Building an Online Barcode and QR Code Scanning App with Python Django
Barcodes and QR codes are essential tools across various industries, including healthcare, finance, and education. In this article, we’ll explore how to leverage Dynamsoft’s powerful barcode recognition technologies to create an online barcode and QR code scanning application using Python Django.
This article is Part 5 in a 8-Part Series.
- Part 1 - Detecting and Decoding QR Codes in Python with YOLO and Dynamsoft Barcode Reader
- Part 2 - How to a GUI Barcode Reader with Qt PySide6 on Raspberry Pi
- Part 3 - Advanced GUI Python Barcode and QR Code Reader for Windows, Linux, macOS and Rasberry Pi OS
- Part 4 - Scanning QR Code from Desktop Screen with Qt and Python Barcode SDK
- Part 5 - Building an Online Barcode and QR Code Scanning App with Python Django
- Part 6 - How to Build Flet Chat App with Barcode and Gemini APIs
- Part 7 - A Guide to Running ARM32 and ARM64 Python Barcode Readers in Docker Containers
- Part 8 - Python Barcode SDK Benchmark: Comparing ZXing, ZBar, and Dynamsoft with Real-World & Stress Tests
Prerequisites
-
Package Installation
pip install dynamsoft-capture-vision-bundle Django -
SDK License
Request a 30-day free trial license.
Supported Barcode Symbologies
Dynamsoft Barcode Reader SDK supports a wide range of barcode symbologies, including:
- Linear Barcodes (1D)
- Code 39 (including Code 39 Extended)
- Code 93
- Code 128
- Codabar
- Interleaved 2 of 5
- EAN-8
- EAN-13
- UPC-A
- UPC-E
- Industrial 2 of 5
- MSI Code
- 2D Barcodes
- QR Code (including Micro QR Code)
- Data Matrix
- PDF417 (including Micro PDF417)
- Aztec Code
- MaxiCode (mode 2-5)
- DotCode
- Patch Code
- GS1 Composite Code
- GS1 DataBar :
- Omnidirectional
- Truncated
- Stacked
- Stacked Omnidirectional
- Limited
- Expanded
- Expanded Stacked
- Postal Codes :
- USPS Intelligent Mail
- Postnet
- Planet
- Australian Post
- UK Royal Mail
Steps to Implement an Online Barcode and QR Code Reader in Python
Follow these steps to build your Django-based barcode and QR code reader:
-
Initialize the Django Project
Start by creating a new Django project:
python -m django startproject djangodbr -
Create the scanbarcode App
Add a new app to your project:
python manage.py startapp scanbarcode -
Set Up Frontend with jQuery
Copy
jquery.min.jsto the<project root>/staticfolder and create anindex.htmlfile in the<project root>/templates/scanbarcodedirectory. Use the following HTML and JavaScript code to handle file uploads:<!DOCTYPE html> <head> <title>Django Online Barcode Reader</title> <meta charset="utf-8"> {% load static %} {% csrf_token %} <script type="text/javascript" src="{% static 'jquery-3.6.0.min.js' %}"></script> </head> <body> <input type="file" id="file" accept="image/*" /> <input id="btnUpload" type="button" value="Read Barcode" onclick="scanBarcode()"> <img id="image" /> <script type="text/javascript"> document.getElementById("file").addEventListener("change", function () { let file = this.files[0]; var fileReader = new FileReader(); fileReader.onload = function () { document.getElementById('image').src = fileReader.result; } fileReader.readAsDataURL(file); }); function scanBarcode() { let formData = new FormData(); formData.append('RemoteFile', document.getElementById('file').files[0], document.getElementById('file').files[0].name); let xhr = new XMLHttpRequest(); xhr.open('POST', '/upload', true); xhr.setRequestHeader("X-CSRFToken", getCookie('csrftoken')); xhr.onreadystatechange = function () { if (xhr.readyState == XMLHttpRequest.DONE && xhr.status == 200) { alert(xhr.responseText); } } xhr.send(formData); } function getCookie(name) { var cookieValue = null; if (document.cookie && document.cookie != '') { var cookies = document.cookie.split(';'); for (var i = 0; i < cookies.length; i++) { var cookie = jQuery.trim(cookies[i]); if (cookie.substring(0, name.length + 1) == (name + '=')) { cookieValue = decodeURIComponent(cookie.substring(name.length + 1)); break; } } } return cookieValue; } </script> </body> </html> -
Define the View for the Web Page
In
scanbarcode/views.py, set the default web page to render theindex.html:def index(request): return render(request, 'scanbarcode/index.html') -
Configure URL Patterns
Create a
urls.pyfile in thescanbarcodedirectory with the following URL patterns:from django.urls import path from . import views urlpatterns = [ path('', views.index, name='index'), path('upload', views.upload, name="upload"), ] -
Integrate Custom URLs
Modify the
<project root>/djangodbr/urls.pyfile to include your app’s URLs:from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path, include urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('', include('scanbarcode.urls')) ] -
Configure Template Directory
Add the path of the template folder to the
TEMPLATESsetting in<project root>/djangodbr/settings.py:TEMPLATES = [ { 'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates', 'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')], 'APP_DIRS': True, 'OPTIONS': { 'context_processors': [ 'django.template.context_processors.debug', 'django.template.context_processors.request', 'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth', 'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages', ], }, }, ] -
Implement Barcode and QR Code Scanning
In
scanbarcode/views.py, add the logic to scan barcodes and QR codes from uploaded images:from django.http import HttpResponse, request from django import template from django.shortcuts import render import os from .models import Image from dynamsoft_capture_vision_bundle import * import json error_code, error_message = LicenseManager.init_license( "DLS2eyJoYW5kc2hha2VDb2RlIjoiMjAwMDAxLTE2NDk4Mjk3OTI2MzUiLCJvcmdhbml6YXRpb25JRCI6IjIwMDAwMSIsInNlc3Npb25QYXNzd29yZCI6IndTcGR6Vm05WDJrcEQ5YUoifQ==") if error_code != EnumErrorCode.EC_OK and error_code != EnumErrorCode.EC_LICENSE_CACHE_USED: print("License initialization failed: ErrorCode:", error_code, ", ErrorString:", error_message) def index(request): return render(request, 'scanbarcode/index.html') def upload(request): out = "No barcode found" if request.method == 'POST': filePath = handle_uploaded_file(request.FILES['RemoteFile'], str(request.FILES['RemoteFile'])) cvr_instance = CaptureVisionRouter() result = cvr_instance.capture( filePath, EnumPresetTemplate.PT_READ_BARCODES.value) items = result.get_items() if len(items) > 0: out = '' for item in items: out += "Barcode Format : " + item.get_format_string() + "\n" out += "Barcode Text : " + item.get_text() + "\n" out += "------------------------------------------------------------\n" return HttpResponse(out) return HttpResponse(out) def handle_uploaded_file(file, filename): if not os.path.exists('upload/'): os.mkdir('upload/') filePath = 'upload/' + filename with open(filePath, 'wb+') as destination: for chunk in file.chunks(): destination.write(chunk) return filePath -
Deploy and Run the Django Barcode and QR Code Reader App
Deploy the app by running the following commands:
python manage.py makemigrations python manage.py migrate --run-syncdb python manage.py runserverOpen a browser and navigate to
127.0.0.1:8000to test the application.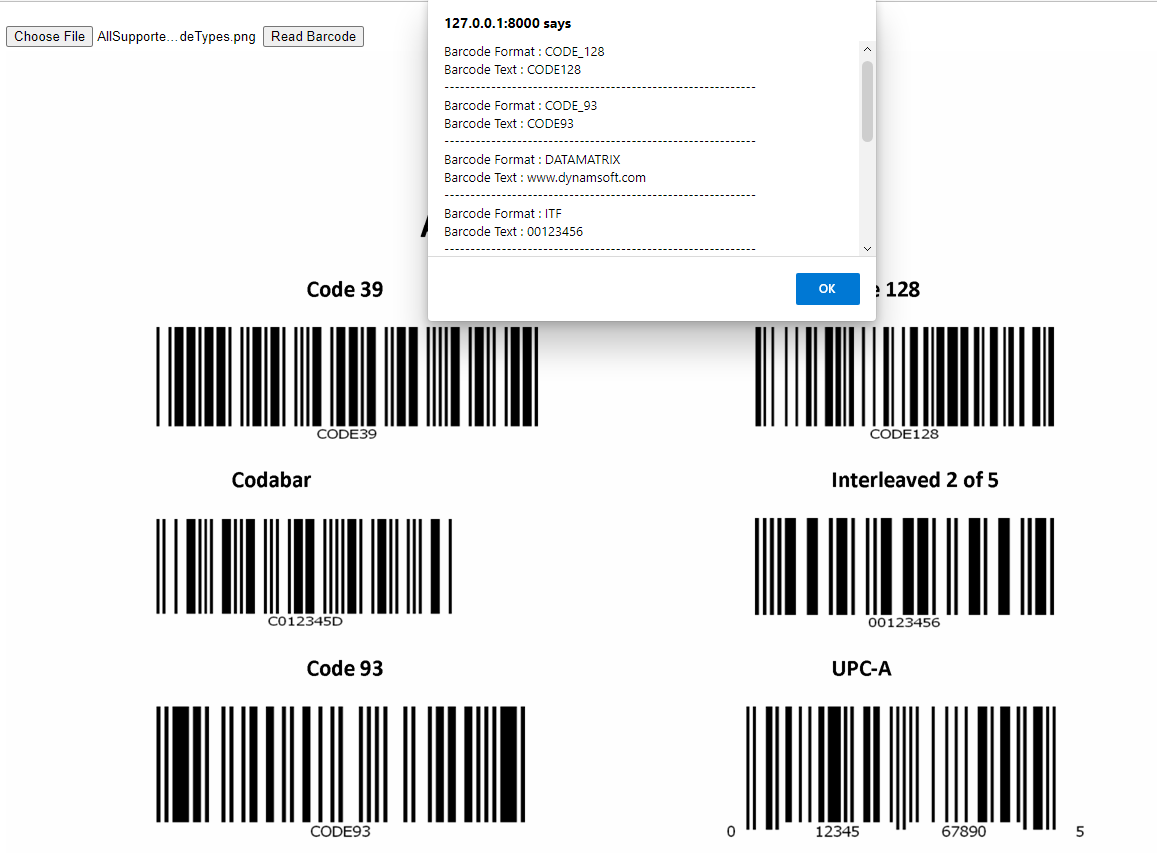
Source Code
https://github.com/yushulx/python-barcode-qrcode-sdk/tree/main/examples/official/django


