Need better scanning performance?
TargetROIDef Object
The TargetROIDef object specifies one or more recognition tasks to be performed on regions of interest (ROIs) within an image.
Example
{
"Name": "TA_1",
"TaskSettingNameArray": [
"LR_0",
"BR_0",
"DN_0"
],
"Location": {
"ReferenceObjectFilter": {
"ReferenceTargetROIDefNameArray": ["TR_0", "TR_1"],
"AtomicResultTypeArray": ["ART_TEXT_LINE", "ART_BARCODE", "ART_FRAME"],
"BarcodeFilteringCondition": {},
"FrameFilteringCondition": {},
"TextLineFilteringCondition": {},
"RegionFilteringCondition": {}
},
"Offset": {
"ReferenceObjectOriginIndex": 0,
"ReferenceObjectType": "ROT_ATOMIC_OBJECT",
"MeasuredByPercentage": 1,
"FirstPoint": [0, 0],
"SecondPoint": [100, 0],
"ThirdPoint": [100, 100],
"FourthPoint": [0, 100]
}
}
}
Parameters
| Parameter Name | Type | Required/Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Name |
String | Required | The unique identifier for this TargetROIDef object. |
TaskSettingNameArray |
String Array | Optional | Array of task setting object names (BarcodeReaderTaskSetting, LabelRecognizerTaskSetting, DocumentNormalizerTaskSetting) defining recognition tasks. |
Location |
Object | Optional | Defines the spatial location where recognition tasks are performed. Consists of ReferenceObjectFilter and Offset parameters. |
BaseTargetROIDefName |
String | Optional | Name of another TargetROIDef object to inherit parameters from. Parameters defined in this object override inherited ones. |
EnableResultsDeduplication |
Integer | Optional | Whether to enable result deduplication (0 or 1). |
In simple terms:
TargetROIDef = Recognition Task Definition + Spatial Location Definition
Recognition Tasks
Recognition tasks configured on a TargetROIDef object include barcode recognition, label recognition, document boundary detection, etc. The atomic result of each task type is the smallest output item: a barcode, text line, table cell, detected quadrilateral, etc. CapturedResult represents a set of all captured atomic result items on an image.
| Task Type | Performed By | Atomic Result Type |
|---|---|---|
| Read Barcodes | Dynamsoft Barcode Reader SDK | BarcodeResultItem |
| Recognize Text Lines | Dynamsoft Label Recognizer SDK | TextResultItem |
| Detect Document Borders | Dynamsoft Document Normalizer SDK | DetectedQuadResultItem |
| Deskew a Document | Dynamsoft Document Normalizer SDK | DeskewedImageResultItem |
| Enhance an Image | Dynamsoft Document Normalizer SDK | EnhancedImageResultItem |
For more details:
Spatial Location
The Location parameter defines the spatial location where recognition tasks are performed. It consists of ReferenceObjectFilter and Offset parameters. The former filters out desired reference regions, and the latter defines a uniform offset relative to the reference regions.
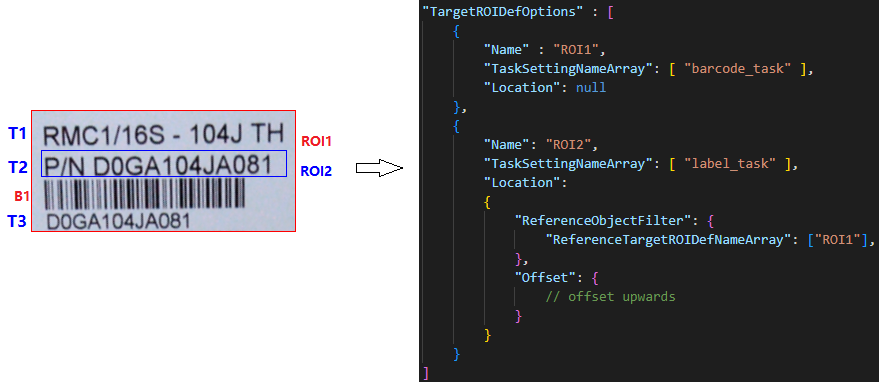
| Concept | Description | Example Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Result | Atomic result of recognition task output. Can be a colour detection region, barcode, text line, table cell, detected quadrilateral, etc. | T1, T2, T3 are three TextLineResultItem objects, and B1 is one BarcodeResultItem object. |
| Reference Region | A physical quadrilateral region. Two types: entire image region and atomic result region. The former is the quadrilateral extent of the original image; the latter is the quadrilateral extent of each atomic result. | ROI1 has one reference region (entire image). ROI2 has three reference regions generated from T1, T2, T3. |
| Target Region | A physical quadrilateral region calculated from a reference region and offset. | ROI1 has one target region equal to the reference region. ROI2 has three target regions calculated by offsets from T1, T2, T3 quadrilateral regions. |
ReferenceObjectFilter
Defines filter conditions for reference objects. You can filter reference objects by TargetROIDefName, atomic result type, and specific atomic result details. Multiple objects may fit the filter conditions. More precise filter conditions yield more accurate reference regions.
| Parameter Name | Type | Required/Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
ReferenceTargetROIDefNameArray |
String Array | Optional | References atomic objects generated by other TargetROIDef objects by name. Intersects with AtomicResultTypeArray to determine final referenced objects. |
AtomicResultTypeArray |
String Array | Optional | Atomic result types that can be used as reference objects. Intersects with ReferenceTargetROIDefNameArray to determine final referenced objects. |
BarcodeFilteringCondition |
Object | Optional | Barcode conditions that can be used as reference objects. |
FrameFilteringCondition |
Object | Optional | Frame conditions that can be used as reference objects. |
TextLineFilteringCondition |
Object | Optional | Text line conditions that can be used as reference objects. |
RegionFilteringCondition |
Object | Optional | Colour region conditions that can be used as reference objects. |
Offset
Defines the offset of the target region from the reference object. If no reference object is defined, the origin is set to the top-left vertex of the original image.

| Parameter Name | Type | Required/Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
ReferenceObjectOriginIndex |
Integer | Optional | Which point of the reference object will be set as the origin of the coordinate system. |
ReferenceObjectType |
String | Optional | Which coordinate system to use when configuring offset parameters based on the reference objects. |
ReferenceXAxis |
Object | Optional | The x-axis of the coordinate system to use when configuring offset parameters based on the reference objects. |
ReferenceYAxis |
Object | Optional | The y-axis of the coordinate system to use when configuring offset parameters based on the reference objects. |
MeasuredByPercentage |
Integer | Optional | Whether to use percentage to measure the points’ coordinates (0 or 1). |
FirstPoint |
Integer Array | Required | The first point of the target region, defining the offset from the origin. |
SecondPoint |
Integer Array | Required | The second point of the target region, defining the offset from the origin. |
ThirdPoint |
Integer Array | Required | The third point of the target region, defining the offset from the origin. |
FourthPoint |
Integer Array | Required | The fourth point of the target region, defining the offset from the origin. |
Usage Examples
Reference the Original Image
You can set an offset based on the original image to localize the ROI without any reference object.
Example: Define ROI from the original image and perform barcode recognition on the upper 50% of the image.
{
"TargetROIDefOptions": [
{
"Name": "ROI_0",
"TaskSettingNameArray": ["barcode_task"],
"Location": {
"ReferenceObjectFilter": null,
"Offset": {
"MeasuredByPercentage": 1,
"FirstPoint": [0, 0],
"SecondPoint": [100, 0],
"ThirdPoint": [100, 50],
"FourthPoint": [0, 50]
}
}
}
]
}
Reference Another TargetROIDef
If significant objects can help localize the targeting content, define filter conditions to localize reference objects first, then capture the targeting content.
Example: Use barcode location to extract text line information.

{
"TargetROIDefOptions": [
{
"Name": "ROI_0",
"TaskSettingNameArray": ["barcode_task"],
"Location": null
},
{
"Name": "ROI_1",
"TaskSettingNameArray": ["text_task"],
"Location": {
"ReferenceObjectFilter": {
"ReferenceTargetROIDefNameArray": ["ROI_0"],
"AtomicResultTypeArray": ["ART_BARCODE"],
"BarcodeFilteringCondition": {
"BarcodeFormatIds": ["BF_CODE_128"],
"BarcodeTextRegExPattern": "ReferenceObject"
}
},
"Offset": {
"MeasuredByPercentage": 1,
"FirstPoint": [20, 140],
"SecondPoint": [60, 140],
"ThirdPoint": [60, 170],
"FourthPoint": [20, 170]
}
}
}
]
}


