How to Resize Raspbian Image for QEMU on Windows
Raspbian is a free operating system based on Debian. It is the recommended operating system for Raspberry Pi. If you do not have a Raspberry Pi, you can experience Raspbian by running the OS image in the emulator - QEMU. In this article, I want to share how to resize the Raspbian image on Windows.
Raspbian and QEMU for Windows
Why do I Need to Resize the Raspbian Image?
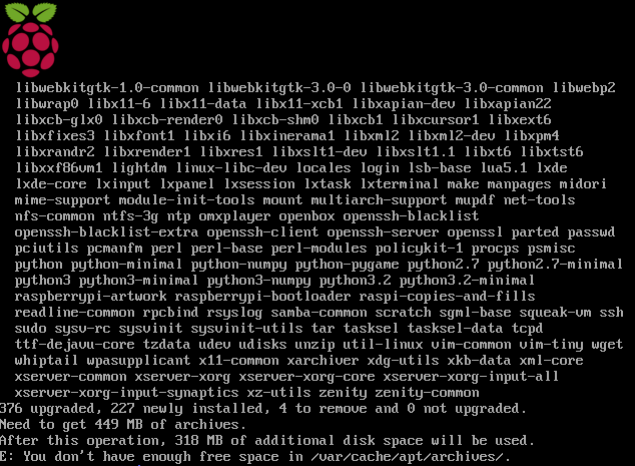
The Raspbian image contained in the package is not the latest. Therefore, I want to upgrade the OS with following commands:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
Unluckily, when I was trying to upgrade the system, I suffered the lack of space.
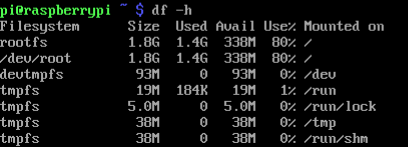
How much storage space can I use? Get the available disk space as follows:
df -h
Here is the way I tried in order to free up space:
sudo apt-get clean
The outcome is storage space is still not enough. The only solution is to add extra space.
Adding Storage Space to Raspbian Image File (*.img)
According to the answer from StackOverflow, I have verified the steps on Windows:
Steps to resize the *.img file
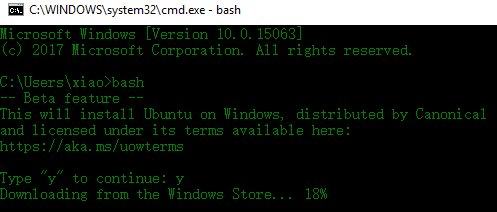
Install Ubuntu on Windows 10.
Check the original image size and resize it with command `truncate’:
truncate -s +2G raspbian.img
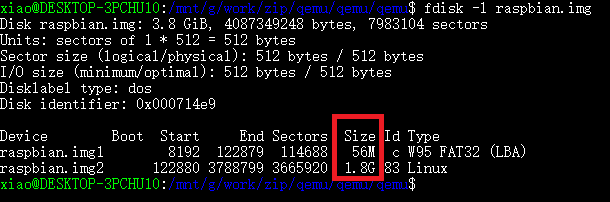
List the partition tables for the image file:
fdisk -l raspbian.img
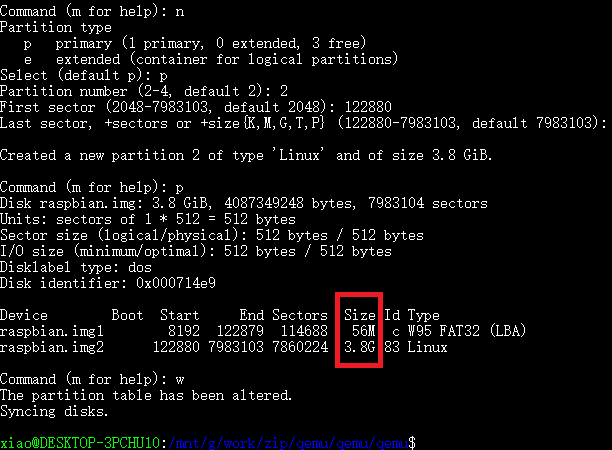
Although the image size changes to 3.8G, the partition is still 1.8G. We need to re-partition the disk with `fdisk’:
fdisk raspbian.img
Use d' to delete the second partition and use p` to print the current partition tables.
Create a new partition with n:
The start sector of the second partition is 122880. Don’t forget to enter w to commit the change.
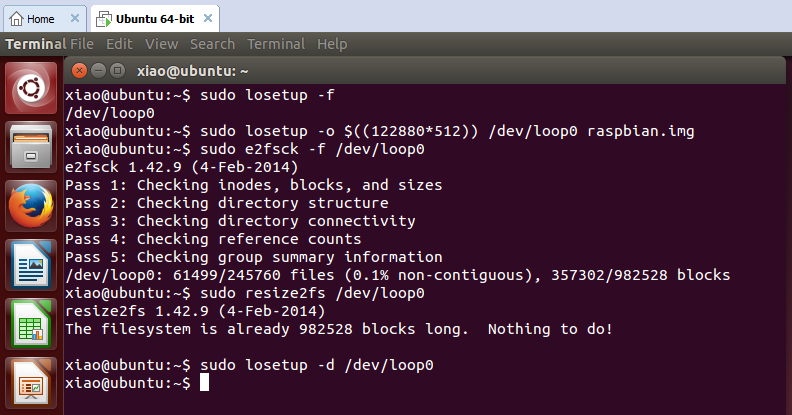
The final step is to use resize2fs to resize the ext4 (check the file system type with command df -T) file system.
We need to use losetup to mount the image. To find an unused loop device, use the following command:
losetup -f
Unfortunately, it failed. Here is the error message I got:
> **losetup: cannot find an unused loop device: No such file or directory**.
There are no /dev/loop* devices! The function is not supported on Windows 10 yet.
Now process the image file in a Linux virtual machine.
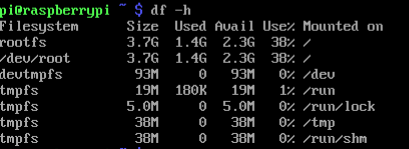
Boot QEMU with the new image file:
Extra storage space is added.