Image Processing Techniques for OCR
We need to use OCR in various scenarios, whether we want to scan the credit card number with our phone or extract text from documents. Dynamsoft Label Recognition (DLR) and Dynamic Web TWAIN (DWT) have the OCR ability to accurately read text.
Although generally they can do a good job, we can use various image processing techniques to improve the result.
Whiten Up/Remove Shadows
Bad lighting may affect the OCR result. We can whiten up images or remove shadows from images to improve the result.
Invert
Text with a light color can be difficult to locate and recognize as the OCR engine is generally trained against text with a dark color.

It will be easier to recognize if we invert its color.

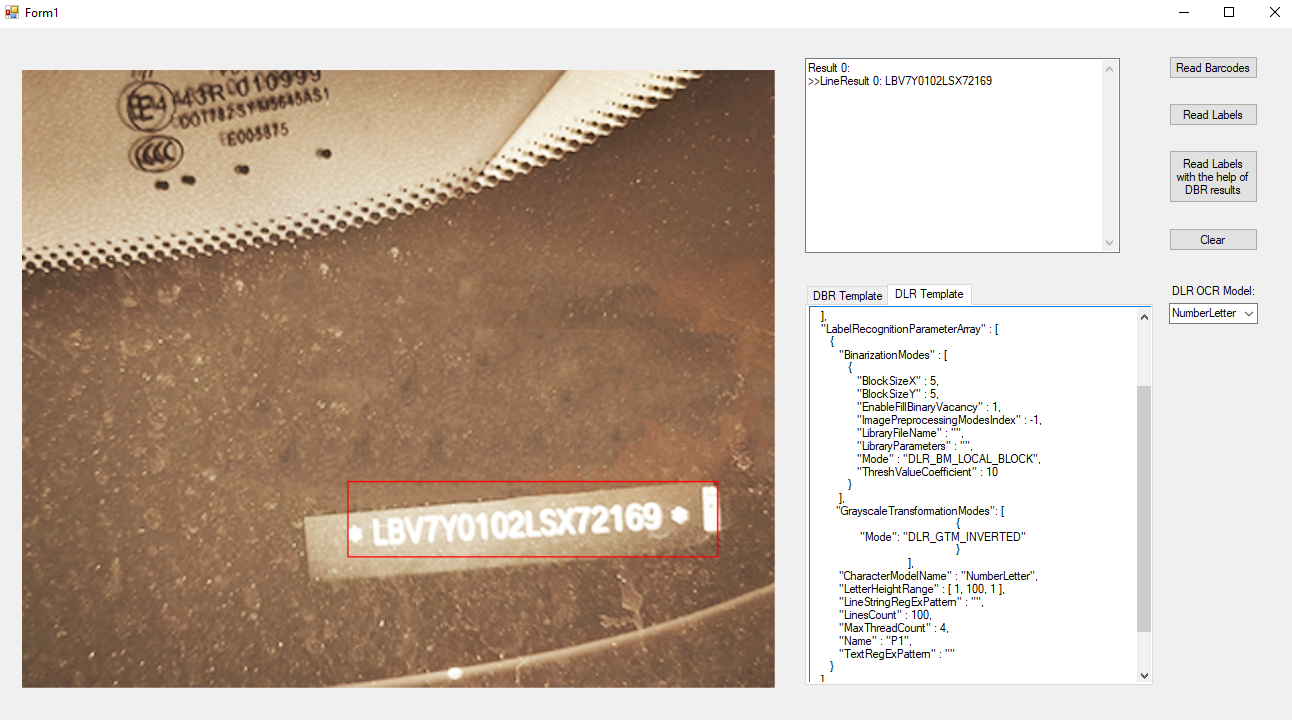
In DLR, there is a GrayscaleTransformationModes parameter which we can use to do the inversion.
Here are the settings in JSON:
"GrayscaleTransformationModes": [
{
"Mode": "DLR_GTM_INVERTED"
}
]
DLR .net’s reading result:
Rescale
If the height of letters is too low, the OCR engine may not give a good result. Generally the image should better have a DPI of at least 300.
Starting from DLR 1.1, there is a ScaleUpModes parameter to scale up letters. Of course, we can also scale the image by ourselves.
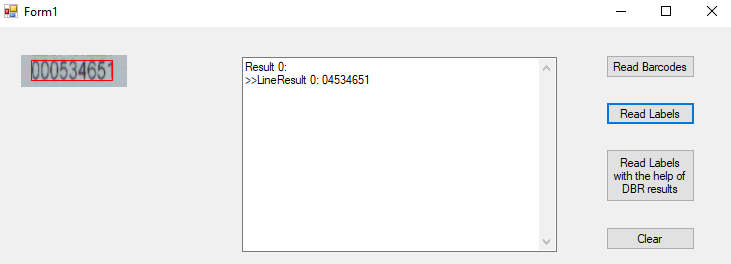
Directly reading the image gives a wrong result:
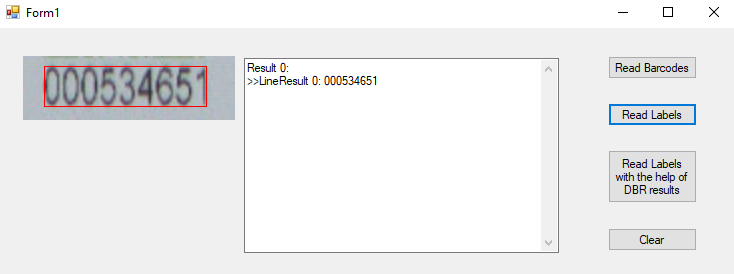
After scaling up the image by 2 times, the result is correct:
Deskew
It is okay if the text is a bit skewed. But if it is too skewed, the result will be impacted significantly. We need to deskew the image to improve the result.
We can use Hough Line Transform in OpenCV to do this.
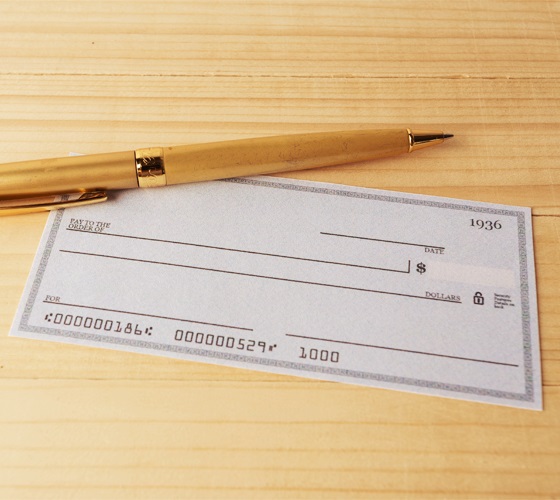

Here is the code to deskew the image above.
#coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
import cv2
import math
from PIL import Image
def deskew():
src = cv2.imread("neg.jpg",cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(src, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
kernel = np.ones((5,5),np.uint8)
erode_Img = cv2.erode(gray,kernel)
eroDil = cv2.dilate(erode_Img,kernel) # erode and dilate
showAndWaitKey("eroDil",eroDil)
canny = cv2.Canny(eroDil,50,150) # edge detection
showAndWaitKey("canny",canny)
lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(canny, 0.8, np.pi / 180, 90,minLineLength=100,maxLineGap=10) # Hough Lines Transform
drawing = np.zeros(src.shape[:], dtype=np.uint8)
maxY=0
degree_of_bottomline=0
index=0
for line in lines:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = line[0]
cv2.line(drawing, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 1, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
k = float(y1-y2)/(x1-x2)
degree = np.degrees(math.atan(k))
if index==0:
maxY=y1
degree_of_bottomline=degree # take the degree of the line at the bottom
else:
if y1>maxY:
maxY=y1
degree_of_bottomline=degree
index=index+1
showAndWaitKey("houghP",drawing)
img=Image.fromarray(src)
rotateImg = img.rotate(degree_of_bottomline)
rotateImg_cv = np.array(rotateImg)
cv2.imshow("rotateImg",rotateImg_cv)
cv2.imwrite("deskewed.jpg",rotateImg_cv)
cv2.waitKey()
def showAndWaitKey(winName,img):
cv2.imshow(winName,img)
cv2.waitKey()
if __name__ == "__main__":
deskew()
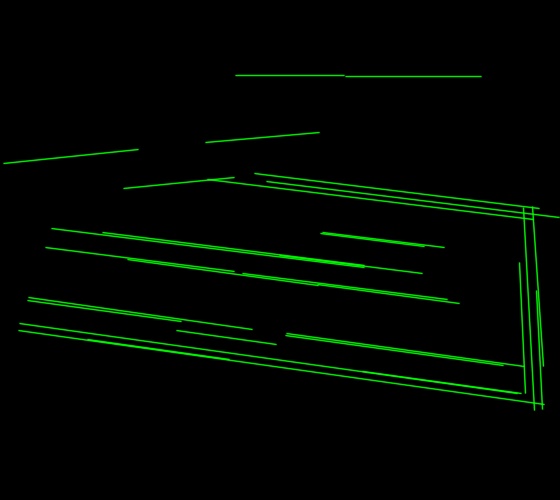
Lines detected:
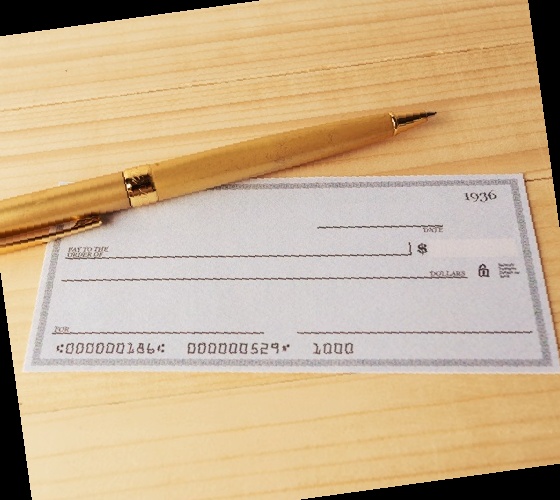
Deskewed:

But for the image below, it is difficult to decide whether the degree to rotate should be plus 180 or not.

The default rotated result:

Since the text is aligned with a barcode, we can use Dynamsoft Barcode Reader to read the barcode and get the correct rotation degree.
Using the online barcode reader, we can see that the barcode reading result contains the detected angel.
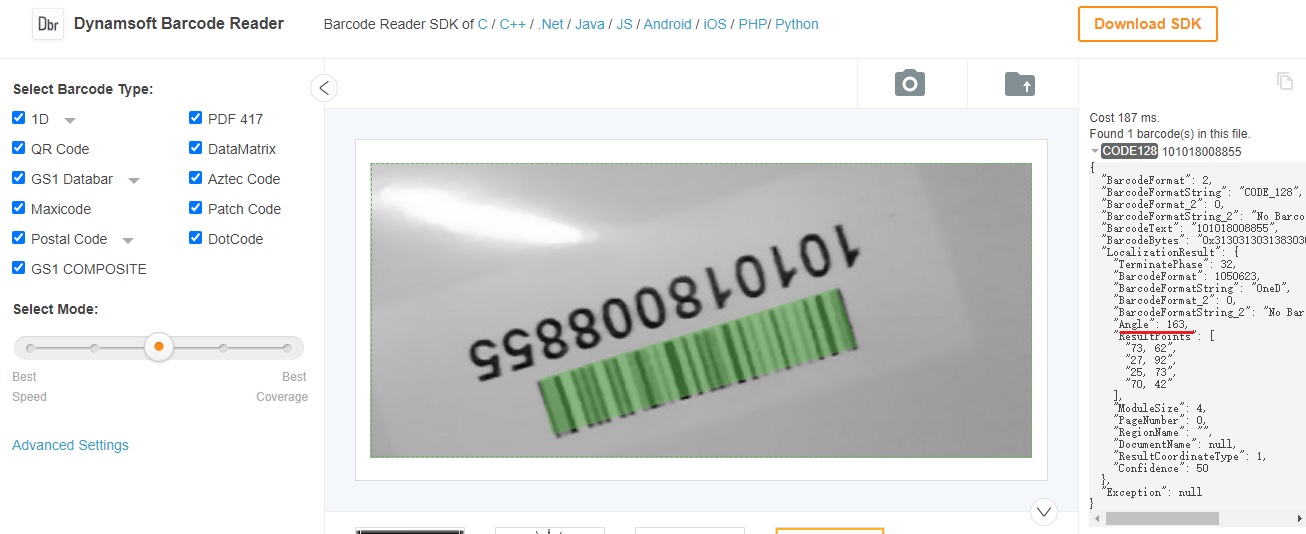
Then we can correctly rotate the image.

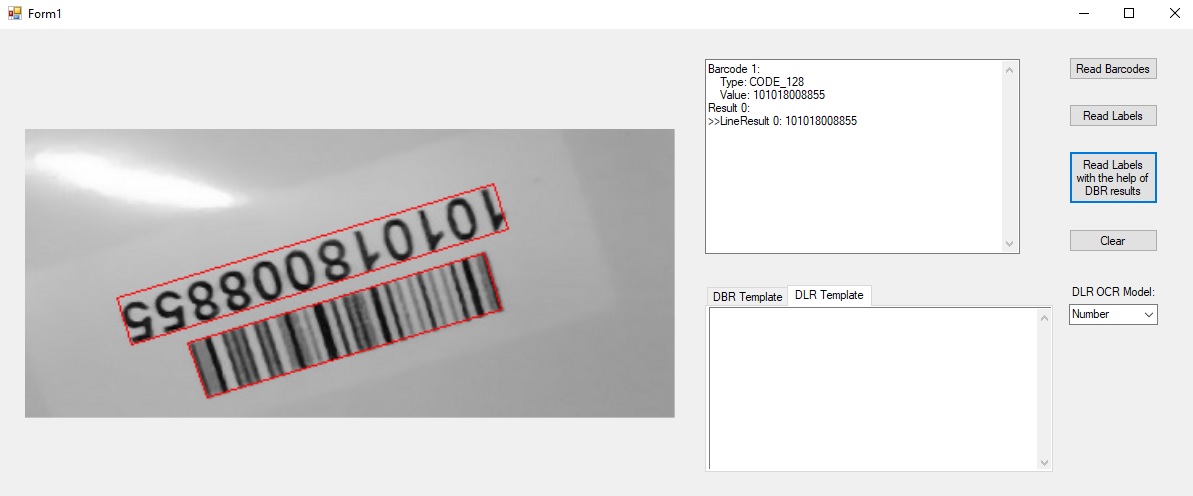
We can use DLR to read the text with the help of DBR. This article shares how to combine DBR and DLR to read text near barcodes.
Result:
Contact Support
If you still have problems after trying these techniques, you can contact us for help.


