Building a Java Barcode Scanner with Camera SDK, ZXing, and Dynamsoft Barcode Reader
Java Development Kit (JDK) does not provide a built-in API for camera access. A common workaround is to use OpenCV with Java bindings (such as JavaCV). However, OpenCV is a fairly large library, which may not be suitable for all applications.
In this tutorial, we will demonstrate how to build a Java Camera SDK by wrapping the LiteCam C++ SDK, and then integrate it with ZXing and Dynamsoft Barcode Reader to create a complete barcode scanning solution — from setup to deployment.
Demo: Java Barcode Scanner & Reader
Prerequisites
System Requirements
- Java JDK 8+ and Maven 3.6+
- A camera device (for scanning)
- Platform dependencies: Windows (Visual Studio), Linux (
libx11-dev libv4l-dev), macOS (Xcode) - A 30-day free trial license for Dynamsoft Barcode Reader
Platform-Specific Requirements
Windows
- Visual Studio 2019 or later (for building from source)
- Media Foundation (included with Windows)
- Windows 10/11 recommended
Linux
sudo apt update
sudo apt install libx11-dev libv4l-dev
macOS
- Xcode development tools (for building from source)
- AVFoundation framework (included with macOS)
Project Overview
This project consists of two main components:
- LiteCam SDK: A lightweight, cross-platform Java camera capture library
-
Maven Barcode Scanner: A full-featured barcode scanning application with dual detection engines
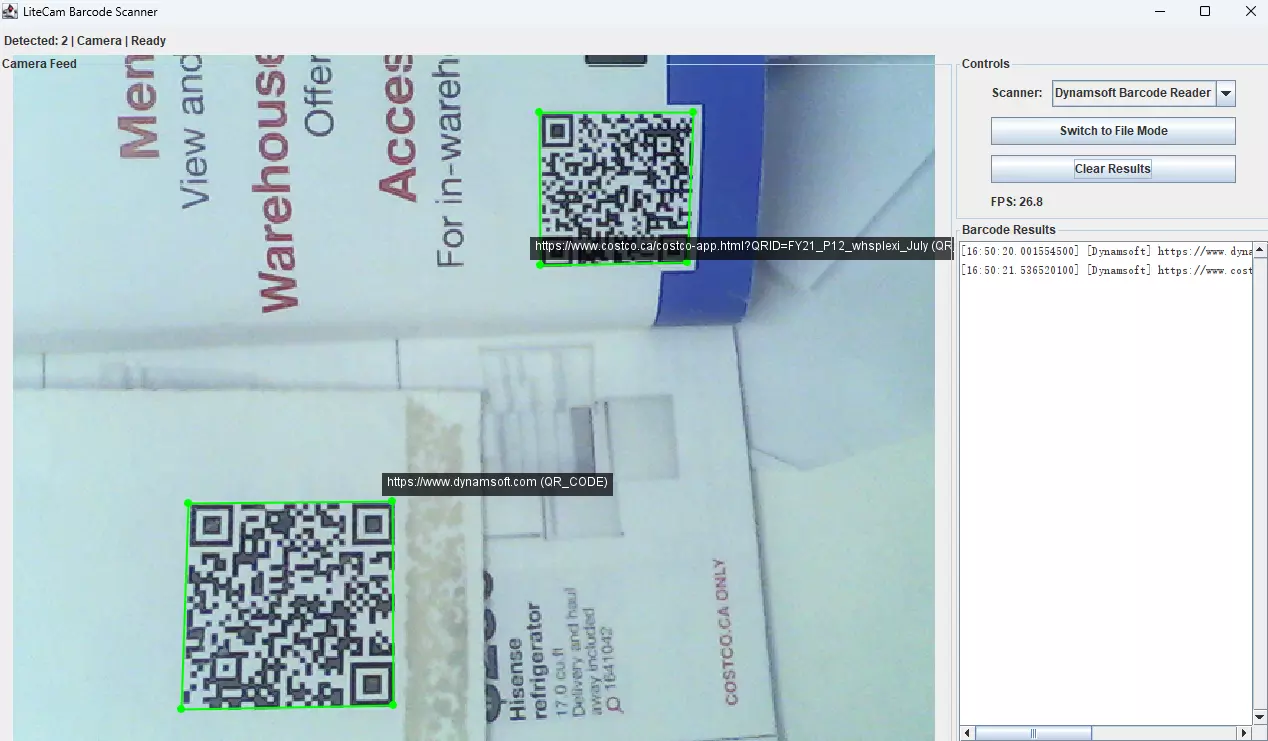
Key Features
- Real-time Camera Feed: High-performance camera capture using native JNI
- Dual Barcode Engines: Switch between ZXing (open-source) and Dynamsoft (enterprise)
- Visual Overlays: Real-time barcode highlighting with coordinates
- File Mode Support: Drag-and-drop image processing
- Cross-Platform: Windows, macOS, and Linux support
- Convenience Scripts: Cross-platform build and run scripts for easy development
LiteCam SDK Overview
LiteCam is a lightweight C++ camera SDK. A JNI bridge turns it into a Java-compatible library.
Core Features
- Cross-Platform Video Capture: Uses platform-native APIs (Media Foundation, V4L2, AVFoundation)
- RGB Frame Access: Direct access to uncompressed RGB data
- JNI Integration: Optimized native bridge for Java applications
- Resolution Control: Support for multiple resolutions and frame rates
Architecture
┌─────────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ Java App │────│ LiteCam │────│ Native Camera │
│ │ │ JNI Bridge │ │ APIs │
└─────────────────┘ └──────────────┘ └─────────────────┘
Supported Platforms
| Platform | Camera API | Display |
|---|---|---|
| Windows | Media Foundation | GDI/DirectX |
| Linux | Video4Linux (V4L2) | X11 |
| macOS | AVFoundation | Cocoa |
Barcode Scanner Application
The Maven Barcode Scanner application demonstrates advanced integration of camera capture with multiple barcode detection engines.
Architecture Overview
┌──────────────────┐
│ Swing GUI │
├──────────────────┤
│ Camera Panel │ ← Live preview with overlays
│ Controls Panel │ ← Engine selection, modes
│ Results Panel │ ← Detection history
└──────────────────┘
│
├────────────────────┤
│ Core Engine │
├────────────────────┤
│ ┌────────────────┐ │
│ │ LiteCam SDK │ │ ← Camera capture
│ └────────────────┘ │
│ ┌────────────────┐ │
│ │ ZXing Engine │ │ ← Open-source detection
│ └────────────────┘ │
│ ┌────────────────┐ │
│ │ Dynamsoft DBR │ │ ← Enterprise detection
│ └────────────────┘ │
└────────────────────┘
Detection Engines Comparison
| Feature | ZXing | Dynamsoft DBR |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Free (Apache 2.0) | Commercial license |
| Accuracy | Good | Excellent |
| Speed | Fast | Very Fast |
| Damaged Codes | Limited | Advanced |
| Multi-detection | Basic | Advanced |
Project Structure
The project is organized into two main components:
├── README.md # Project overview and quick start
├── build-jar.ps1/.sh # Scripts to build LiteCam SDK
├── run-litecam.ps1/.sh # Scripts to test LiteCam SDK
├── litecam.jar # Pre-built Camera SDK with natives
├── include/ # C++ headers for camera implementation
├── src/ # C++ camera implementation (cross-platform)
├── java-src/ # Basic LiteCam Java SDK source
│ └── com/example/litecam/
│ ├── LiteCam.java # Main camera API
│ └── LiteCamViewer.java # Simple camera viewer test
└── maven-example/ # Complete Barcode Scanner Application
├── pom.xml # Maven dependencies and build config
├── build.ps1/.sh # Build scripts for barcode scanner
├── run.ps1/.sh # Run scripts for barcode scanner
├── src/main/java/com/example/litecam/
│ └── BarcodeScanner.java # Main barcode scanning application
└── target/ # Maven build output
└── litecam-barcode-scanner-1.0.0.jar
Java Camera SDK Development
Step 1: JNI for LiteCam C++ Integration
Create a LiteCamJNI.cpp file to wrap the LiteCam C++ SDK, enabling access from Java:
#include "Camera.h"
#include <jni.h>
#include <vector>
#include <mutex>
#include <string>
struct CameraEntry
{
int id;
Camera *cam;
};
static std::mutex g_mutex;
static std::vector<CameraEntry> g_cameras;
static int g_nextId = 1;
static Camera *getCamera(int handle)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(g_mutex);
for (auto &e : g_cameras)
if (e.id == handle)
return e.cam;
return nullptr;
}
static int registerCamera(Camera *c)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(g_mutex);
int id = g_nextId++;
g_cameras.push_back({id, c});
return id;
}
static void unregisterCamera(int handle)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(g_mutex);
for (auto it = g_cameras.begin(); it != g_cameras.end(); ++it)
{
if (it->id == handle)
{
delete it->cam;
g_cameras.erase(it);
return;
}
}
}
static jclass findAndGlobalRef(JNIEnv *env, const char *name)
{
jclass local = env->FindClass(name);
return (jclass)env->NewGlobalRef(local);
}
extern "C"
{
JNIEXPORT jobjectArray JNICALL Java_com_example_litecam_LiteCam_listDevices(JNIEnv *env, jclass)
{
auto devices = ListCaptureDevices();
jclass stringClass = env->FindClass("java/lang/String");
jobjectArray arr = env->NewObjectArray((jsize)devices.size(), stringClass, nullptr);
for (jsize i = 0; i < (jsize)devices.size(); ++i)
{
#ifdef _WIN32
char buffer[512];
wcstombs_s(nullptr, buffer, devices[i].friendlyName, sizeof(buffer));
env->SetObjectArrayElement(arr, i, env->NewStringUTF(buffer));
#else
env->SetObjectArrayElement(arr, i, env->NewStringUTF(devices[i].friendlyName));
#endif
}
return arr;
}
JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL Java_com_example_litecam_LiteCam_open(JNIEnv *env, jobject self, jint deviceIndex)
{
auto cam = new Camera();
if (!cam->Open(deviceIndex))
{
delete cam;
return 0;
}
return registerCamera(cam);
}
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_com_example_litecam_LiteCam_nativeClose(JNIEnv *, jobject, jint handle)
{
unregisterCamera(handle);
}
JNIEXPORT jintArray JNICALL Java_com_example_litecam_LiteCam_listSupportedResolutions(JNIEnv *env, jobject, jint handle)
{
Camera *cam = getCamera(handle);
if (!cam)
return nullptr;
auto mts = cam->ListSupportedMediaTypes();
// Flatten as width,height pairs sequentially.
jintArray arr = env->NewIntArray((jsize)(mts.size() * 2));
std::vector<jint> tmp;
tmp.reserve(mts.size() * 2);
for (auto &m : mts)
{
tmp.push_back((jint)m.width);
tmp.push_back((jint)m.height);
}
env->SetIntArrayRegion(arr, 0, (jsize)tmp.size(), tmp.data());
return arr;
}
JNIEXPORT jboolean JNICALL Java_com_example_litecam_LiteCam_setResolution(JNIEnv *, jobject, jint handle, jint w, jint h)
{
Camera *cam = getCamera(handle);
if (!cam)
return JNI_FALSE;
return cam->SetResolution(w, h) ? JNI_TRUE : JNI_FALSE;
}
JNIEXPORT jboolean JNICALL Java_com_example_litecam_LiteCam_captureFrame(JNIEnv *env, jobject, jint handle, jobject byteBuffer)
{
Camera *cam = getCamera(handle);
if (!cam)
return JNI_FALSE;
FrameData frame = cam->CaptureFrame();
if (!frame.rgbData)
return JNI_FALSE;
unsigned char *dst = (unsigned char *)env->GetDirectBufferAddress(byteBuffer);
if (!dst)
{
ReleaseFrame(frame);
return JNI_FALSE;
}
size_t expected = (size_t)(frame.width * frame.height * 3);
memcpy(dst, frame.rgbData, expected < frame.size ? expected : frame.size);
ReleaseFrame(frame);
return JNI_TRUE;
}
JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL Java_com_example_litecam_LiteCam_getFrameWidth(JNIEnv *, jobject, jint handle)
{
Camera *cam = getCamera(handle);
if (!cam)
return 0;
return (jint)cam->frameWidth;
}
JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL Java_com_example_litecam_LiteCam_getFrameHeight(JNIEnv *, jobject, jint handle)
{
Camera *cam = getCamera(handle);
if (!cam)
return 0;
return (jint)cam->frameHeight;
}
} // extern C
Step 2: CMake for JNI Build
The following CMakeLists.txt file is used to build the JNI shared library:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.15)
# Project name and version
project(CameraProject VERSION 1.0 LANGUAGES CXX)
# Set C++ standard
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED True)
# Build type
if(NOT CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Release)
endif()
# Define include directories
set(INCLUDE_DIR ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/include)
# Platform detection
if(WIN32)
set(PLATFORM_NAME "windows")
elseif(APPLE)
set(PLATFORM_NAME "macos")
elseif(UNIX)
set(PLATFORM_NAME "linux")
else()
set(PLATFORM_NAME "unknown")
endif()
# Architecture detection
if(CMAKE_SIZEOF_VOID_P EQUAL 8)
set(ARCH_NAME "x86_64")
else()
set(ARCH_NAME "x86")
endif()
# Compiler-specific settings
if(MSVC)
# Set runtime library for Windows
if(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE STREQUAL "Debug")
set(CMAKE_MSVC_RUNTIME_LIBRARY "MultiThreadedDebug")
else()
set(CMAKE_MSVC_RUNTIME_LIBRARY "MultiThreaded")
endif()
# Enable parallel compilation
add_compile_options(/MP)
# Disable specific warnings
add_compile_options(/wd4251 /wd4275)
# Enable UTF-8 encoding
add_compile_options(/utf-8)
endif()
# Define source files for the Camera library based on platform
if (WIN32)
set(LIBRARY_SOURCES
src/CameraWindows.cpp
src/CameraPreviewWindows.cpp
)
elseif (UNIX AND NOT APPLE)
set(LIBRARY_SOURCES
src/CameraLinux.cpp
src/CameraPreviewLinux.cpp
)
elseif (APPLE)
# Support universal binaries on macOS
set(CMAKE_OSX_ARCHITECTURES "x86_64;arm64")
# Ensure that Objective-C++ source files are compiled as Objective-C++
set(LIBRARY_SOURCES
src/CameraMacOS.mm
src/CameraPreviewMacOS.mm
)
set_source_files_properties(src/CameraMacOS.mm src/CameraPreviewMacOS.mm PROPERTIES COMPILE_FLAGS "-x objective-c++")
# Set main.cpp to be treated as Objective-C++ for macOS
set_source_files_properties(src/main.cpp PROPERTIES COMPILE_FLAGS "-x objective-c++")
endif()
# Add JNI wrapper source (common for all platforms)
list(APPEND LIBRARY_SOURCES
src/LiteCamJNI.cpp
)
# Define source files for the executable
set(EXECUTABLE_SOURCES
src/main.cpp
)
# Add the Camera shared library
add_library(litecam SHARED ${LIBRARY_SOURCES})
# Set library properties
set_target_properties(litecam PROPERTIES
VERSION ${PROJECT_VERSION}
SOVERSION ${PROJECT_VERSION_MAJOR}
OUTPUT_NAME "litecam"
)
# Platform-specific library naming
if(WIN32)
set_target_properties(litecam PROPERTIES
PREFIX ""
SUFFIX ".dll"
)
elseif(APPLE)
set_target_properties(litecam PROPERTIES
PREFIX "lib"
SUFFIX ".dylib"
)
else()
set_target_properties(litecam PROPERTIES
PREFIX "lib"
SUFFIX ".so"
)
endif()
# Set include directories for the Camera library
target_include_directories(litecam PUBLIC
$<BUILD_INTERFACE:${INCLUDE_DIR}>
$<INSTALL_INTERFACE:include>
)
# Define the CAMERA_EXPORTS macro for the shared library
target_compile_definitions(litecam PRIVATE
CAMERA_EXPORTS
LITECAM_VERSION_MAJOR=${PROJECT_VERSION_MAJOR}
LITECAM_VERSION_MINOR=${PROJECT_VERSION_MINOR}
LITECAM_VERSION_PATCH=${PROJECT_VERSION_PATCH}
)
# Platform-specific dependencies for the Camera library
if (UNIX AND NOT APPLE)
# Linux dependencies
find_package(X11 REQUIRED)
find_package(PkgConfig REQUIRED)
# Check for Video4Linux2
pkg_check_modules(V4L2 libv4l2)
if (X11_FOUND)
target_include_directories(litecam PUBLIC ${X11_INCLUDE_DIR})
target_link_libraries(litecam PRIVATE ${X11_LIBRARIES} pthread)
endif()
if (V4L2_FOUND)
target_include_directories(litecam PRIVATE ${V4L2_INCLUDE_DIRS})
target_link_libraries(litecam PRIVATE ${V4L2_LIBRARIES})
else()
message(WARNING "Video4Linux2 not found - camera functionality may be limited")
endif()
elseif (APPLE)
# macOS dependencies
find_library(COCOA_LIBRARY Cocoa REQUIRED)
find_library(AVFOUNDATION_LIBRARY AVFoundation REQUIRED)
find_library(COREMEDIA_LIBRARY CoreMedia REQUIRED)
find_library(COREVIDEO_LIBRARY CoreVideo REQUIRED)
find_library(OBJC_LIBRARY objc REQUIRED)
target_link_libraries(litecam PRIVATE
${COCOA_LIBRARY}
${AVFOUNDATION_LIBRARY}
${COREMEDIA_LIBRARY}
${COREVIDEO_LIBRARY}
${OBJC_LIBRARY}
)
elseif (WIN32)
# Windows dependencies
target_link_libraries(litecam PRIVATE
ole32
uuid
mfplat
mf
mfreadwrite
mfuuid
)
endif()
# JNI support - enhanced detection
find_package(JNI)
if (JNI_FOUND)
target_include_directories(litecam PRIVATE ${JNI_INCLUDE_DIRS})
target_compile_definitions(litecam PRIVATE LITECAM_JNI_ENABLED)
# Add JNI libraries on some platforms
if(WIN32)
# Windows doesn't typically need to link JNI libraries
elseif(APPLE)
# macOS typically has JNI in the framework
else()
# Linux might need explicit JNI library linking
if(JNI_LIBRARIES)
target_link_libraries(litecam PRIVATE ${JNI_LIBRARIES})
endif()
endif()
endif()
# Optional: Add position independent code for shared library
set_property(TARGET litecam PROPERTY POSITION_INDEPENDENT_CODE ON)
# Add the camera_capture executable
add_executable(camera_capture ${EXECUTABLE_SOURCES})
# Set executable properties
set_target_properties(camera_capture PROPERTIES
OUTPUT_NAME "camera_capture"
)
# Link the Camera library to the executable
target_link_libraries(camera_capture PRIVATE litecam)
# Include the shared library's headers in the executable
target_include_directories(camera_capture PRIVATE ${INCLUDE_DIR})
# For macOS, link against the frameworks for the executable too
if (APPLE)
target_link_libraries(camera_capture PRIVATE
${COCOA_LIBRARY}
${AVFOUNDATION_LIBRARY}
${COREMEDIA_LIBRARY}
${COREVIDEO_LIBRARY}
${OBJC_LIBRARY}
)
endif()
# Installation rules (optional)
install(TARGETS litecam camera_capture
EXPORT CameraProjectTargets
LIBRARY DESTINATION lib
ARCHIVE DESTINATION lib
RUNTIME DESTINATION bin
INCLUDES DESTINATION include
)
install(DIRECTORY ${INCLUDE_DIR}/
DESTINATION include
FILES_MATCHING PATTERN "*.h"
)
# Export targets for find_package support
install(EXPORT CameraProjectTargets
FILE CameraProjectTargets.cmake
NAMESPACE CameraProject::
DESTINATION lib/cmake/CameraProject
)
# Generate and install package config files
include(CMakePackageConfigHelpers)
configure_package_config_file(
"${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake/CameraProjectConfig.cmake.in"
"${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/CameraProjectConfig.cmake"
INSTALL_DESTINATION lib/cmake/CameraProject
)
write_basic_package_version_file(
"${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/CameraProjectConfigVersion.cmake"
VERSION ${PROJECT_VERSION}
COMPATIBILITY SameMajorVersion
)
Step 3: The Java Camera Class with JNI
package com.example.litecam;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class LiteCam implements AutoCloseable {
static {
boolean loaded = false;
try {
loaded = loadBundled();
} catch (Throwable t) {
}
if (!loaded) {
System.loadLibrary("litecam");
}
}
private static boolean loadBundled() throws Exception {
String os = System.getProperty("os.name").toLowerCase();
String arch = System.getProperty("os.arch").toLowerCase();
String osToken;
if (os.contains("win")) osToken = "windows"; else if (os.contains("mac") || os.contains("darwin")) osToken = "macos"; else if (os.contains("nux") || os.contains("linux")) osToken = "linux"; else return false;
String archToken;
if (arch.contains("aarch64") || arch.contains("arm64")) archToken = "arm64"; else if (arch.contains("64")) archToken = "x86_64"; else archToken = arch; // fallback
String libBase = "litecam";
String ext = osToken.equals("windows") ? ".dll" : (osToken.equals("macos") ? ".dylib" : ".so");
String resourcePath = "/natives/" + osToken + "-" + archToken + "/" + (osToken.equals("windows") ? libBase + ext : "lib" + libBase + ext);
try (java.io.InputStream in = LiteCam.class.getResourceAsStream(resourcePath)) {
if (in == null) return false;
java.nio.file.Path tempFile = java.nio.file.Files.createTempFile(libBase + "-", ext);
try (java.io.OutputStream out = java.nio.file.Files.newOutputStream(tempFile)) {
byte[] buf = new byte[8192]; int r; while ((r = in.read(buf)) != -1) out.write(buf, 0, r);
}
tempFile.toFile().deleteOnExit();
System.load(tempFile.toAbsolutePath().toString());
return true;
}
}
private int handle = 0;
// Native methods
public static native String[] listDevices();
private native int open(int deviceIndex);
private native void nativeClose(int handle);
public native int[] listSupportedResolutions(int handle);
public native boolean setResolution(int handle, int width, int height);
public native boolean captureFrame(int handle, ByteBuffer rgbOut);
public native int getFrameWidth(int handle);
public native int getFrameHeight(int handle);
public void openDevice(int index) {
if (handle != 0) throw new IllegalStateException("Already opened");
handle = open(index);
if (handle == 0) throw new RuntimeException("Failed to open camera index " + index);
}
public void closeDevice() {
if (handle != 0) {
nativeClose(handle);
handle = 0;
}
}
@Override
public void close() { closeDevice(); }
public List<int[]> getSupportedResolutions() {
int[] flat = listSupportedResolutions(handle);
List<int[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (flat != null) {
for (int i=0;i+1<flat.length;i+=2) {
list.add(new int[]{flat[i], flat[i+1]});
}
}
return list;
}
public boolean setResolution(int w, int h) { return setResolution(handle, w, h); }
public int getWidth() { return getFrameWidth(handle); }
public int getHeight() { return getFrameHeight(handle); }
public boolean grabFrame(ByteBuffer dst) { return captureFrame(handle, dst); }
public boolean isOpen() { return handle != 0; }
}
Step 4: Build JNI Shared Library and JAR Package
- Build native library with CMake:
mkdir build cd build cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release cmake --build . --config Release -
Compile Java sources:
cd .. javac -d build -h include java-src/com/example/litecam/*.java -
Create JAR with native library:
jar cf litecam.jar -C build com jar uf litecam.jar build/litecam.dll # or .dylib on macOS, .so on Linux
Java Barcode Scanner Development
The following code snippet demonstrates the basic usage of LiteCam, ZXing, and Dynamsoft Barcode Reader APIs.
LiteCam
LiteCam cam = new LiteCam();
String[] devices = LiteCam.listDevices();
for (int i = 0; i < devices.length; i++) {
System.out.println(i + ": " + devices[i]);
}
cam.openDevice(0);
cam.setResolution(640, 480);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(640 * 480 * 3);
if (cam.grabFrame(buffer)) {
byte[] frameData = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(frameData);
}
cam.close();
ZXing
import com.google.zxing.*;
import com.google.zxing.client.j2se.BufferedImageLuminanceSource;
import com.google.zxing.common.HybridBinarizer;
import com.google.zxing.multi.GenericMultipleBarcodeReader;
public class ZXingDetector {
private MultiFormatReader reader;
private GenericMultipleBarcodeReader multiReader;
public void initialize() {
reader = new MultiFormatReader();
multiReader = new GenericMultipleBarcodeReader(reader);
}
public List<Result> detectBarcodes(BufferedImage image) {
List<Result> results = new ArrayList<>();
try {
LuminanceSource source = new BufferedImageLuminanceSource(image);
BinaryBitmap bitmap = new BinaryBitmap(new HybridBinarizer(source));
try {
Result[] multiResults = multiReader.decodeMultiple(bitmap);
results.addAll(Arrays.asList(multiResults));
} catch (NotFoundException e) {
try {
Result singleResult = reader.decode(bitmap);
results.add(singleResult);
} catch (NotFoundException ignored) {
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.debug("ZXing detection failed: {}", e.getMessage());
}
return results;
}
}
Dynamsoft Barcode Reader
import com.dynamsoft.dbr.*;
import com.dynamsoft.core.basic_structures.ImageData;
public class DynamsoftDetector {
private CaptureVisionRouter cvRouter;
public void initialize() throws Exception {
LicenseManager.initLicense("LICENSE-KEY");
cvRouter = new CaptureVisionRouter();
}
public List<BarcodeResultItem> detectBarcodes(BufferedImage image) {
List<BarcodeResultItem> results = new ArrayList<>();
try {
ImageData imageData = createImageData(image);
CapturedResult result = cvRouter.capture(imageData,
EnumPresetTemplate.PT_READ_BARCODES);
DecodedBarcodesResult barcodeResult = result.getDecodedBarcodesResult();
if (barcodeResult != null) {
BarcodeResultItem[] items = barcodeResult.getItems();
if (items != null) {
results.addAll(Arrays.asList(items));
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Dynamsoft detection failed: {}", e.getMessage());
}
return results;
}
private ImageData createImageData(BufferedImage image) {
}
}
Source Code
https://github.com/yushulx/java-jni-barcode-qrcode-reader/tree/main/examples/barcode-scanner


