Scanning QR Code from Desktop Screen with Qt and Python Barcode SDK
In everyday life, we often use our smartphones to scan QR codes. However, when working on a computer, using a smartphone isn’t always the most convenient option for scanning QR codes that appear on your screen. Photos taken from monitors can have Moiré patterns, which can interfere with QR code recognition. Additionally, you might want to use the decoded information directly on your PC, such as a URL to open a website. This article will guide you through creating a simple Python barcode reader that makes QR code scanning directly from your desktop screen easy and efficient.
This article is Part 4 in a 8-Part Series.
- Part 1 - Detecting and Decoding QR Codes in Python with YOLO and Dynamsoft Barcode Reader
- Part 2 - How to a GUI Barcode Reader with Qt PySide6 on Raspberry Pi
- Part 3 - Advanced GUI Python Barcode and QR Code Reader for Windows, Linux, macOS and Rasberry Pi OS
- Part 4 - Scanning QR Code from Desktop Screen with Qt and Python Barcode SDK
- Part 5 - Building an Online Barcode and QR Code Scanning App with Python Django
- Part 6 - How to Build Flet Chat App with Barcode and Gemini APIs
- Part 7 - A Guide to Running ARM32 and ARM64 Python Barcode Readers in Docker Containers
- Part 8 - Python Barcode SDK Benchmark: Comparing ZXing, ZBar, and Dynamsoft with Real-World & Stress Tests
Prerequisites
-
OpenCV
python3 -m pip install opencv-python -
PySide6
python3 -m pip install PySide6 -
Dynamsoft Barcode Reader
python3 -m pip install dynamsoft-capture-vision-bundle
Steps to Read QR Codes from Desktop Screens with Python
To enhance the GUI Python barcode reader built with Qt for Python, OpenCV, and Dynamsoft Barcode Reader, we’ll add screen snipping functionality. Drawing inspiration from this snipping tool implementation, we’ll follow these steps to implement screenshot functionality:
- Create a custom Qt widget that overlays the screen.
- Draw the selected area in the
paintEvent()function as the mouse moves. - Capture the image of the selected area using
PIL.ImageGrab.grab()when the mouse is released.
Adding Buttons for Snipping Events
Open the design.ui file in Qt Designer and add two buttons to trigger snipping events.
After saving the updated layout, compile the UI file to a Python file:
PySide6-uic design.ui -o design.py
In app_advanced.py, connect the new buttons to their respective slot functions:
self.ui.pushButton_area.clicked.connect(self.snipArea)
self.ui.pushButton_full.clicked.connect(self.snipFull)
Creating a Custom Qt Widget
Create a new file SnippingTool.py and define a custom Qt widget for screen snipping:
import numpy as np
import cv2
from PIL import ImageGrab
from PySide6 import QtWidgets, QtCore, QtGui
from PySide6.QtCore import Qt
class SnippingWidget(QtWidgets.QWidget):
is_snipping = False
def __init__(self, parent=None, app=None):
super(SnippingWidget, self).__init__()
self.parent = parent
self.setWindowFlags(Qt.WindowStaysOnTopHint)
self.screen = app.primaryScreen()
self.setGeometry(0, 0, self.screen.size().width(), self.screen.size().height())
self.begin = QtCore.QPoint()
self.end = QtCore.QPoint()
self.onSnippingCompleted = None
def start(self):
SnippingWidget.is_snipping = True
self.setWindowOpacity(0.3)
QtWidgets.QApplication.setOverrideCursor(QtGui.QCursor(QtCore.Qt.CrossCursor))
self.show()
Ensure the widget’s size matches the screen resolution obtained from the primaryScreen() function.
Handling Mouse Events
Implement the mouse event handlers to define the selected area:
def mousePressEvent(self, event):
self.begin = event.pos()
self.end = self.begin
self.update()
def mouseMoveEvent(self, event):
self.end = event.pos()
self.update()
def mouseReleaseEvent(self, event):
SnippingWidget.is_snipping = False
QtWidgets.QApplication.restoreOverrideCursor()
x1 = min(self.begin.x(), self.end.x())
y1 = min(self.begin.y(), self.end.y())
x2 = max(self.begin.x(), self.end.x())
y2 = max(self.begin.y(), self.end.y())
self.repaint()
QtWidgets.QApplication.processEvents()
self.close()
Draw a rectangle to indicate the selected area in the paintEvent() function:
def paintEvent(self, event):
if SnippingWidget.is_snipping:
brush_color = (128, 128, 255, 100)
lw = 3
opacity = 0.3
else:
self.begin = QtCore.QPoint()
self.end = QtCore.QPoint()
brush_color = (0, 0, 0, 0)
lw = 0
opacity = 0
self.setWindowOpacity(opacity)
qp = QtGui.QPainter(self)
qp.setPen(QtGui.QPen(QtGui.QColor('black'), lw))
qp.setBrush(QtGui.QColor(*brush_color))
rect = QtCore.QRectF(self.begin, self.end)
qp.drawRect(rect)
Capturing Screen Images
Use the PIL library to capture images from the screen after releasing the mouse:
-
Capture a selected area:
img = ImageGrab.grab(bbox=(x1, y1, x2, y2)) try: img = cv2.cvtColor(np.array(img), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR) except: img = None -
Capture the full screen:
img = ImageGrab.grab(bbox=(0, 0, self.screen.size().width(), self.screen.size().height()))
Minimizing and Restoring the Application Window
To avoid blocking the snipping area, minimize the application window before starting the snipping widget and restore it afterward:
def onSnippingCompleted(self, frame):
self.setWindowState(Qt.WindowMaximized)
if frame is None:
return
frame, self._results = self._barcodeManager.decode_frame(frame)
self.showResults(frame, self._results)
def snipArea(self):
self.setWindowState(Qt.WindowMinimized)
self.snippingWidget.start()
def snipFull(self):
self.setWindowState(Qt.WindowMinimized)
self.snippingWidget.fullscreen()
Testing the Screen QR Reader
-
Run the barcode recognition program:
python3 app_advanced.py - Search Google for QR code.
-
Click the
Select Areabutton to scan one or multiple QR codes displayed in the search results.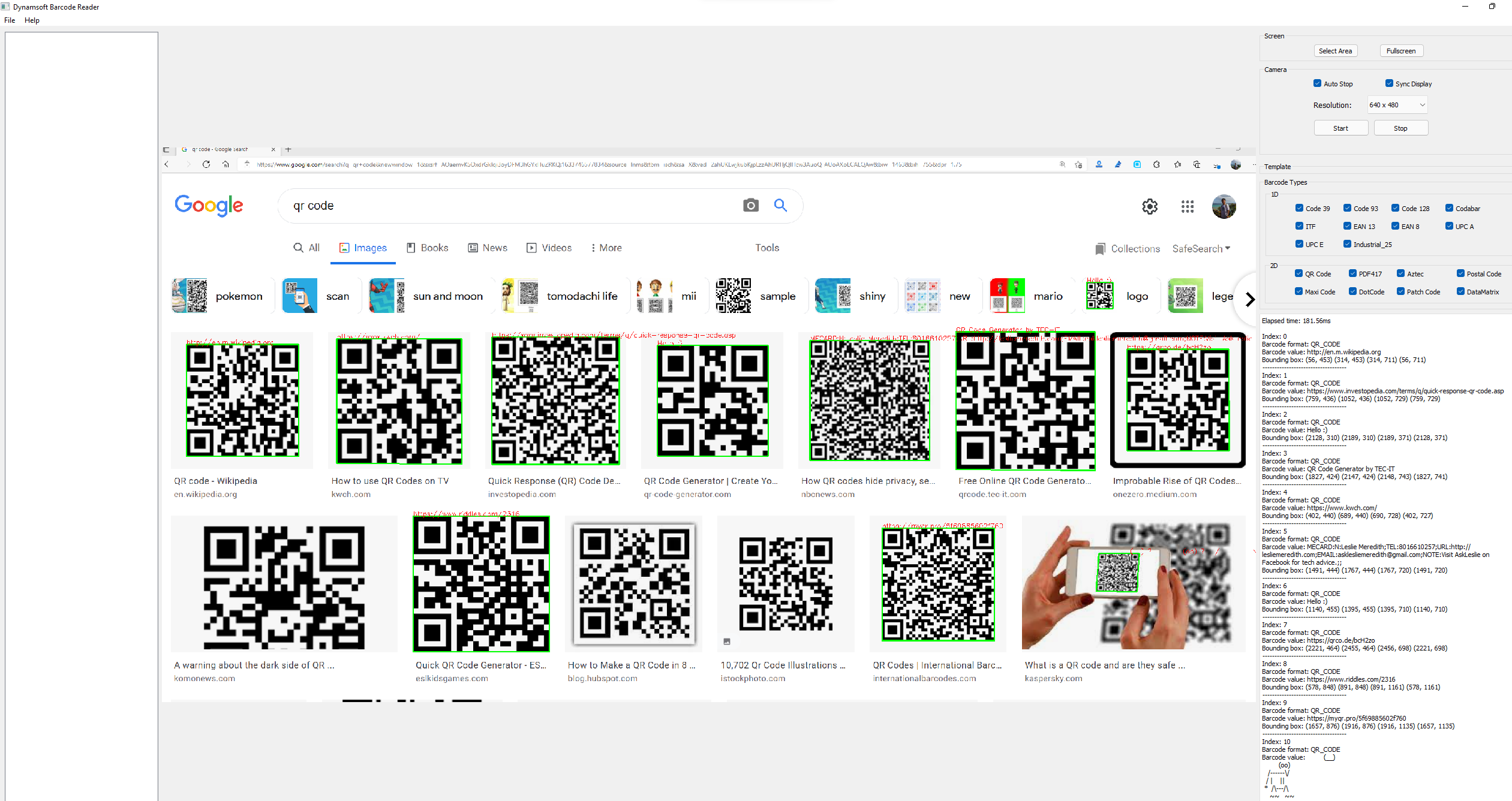
Alternatively, you can perform a full-screen barcode scan with a single click.
Source Code
https://github.com/yushulx/python-barcode-qrcode-sdk/tree/main/examples/official/qt_gui


