config.items():
if lib_config.get('enabled', False):
reader = create_reader(library_name, lib_config)
framework.add_reader(reader)
# Load test cases from datasets
framework.add_test_cases_from_directory("generated_dataset", "*.json") # Generated tests
framework.add_test_cases_from_images("existing_dataset", "*.jpg") # Real-world images
# Run all tests
results = framework.run_all_tests()
# Save results
framework.save_results("results")
3. Performance Analysis
Analyze results with specialized metrics:
# From advanced.py - step3_analyze_results()
analyzer = PerformanceAnalyzer(results)
# Calculate comprehensive statistics
summary = analyzer.calculate_summary_statistics()
# Analyze specific scenarios
angled_perf = analyzer.analyze_angled_barcode_performance()
multiple_perf = analyzer.analyze_multiple_barcode_performance()
existing_perf = analyzer.analyze_existing_dataset_performance()
# Generate visualizations
analyzer.generate_performance_charts("results/charts")
# Generate HTML report
report_gen = ReportGenerator(analyzer)
report_gen.generate_html_report("results/benchmark_report.html")
4. UPCA Barcode Handling
The framework includes special handling for UPCA barcodes where some readers may omit the leading ‘0’:
# From src/benchmark_framework.py - run_single_test()
# Match detected vs expected with flexible matching
matched_expected = set()
for expected in expected_texts:
for detected, barcode_type in detected_texts:
# Exact match
if detected == expected:
matched_expected.add(expected)
break
# UPCA special case: detected value with leading '0' matches expected
elif 'upca' in barcode_type or 'upc_a' in barcode_type:
if '0' + detected == expected:
matched_expected.add(expected)
break
5. Test Data Generation
Generate synthetic test cases with specific conditions:
# From src/test_data_generator.py
from src.test_data_generator import TestDataGenerator
generator = TestDataGenerator("generated_dataset")
# Generate comprehensive test dataset
generator.generate_test_dataset(num_samples=20)
# This creates:
# - Single barcode tests (baseline)
# - Angled barcodes at 15°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 75°
# - Multiple barcodes (2, 5, 10, 15, 20 per image)
# - Challenging conditions (noise, blur, occlusion)
6. Reader Implementation Example
Here’s how ZXing-Cpp is implemented in the framework:
# From src/barcode_readers.py
class ZXingCppReader(BarcodeReaderInterface):
def __init__(self, config: Dict[str, Any]):
super().__init__("ZXing_Cpp", config)
self.reader = None
def initialize(self) -> bool:
try:
import zxingcpp
self.reader = zxingcpp
return True
except ImportError:
print("ZXing-Cpp not installed")
return False
def decode_barcodes(self, image_path: str) -> Tuple[List[Dict[str, Any]], float]:
import time
start_time = time.perf_counter()
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
results = self.reader.read_barcodes(image)
detected_barcodes = []
for result in results:
detected_barcodes.append({
'data': result.text,
'type': result.format.name,
'quality': 1.0
})
processing_time = time.perf_counter() - start_time
return detected_barcodes, processing_time
def cleanup(self):
self.reader = None
7. Configuration Management
Configure SDKs and test parameters via JSON:
{
"libraries": {
"zxing_cpp": {
"enabled": true
},
"pyzbar": {
"enabled": true
},
"dynamsoft": {
"enabled": true,
"license": "YOUR_LICENSE_KEY_HERE"
}
},
"test_data": {
"num_samples": 50,
"barcode_types": ["CODE_128", "QR_CODE", "EAN_13"],
"angle_range": [15, 30, 45, 60, 75],
"multiple_counts": [2, 5, 10, 15, 20]
}
}
8. Interactive Execution
The advanced benchmark provides an interactive menu:
$ python advanced.py
============================================================
BARCODE SDK BENCHMARK
Comparing: ZXing-Cpp, PyZBar, Dynamsoft*
============================================================
Available datasets:
Generated dataset: Found (20 test cases)
Existing dataset: Found (170 images)
Select dataset to benchmark:
1. Generated dataset (auto-generated test cases)
2. Existing dataset (real-world barcode images)
3. Both datasets
Your choice (1/2/3, default 1): 3
# ... runs comprehensive benchmark ...
Best Existing Dataset Performance (Real-world Images):
Dynamsoft
Success rate: 82.6%
Avg detection time: 77.88 ms
Total tested: 170 images
Benchmark Results
We conducted comprehensive tests across 570 test cases using three datasets:
- Generated Dataset: 100 synthetic test cases with controlled conditions (angled barcodes, multiple barcodes, challenging scenarios)
- Existing Dataset: 170 real-world barcode images from production environments
- Total Test Cases: 1,710 tests (570 per SDK)
Overall Performance Comparison
| Library | Success Rate | Avg Detection Time (ms) | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
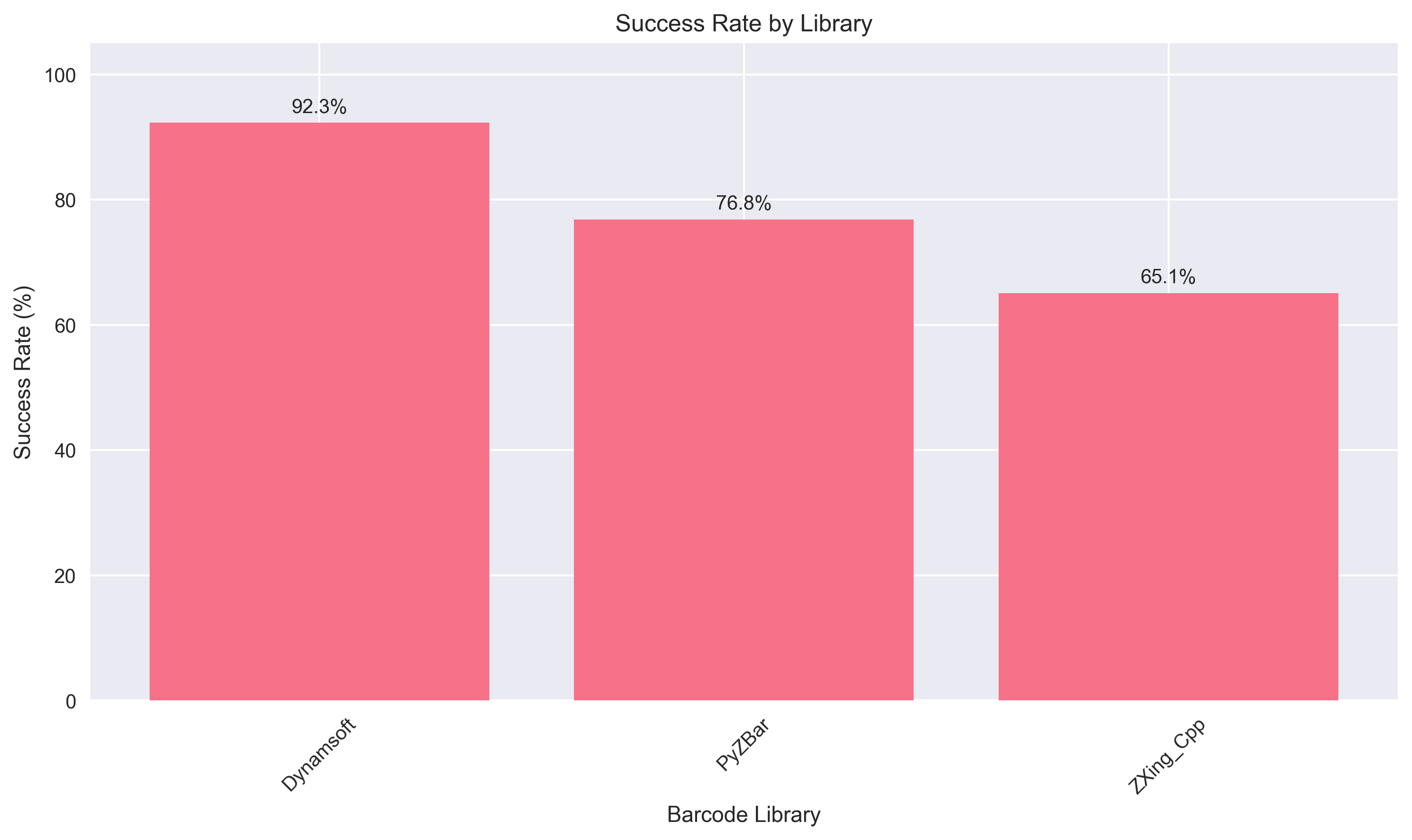
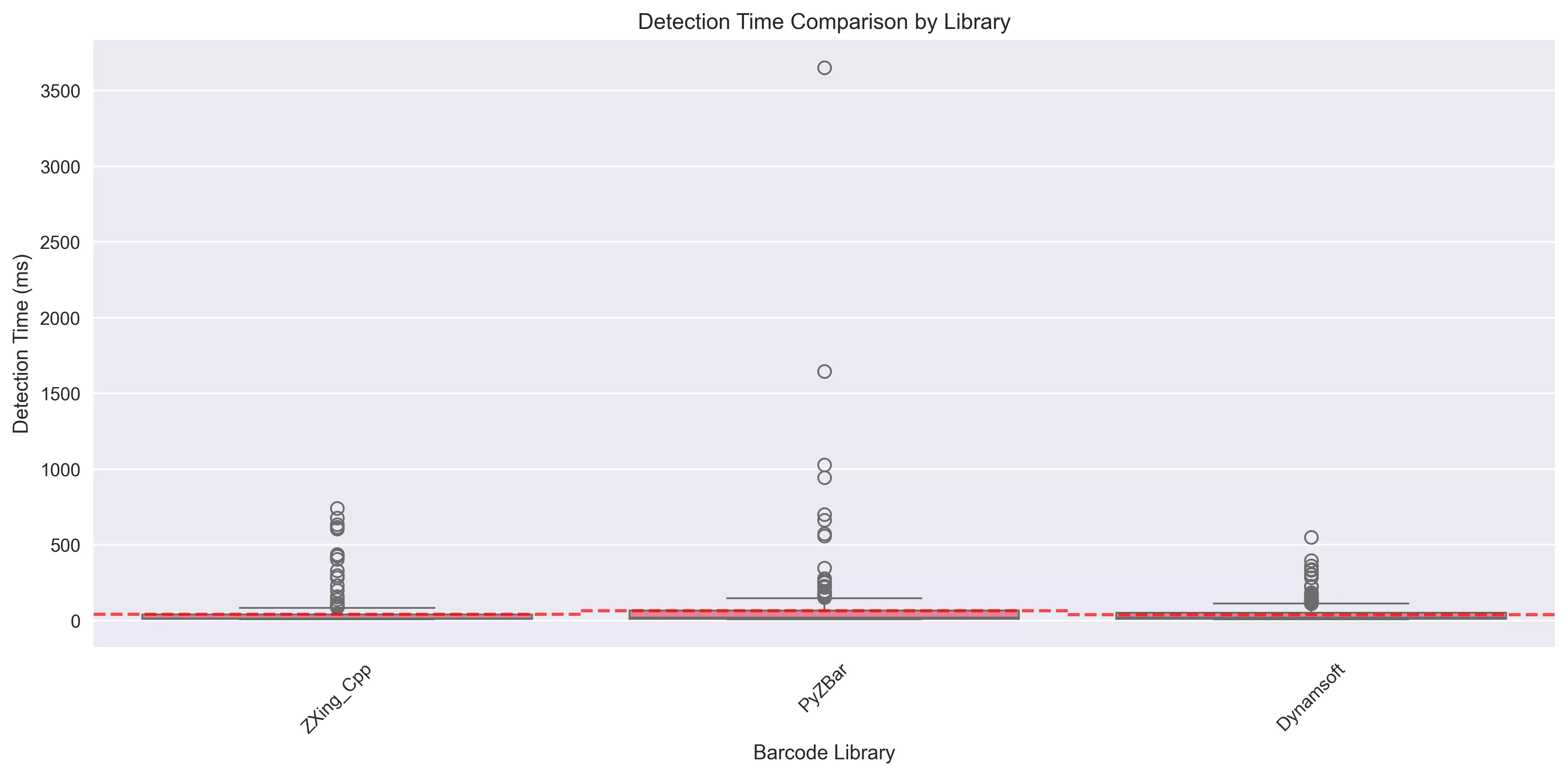
| Dynamsoft | 92.3% | 47.7 ms | Enterprise applications requiring high accuracy |
| PyZBar | 76.8% | 111.5 ms | Open-source projects with moderate requirements |
| ZXing-Cpp | 65.1% | 40.2 ms | Speed-critical applications with simple barcodes |
Key Findings:
- Dynamsoft leads in accuracy with 92.3% success rate, achieving excellent results across all scenarios
- ZXing-Cpp is the fastest at 40.2ms average detection time, ideal for real-time applications
- PyZBar offers a balanced trade-off between accuracy and performance for open-source projects
Performance by Test Scenario
1. Single Barcode Detection (Baseline)
All three libraries achieved 100% success rate on single, well-positioned barcodes, with detection times:
| Library | Avg Detection Time (ms) |
|---|---|
| PyZBar | 10.9 ms |
| ZXing-Cpp | 13.2 ms |
| Dynamsoft | 11.2 ms |
Analysis: All SDKs perform excellently under ideal conditions. The small differences in speed are negligible for most applications.
2. Angled Barcode Detection (15°-75° rotation)
This test evaluates rotation invariance - a critical feature for real-world scanning:
| Library | Success Rate | Avg Detection Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|
| Dynamsoft | 100% | 15.3 ms |
| PyZBar | 60% | 24.2 ms |
| ZXing-Cpp | 55% | 12.3 ms |
Analysis:
- Dynamsoft achieved perfect 100% detection across all rotation angles (15°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 75°)
- PyZBar and ZXing-Cpp struggled with angles beyond 30°, dropping to below 60% success
- For applications requiring rotation tolerance (mobile scanning, automated kiosks), Dynamsoft is the clear winner
3. Multiple Barcode Detection (2-20 codes per image)
Testing batch processing capability with 2, 5, 10, 15, and 20 barcodes per image:
| Library | Success Rate | Avg Detection Time (ms) | Max Codes Detected |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dynamsoft | 91.3% | 69.1 ms | 20 |
| PyZBar | 85.0% | 48.4 ms | 20 |
| ZXing-Cpp | 23.8% | 42.1 ms | 10 (inconsistent) |
Analysis:
- Dynamsoft excels at detecting multiple codes with 91.3% success, reliable up to 20 barcodes
- PyZBar performs well (85%) but occasionally misses codes in dense scenarios
- ZXing-Cpp struggles significantly with multiple codes, achieving only 23.8% success rate
- For warehouse, logistics, or batch scanning applications, Dynamsoft or PyZBar are recommended
4. Challenging Conditions (Noise, Blur, Occlusion)
Stress testing with degraded image quality:
| Library | Success Rate | Avg Detection Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|
| Dynamsoft | 47.5% | 44.7 ms |
| PyZBar | 42.5% | 29.0 ms |
| ZXing-Cpp | 35.0% | 12.8 ms |
Analysis:
- All libraries see significant performance drops in challenging conditions
- Dynamsoft maintains the highest success rate (47.5%) even with noise and blur
- ZXing-Cpp is fastest but sacrifices accuracy in difficult scenarios
- For outdoor scanning, damaged labels, or poor lighting, Dynamsoft provides the best resilience
5. Existing Dataset (Real-World Production Images)
Performance on 170 real-world barcode images from production environments:
| Library | Success Rate | Avg Detection Time (ms) | Images Decoded |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dynamsoft | 90.6% | 95.5 ms | 154/170 |
| PyZBar | 71.2% | 316.8 ms | 121/170 |
| ZXing-Cpp | 65.9% | 90.7 ms | 112/170 |
Analysis:
- Dynamsoft decoded 154 out of 170 real-world images (90.6%), demonstrating superior robustness
- PyZBar shows slower performance (316.8ms) on complex real-world images but maintains decent accuracy
- ZXing-Cpp offers fast processing (90.7ms) but lower success rate on production images
- For production deployments, Dynamsoft’s 90.6% success rate justifies the commercial investment
Performance Charts
The benchmark generates several interactive visualizations:
- Success Rate Comparison - Bar chart showing accuracy by library and scenario
- Detection Time Comparison - Box plots showing speed distributions
- Focus Area Performance - Heatmap of success rates across test categories
- Performance Distributions - Violin plots of detection time variance
Recommendations by Use Case
| Use Case | Recommended SDK | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Enterprise/Production | Dynamsoft | Highest accuracy (92.3%), excellent rotation handling, best real-world performance |
| High-Speed Scanning | ZXing-Cpp | Fastest detection (40.2ms), perfect for simple barcodes in controlled environments |
| Open-Source Projects | PyZBar | Good balance of accuracy (76.8%) and open-source licensing |
| Mobile Apps (rotation) | Dynamsoft | 100% success on angled barcodes, critical for handheld scanning |
| Batch Processing | Dynamsoft | 91.3% success with multiple codes, reliable up to 20 codes per image |
| Budget-Constrained | ZXing-Cpp or PyZBar | Free open-source options with acceptable performance for simple scenarios |
| Poor Image Quality | Dynamsoft | 47.5% success in challenging conditions vs 35-42% for others |
Cost-Benefit Analysis
While Dynamsoft is a commercial product requiring a license, the benchmark demonstrates clear value:
- 26.2% higher accuracy than ZXing-Cpp (92.3% vs 65.1%)
- Perfect rotation handling vs 55-60% for open-source alternatives
- 90.6% real-world success translates to fewer failed scans in production
- Official support, regular updates, and cross-platform consistency
For production environments where failed scans impact user experience, inventory accuracy, or operational efficiency, the commercial license cost is offset by reduced support burden and improved reliability.
Simple Benchmark: Excel Report Generation
The simple.py script uses openpyxl to generate an Excel report with color-coded results for quick visual inspection.
How it works:
```python
from openpyxl import Workbook
def dataset(directory=None, cvr_instance=None):
if directory != None:
print(directory)
files = os.listdir(directory)
files = [f for f in files if f.endswith('.jpg') or f.endswith('.png')]
total_count = len(files)
if total_count == 0:
print('No image files')
return
# Create a .xlsx file
datafile = 'benchmark.xlsx'
wb = data.get_workbook(datafile)
index = 2
print('Total count of barcode image files: {}'.format(total_count))
zbar_count = 0
dbr_count = 0
zxing_count = 0
for filename in files:
file_path = os.path.join(directory, filename)
expected_result = filename.split('_')[0]
r1 = ''
r2 = ''
r3 = ''
# ZBar
zbar_results = zbar_decode(file_path)
if zbar_results != None:
for zbar_result in zbar_results:
zbar_text = zbar_result.data.decode("utf-8")
r1 = zbar_text
print('r1: {}'.format(zbar_text))
if r1 == expected_result:
zbar_count += 1
break
elif 'upca' in zbar_result.type.lower():
if '0' + r1 == expected_result:
zbar_count += 1
r1 = expected_result
break
else:
print('Fail to decode {}'.format(filename))
# DBR
if cvr_instance != None:
dbr_results = dbr_decode(cvr_instance, file_path)
items = dbr_results.get_items()
if len(items) > 0:
for item in items:
r2 = item.get_text()
print('r2: {}'.format(r2))
if r2 == expected_result:
dbr_count += 1
break
elif 'upc_a' in item.get_format_string().lower():
if '0' + r2 == expected_result:
dbr_count += 1
r2 = expected_result
break
else:
print("DBR failed to decode {}".format(filename))
# ZXing
print('ZXing decoding {}'.format(filename))
zxing_results = zxing_decode(file_path)
if zxing_results != None:
for result in zxing_results:
r3 = result.text
if r3 == expected_result:
zxing_count += 1
print('r3: {}'.format(r3))
break
elif 'upca' in str(result.format).lower():
if '0' + r3 == expected_result:
zxing_count += 1
r3 = expected_result
break
else:
print('ZXing failed to decode {}'.format(filename))
# Add results to .xlsx file
data.update_row(wb, index, filename, expected_result, r1, r2, r3)
index += 1
r1 = 0
r2 = 0
r3 = 0
zbar_rate = zbar_count * 100 / total_count
r1 = '{0:.2f}%'.format(zbar_rate)
print('ZBar recognition rate: {0:.2f}%'.format(zbar_rate))
if cvr_instance != None:
dbr_rate = dbr_count * 100 / total_count
r2 = '{0:.2f}%'.format(dbr_rate)
print('DBR recognition rate: {0:.2f}%'.format(dbr_rate))
zxing_rate = zxing_count * 100 / total_count
r3 = '{0:.2f}%'.format(zxing_rate)
print('ZXing recognition rate: {0:.2f}%'.format(zxing_rate))
data.set_recognition_rate(wb, index, r1, r2, r3)
# Save data to .xlsx file
data.save_workbook(wb, datafile)
```
Run the script and check the generated Excel file for the barcode detection results:
Advanced Benchmark: Comprehensive Analysis
For more sophisticated testing, advanced.py provides:
Test Scenarios
- Single Barcodes - Baseline performance testing
- Angled Barcodes (15°-75°) - Real-world rotation handling
- Multiple Barcodes (2-20 per image) - Batch processing efficiency
- Challenging Conditions - Noise, blur, occlusion tests
- Existing Dataset - Real-world production images
Output Reports
- HTML Report (
results/benchmark_report.html) - Interactive charts and detailed analysis - CSV Summary (
results/summary_results.csv) - Tabular performance data - JSON Results (
results/detailed_results.json) - Raw benchmark data - Performance Charts (
results/charts/) - Visual comparisons
Key Metrics
- Detection Time (ms) - Speed comparison across SDKs
- Success Rate (%) - Accuracy under various conditions
- Competitive Analysis - Strengths and weaknesses by scenario
Dataset Selection
The advanced benchmark allows you to choose:
- Generated dataset - Controlled test scenarios
- Existing dataset - Real-world barcode images (170 images)
- Both datasets - Comprehensive evaluation
Configuration
Edit config/benchmark_config.json to enable/disable SDKs:
{
"libraries": {
"zxing_cpp": {"enabled": true},
"pyzbar": {"enabled": true},
"dynamsoft": {
"enabled": true,
"license": "YOUR_LICENSE_KEY_HERE"
}
},
"test_data": {
"num_samples": 50
}
}
Project Structure
├── simple.py # Quick benchmark with Excel output
├── advanced.py # Comprehensive benchmark framework
├── existing_dataset/ # Real-world barcode images
├── generated_dataset/ # Auto-generated test cases
├── results/ # Benchmark outputs
├── src/ # Framework modules
│ ├── barcode_readers.py # SDK implementations
│ ├── benchmark_framework.py # Core testing logic
│ ├── performance_analysis.py # Metrics and reporting
│ └── test_data_generator.py # Synthetic data generation
└── config/ # Configuration files
Conclusion
This comprehensive benchmark of 1,710 test cases across real-world and synthetic datasets reveals clear performance patterns for Python barcode SDKs:
Winner by Accuracy: Dynamsoft Barcode Reader (92.3%)
- Excels in all scenarios: angled barcodes (100%), multiple codes (91.3%), real-world images (90.6%)
- Best choice for production environments where accuracy is critical
- Commercial license justified by 26% higher accuracy than open-source alternatives
Winner by Speed: ZXing-Cpp (40.2ms)
- Fastest detection across all SDKs
- Perfect for simple, well-positioned barcodes in controlled environments
- Limited by poor rotation tolerance and multiple barcode handling
Best Open-Source Balance: PyZBar (76.8%, 111.5ms)
- Solid accuracy for an open-source solution
- Good at multiple barcode detection (85%)
- Trade-off: slower speed, especially on complex images
Decision Matrix
Choose Dynamsoft if:
- Accuracy is mission-critical (enterprise, healthcare, logistics)
- You need reliable rotation handling (mobile apps, handheld scanners)
- Processing multiple codes per image (warehouse, inventory)
- Working with real-world production images with varying quality
Choose ZXing-Cpp if:
- Speed is paramount and barcodes are simple
- Operating in controlled environments (kiosks, fixed scanners)
- Budget constraints require open-source
- Single barcode scenarios with good positioning
Choose PyZBar if:
- You need open-source with better accuracy than ZXing
- Processing multiple barcodes in controlled orientations
- Speed is less critical than accuracy
- Community support and LGPL licensing fit your requirements
Running Your Own Benchmark
Clone the repository and run the benchmark framework:
# Clone repository
git clone https://github.com/yushulx/python-barcode-qrcode-sdk.git
cd python-barcode-qrcode-sdk/examples/official/zxing_zbar
# Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
# Run quick benchmark (Excel output)
python simple.py -d existing_dataset
# Run comprehensive benchmark (HTML reports)
python advanced.py
The framework is extensible - you can add new SDKs by implementing the BarcodeReaderInterface and updating the configuration file.
Source Code
https://github.com/yushulx/python-barcode-qrcode-sdk/tree/main/examples/official/zxing_zbar


