How to a GUI Barcode Reader with Qt PySide6 on Raspberry Pi
If you’re aiming to develop a cross-platform GUI application using Python and Qt, your primary options are PyQt and PySide. Both offer Qt bindings for Python, but they differ mainly in licensing: PyQt5 requires either a GPL or a commercial license, while PySide6 is licensed under LGPL, making it more flexible for commercial applications. Given that PySide6 is officially recommended and up-to-date with the latest Qt features, we’ll use it alongside Dynamsoft’s Python Barcode SDK to build a robust GUI barcode reader app for Raspberry Pi.
This article is Part 2 in a 8-Part Series.
- Part 1 - Detecting and Decoding QR Codes in Python with YOLO and Dynamsoft Barcode Reader
- Part 2 - How to a GUI Barcode Reader with Qt PySide6 on Raspberry Pi
- Part 3 - Advanced GUI Python Barcode and QR Code Reader for Windows, Linux, macOS and Rasberry Pi OS
- Part 4 - Scanning QR Code from Desktop Screen with Qt and Python Barcode SDK
- Part 5 - Building an Online Barcode and QR Code Scanning App with Python Django
- Part 6 - How to Build Flet Chat App with Barcode and Gemini APIs
- Part 7 - A Guide to Running ARM32 and ARM64 Python Barcode Readers in Docker Containers
- Part 8 - Python Barcode SDK Benchmark: Comparing ZXing, ZBar, and Dynamsoft with Real-World & Stress Tests
Prerequisites
-
OpenCV
python3 -m pip install opencv-python -
PySide6
python3 -m pip install PySide6 -
Dynamsoft Barcode Reader
python3 -m pip install dynamsoft-capture-vision-bundle
Building the GUI Barcode Reader on Raspberry Pi OS
UI Widgets Setup
-
Button for Loading Image Files:
Allow users to load images for barcode scanning.
self.btn = QPushButton("Load an image") self.btn.clicked.connect(self.pickFile) def pickFile(self): filename = QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(self, 'Open file', self._path, "Barcode images (*)") if filename is None or filename[0] == '': self.showMessageBox("No file selected") return -
Button for Opening the Live Camera Stream:
Enable live scanning from a connected webcam.
btnCamera = QPushButton("Open camera") btnCamera.clicked.connect(self.openCamera) self.timer = QTimer() self.timer.timeout.connect(self.nextFrameUpdate) def openCamera(self): if not self._cap.isOpened(): self.showMessageBox("Failed to open camera.") return self.timer.start(1000./24) -
Button for Stopping the Camera Stream:
Allow users to stop the live camera stream.
btnCamera = QPushButton("Stop camera") btnCamera.clicked.connect(self.stopCamera) def stopCamera(self): self.timer.stop() -
Label for Displaying Camera Frames and a Text Area for Barcode Decoding Results:
Show the live video feed and display barcode results.
self.label = QLabel() self.label.setFixedSize(self.WINDOW_WIDTH - 30, self.WINDOW_HEIGHT - 160) self.results = QTextEdit() def showResults(self, frame, results): frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) image = QImage(frame, frame.shape[1], frame.shape[0], frame.strides[0], QImage.Format_RGB888) pixmap = QPixmap.fromImage(image) pixmap = self.resizeImage(pixmap) self.label.setPixmap(pixmap) self.results.setText(results)
Integrating OpenCV for Image and Video Capture
Use OpenCV to handle image loading and capture frames from the webcam:
frame = cv2.imread(filename)
self._cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
self._cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, 640)
self._cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, 480)
ret, frame = self._cap.read()
Efficient Barcode Decoding with Multiprocessing
To integrate the barcode decoding API, a straightforward approach would be to invoke the decoding method as soon as we capture a frame:
def nextFrameSlot(self):
ret, frame = self._cap.read()
if not ret:
self.showMessageBox('Failed to get camera frame!')
return
frame, results = self._manager.decode_frame(frame)
self.showResults(frame, results)
However, this method is impractical for use on Raspberry Pi. Barcode scanning is a CPU-intensive task, and if it takes too long, it will block the UI thread, causing performance issues. To address this, we need to run the UI and barcode recognition code in separate threads. Unfortunately, due to Python’s Global Interpreter Lock (GIL), using Python threads won’t provide the desired performance improvements. A potential alternative is to use QThread, which operates similarly to Python threads. Let’s evaluate the performance of QThread with the following implementation:
class WorkerSignals(QObject):
result = Signal(object)
class BarcodeManager(QThread):
def __init__(self, license):
super(BarcodeManager, self).__init__()
self.signals = WorkerSignals()
self._reader = BarcodeReader()
self._reader.init_license(license)
settings = self._reader.get_runtime_settings()
settings.max_algorithm_thread_count = 1
self._reader.update_runtime_settings(settings)
self.frameQueue = Queue(1)
def register_callback(self, fn):
self.signals.result.connect(fn)
def run(self):
while True:
try:
frame = self.frameQueue.get(False, 10)
if type(frame) is str:
break
except:
time.sleep(0.01)
continue
try:
results = self._reader.decode_buffer(frame)
self.signals.result.emit(results)
except BarcodeReaderError as error:
print(error)
Testing shows that QThread does not significantly improve performance. Thus, the most effective solution is to offload barcode decoding to a separate Python Process using the multiprocessing module:
from multiprocessing import Process, Queue
import time
import numpy as np
from dynamsoft_capture_vision_bundle import *
def process_barcode_frame(license, frameQueue, resultQueue):
LicenseManager.init_license('LICENSE-KEY')
cvr_instance = CaptureVisionRouter()
while True:
results = None
try:
frame = frameQueue.get(False, 10)
if type(frame) is str:
break
except:
time.sleep(0.01)
continue
results = cvr_instance.capture(frame, EnumPresetTemplate.PT_READ_BARCODES.value)
try:
resultQueue.put(results, False, 10)
except:
pass
def create_decoding_process(license):
size = 1
frameQueue = Queue(size)
resultQueue = Queue(size)
barcodeScanning = Process(target=process_barcode_frame, args=(license, frameQueue, resultQueue))
barcodeScanning.start()
return frameQueue, resultQueue, barcodeScanning
Running the Application
Connect a USB webcam to your Raspberry Pi and run the application:
python3 app.py license.txt
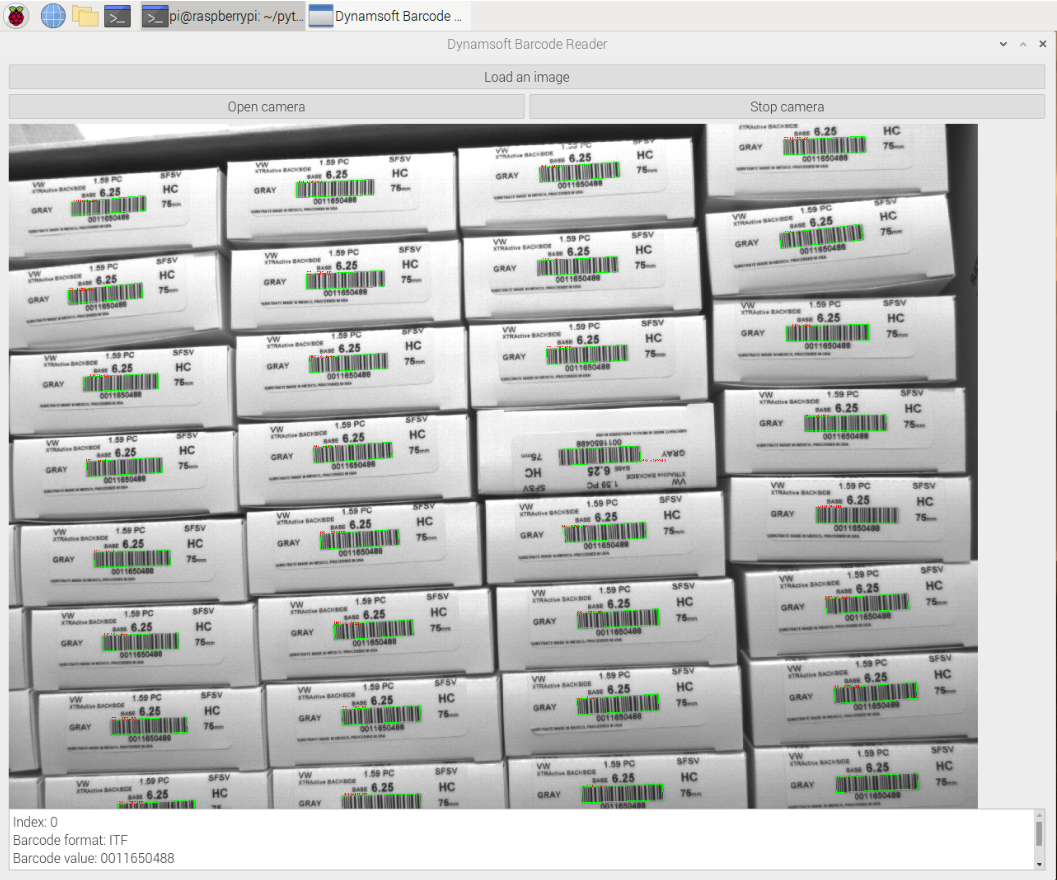
The GUI barcode reader app is not limited to Raspberry Pi—it’s cross-platform and works on Windows, Linux, and macOS as well.
Source Code
https://github.com/yushulx/python-barcode-qrcode-sdk/tree/main/examples/official/qt_gui


