How to Read Barcodes in AWS Lambda with Python
In the previous article, we built a simple barcode reader server in Python and deployed it on Vercel. In this article, we are going to deploy it on AWS Lambda to provide a serverless barcode reading interface.
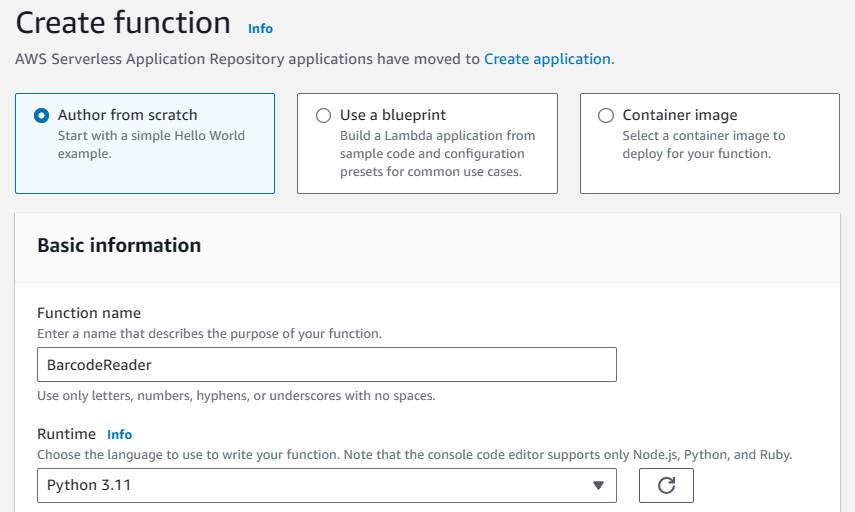
New Function
Create a new AWS Lambda function. Here, we do this in the AWS console.
Add a Layer
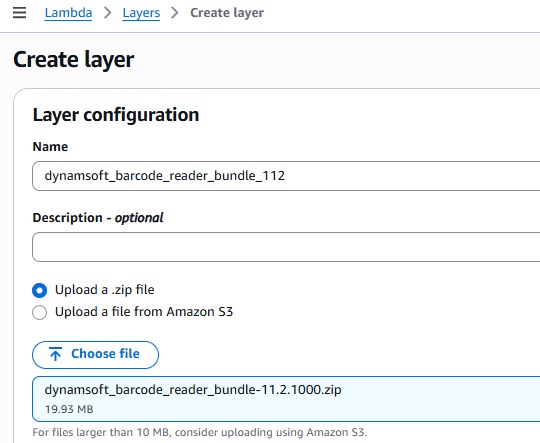
A Lambda layer is a .zip file archive that contains supplementary code or data. Layers usually contain library dependencies, a custom runtime, or configuration files.
Here, we need to add the package of Dynamsoft Barcode Reader in the layer.
- Download the wheel file of Dynamsoft Barcode Reader from pypi.
- Unzip it into a folder named
python. - Zip the folder for uploading as a layer.
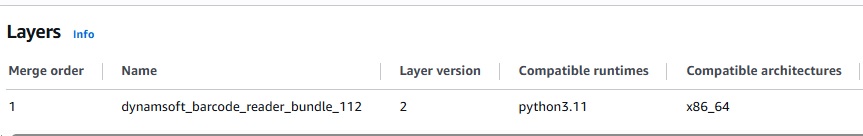
Remember to use the layer for the function:
Write the Handler
Next, modify the handler to use Dynamsoft Barcode Reader.
The handler receives a request like the following:
{
"base64":"<base64-encoded-image>"
}
Then outputs the following:
{"results":
[
{
"barcodeFormat": "QR_CODE",
"barcodeText": "https://www.dynamsoft.com",
"barcodeBytes": "aHR0cHM6Ly93d3cuZHluYW1zb2Z0LmNvbQ==",
"confidence": 82,
"x1": 7,
"y1": 7,
"x2": 93,
"y2": 6,
"x3": 94,
"y3": 94,
"x4": 6,
"y4": 93
}
]
}
-
Import Dynamsoft Barcode Reader and initialize its license. It needs to write caches so that if the license is valid, it does not need to connect to the license server again. Since in AWS Lambda, we can only write to “/tmp”, we need to set a path for saving the cache.
import os from dynamsoft_barcode_reader_bundle import * folder_path = "/tmp/dynamsoft" if not os.path.exists(folder_path): os.makedirs(folder_path) # Sets a directory path for saving the license cache. LicenseManager.set_license_cache_path(folder_path) errorCode, errorMsg = LicenseManager.init_license(DynamsoftLicense)You can apply for a trial license here.
-
In the handler, create a capture vision router instance to read barcodes from the base64.
import base64 def lambda_handler(event, context): if errorCode != EnumErrorCode.EC_OK and errorCode != EnumErrorCode.EC_LICENSE_CACHE_USED: return ("License error: "+ errorMsg) cvr_instance = CaptureVisionRouter() request_body = event["body"] base64_string = json.loads(request_body)["base64"] image_bytes = base64.b64decode(base64_string) result = cvr_instance.capture(image_bytes, EnumPresetTemplate.PT_READ_BARCODES.value) barcode_result = result.get_decoded_barcodes_result() result_dict = {} results = [] if barcode_result != None: for br in barcode_result.get_items(): result = {} result["barcodeFormat"] = br.get_format_string() result["barcodeText"] = br.get_text() result["barcodeBytes"] = str(base64.b64encode(br.get_bytes()))[2:-1] result["confidence"] = br.get_confidence() quad = br.get_location() points = quad.points result["x1"] = points[0].x result["y1"] = points[0].y result["x2"] = points[1].x result["y2"] = points[1].y result["x3"] = points[2].x result["y3"] = points[2].y result["x4"] = points[3].x result["y4"] = points[3].y results.append(result) result_dict["results"] = results return { "statusCode": 200, "body": json.dumps(result_dict) }
Add an API Gateway Trigger
We can add an API gateway as the trigger of the function.
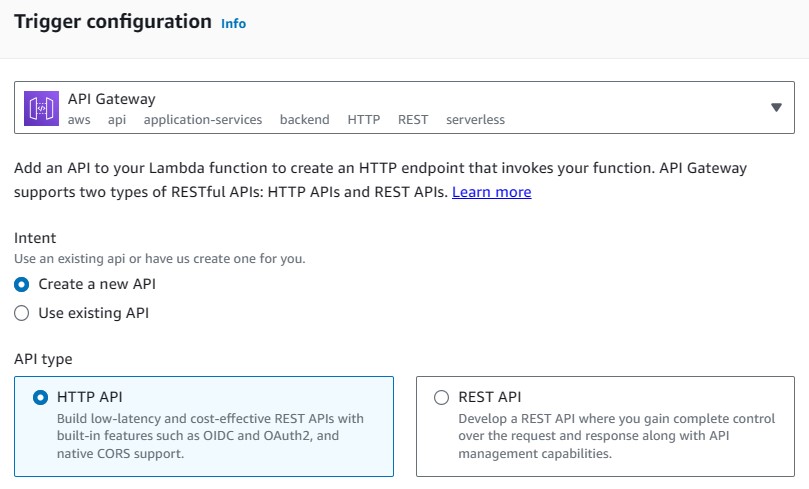
Then, we can call the Lambda function through HTTP.
Here is the Python script to test it:
import base64
import json
import requests
endpoint = "" #like https://*****.execute-api.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/default/BarcodeReader
def get_picture_base64_data(image_path):
with open(image_path, 'rb') as image_file:
base64_data = base64.b64encode(image_file.read())
return base64_data.decode('utf-8')
def decode():
base64 = get_picture_base64_data("./sample_qr.png")
body = {"base64": base64}
json_data = json.dumps(body)
headers = {'Content-type': 'application/json'}
r = requests.post(endpoint, data=json_data, headers=headers)
print(r.json())
if __name__ == "__main__":
decode()
Source Code
The source code of the project is available here: https://github.com/tony-xlh/barcode-reader-aws-lambda/



