The Rise of GS1-128 Barcodes: Why They Are Replacing 1-Dimensional Barcodes

With the rapid advancement of technology, it is evident that the proliferation of GS1-128 barcodes is revolutionizing the barcode utilization landscape. GS1-128 barcodes are progressively replacing conventional 1-dimensional barcodes because of their greater storage capacity, interoperability with modern identifying technologies, and global standardization.
Overview of 1-Dimensional Barcodes: Limitations and Challenges
1-dimensional barcodes find their usage in widespread applications, such as inventory management and product identification. These barcodes have been in use since 1974, but due to their inability to encode complex information and limited data capacity, they are being replaced by superior barcode types. Below are some challenges and limitations with 1D barcodes.
-
Limited Data Capacity: 1D barcodes have a limited data capacity, and as the data size increases, the barcode size also increases. Hence, users limit the size between 8-15 characters. Inability to Encode Alphanumeric Data: Most 1D barcodes are incapable of encoding alphanumeric data, such as special symbols or letters. The only types that can store alphanumeric characters are Code 39, Code 93, and Code 128.
-
Lack of Global Standardization: 1-dimensional barcodes, such as UPC and EAN, can vary by region or industry. This lack of standardization creates difficulties in compatibility and interoperability between barcode systems. It can complicate global supply chains when businesses and trading partners use different barcode standards.
-
Readability and Scanning Issues: Poor print quality, barcode deterioration, and damage can make scanning 1-dimensional barcodes difficult, further leading to errors and delays in workflows.
-
Limited Application Scope: 1-dimensional barcodes are best suited for inventory control and identification processes. They may not be the best choice for complex applications like regulatory compliance or traceability that involve extensive data encoding or system integration.
-
Space Constraints: The more data, the bigger the size of 1-dimensional barcodes. Hence, they are not ideal for use on small products or limited labeling space.
-
Lack of Flexibility for Future Technologies: 1-dimensional barcodes are not flexible enough to adapt to advanced tracking and identification systems. The growing convergence of technologies such as RFID and QR codes within the realms of supply chain management and retail necessitates the utilization of barcodes that can seamlessly coexist with these systems, which 1D barcodes cannot provide.
Introducing GS1-128 Barcode: A Superior 1D Barcode
GS1-128 barcodes are a variant of linear or 1-dimensional barcodes that can encode alphanumeric data effectively. These barcodes are built upon the GS1 system, which ensures their adherence to industry standards and compatibility with various systems and applications. Based on the Code 128 symbology, the GS1-128 barcode can store data with variable lengths. Hence, the barcode is used in several industries and applications, such as traceability, product identification, inventory management, and compliance with industry standards.
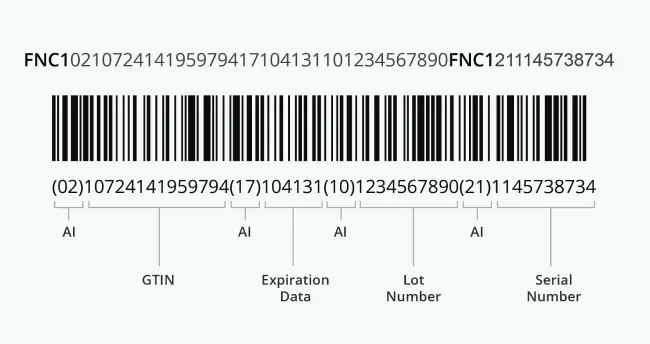
GS1 128 Barcode format
Here’s a GS1 128 barcode example that shows the GS1 128 barcode format:
Advantages of GS1-128 Barcodes
-
Enhanced Data Capacity: The increasing popularity of GS1-128 barcodes can be attributed to their enhanced capacity for information storage and transmission, surpassing that of conventional 1-dimensional barcodes. GS1-128 barcodes may encode alphanumeric data, unlike most 1-dimensional barcodes. This remarkable feature gives businesses more data storage and flexibility. The increased data capacity allows organizations to add batch numbers, expiration dates, and serial numbers to a barcode.
-
Improved Supply Chain Efficiency: Implementing GS1-128 barcodes enhances supply chain efficiency through accuracy and optimized workflows. By seamlessly integrating an extensive array of data within a unified barcode system, these barcodes facilitate expedited and accurate scanning processes, thereby streamlining operational efficiency and minimizing errors. Improved efficiency leads to improved inventory management, logistics optimization, and visibility across the supply chain.
-
Global Standardization and Interoperability: GS1-128 barcodes correspond to GS1 standards, which is one of its main advantages. GS1, a leading global standards body, ensures interoperability and compatibility by promoting synergistic collaboration across sectors and industries. Standardization improves operational efficiency and builds reliability and trust among business partners. Hence, businesses may strategically position themselves with GS1-128 barcodes, a globally recognized standard to streamline communication, supply chain coordination, and data exchange.
-
Regulatory Compliance and Traceability: Enterprises in varied industries must ensure regulatory compliance and product traceability. GS1-128 barcodes fulfill market demands well, as they can encode data such as batch numbers, expiration dates, and regulatory information. This crucial feature allows easy and precise product tracking throughout their lives. GS1-128 barcodes provide product safety and regulatory compliance for pharmaceutical, food & beverage, and consumer goods companies.
Adoption Challenges with GS1-128 Barcodes
Implementing GS1-128 barcodes may encounter various adoption challenges stemming from diverse factors.
-
Existing Infrastructure and Systems: One of the main hurdles encountered in the adoption process is the alignment of GS1-128 barcodes with pre-existing systems and infrastructure. Many businesses possess well-established infrastructures, protocols, and machinery tailored to accommodate conventional 1D barcodes. Hence, implementing GS1-128 barcodes necessitates modifications, potential updates, or even the replacement of current systems, resulting in a significant investment of time and resources.
-
Cost Considerations: GS1-128 barcode integration requires software, hardware, and training costs. Businesses need to invest in GS1-128 barcode printers, scanners, and labeling systems. They may need upgrades or new software to create and decode these barcodes. Staff training is essential for GS1-128 barcode use and integration. The cost of the project depends on its scope and infrastructure.
-
Industry-wide Implementation: GS1-128 barcodes need industry-wide adoption to maximize their potential. Retailers, manufacturers, suppliers, and logistical partners must collaborate to achieve this. Divergent standards, processes, and methods across organizations make industry-wide adoption challenging. Not to mention, educating stakeholders about the benefits and necessity of GS1-128 barcodes takes time and effort.
Coexistence and Integration: The Role of 1-Dimensional Barcodes in the Present

Carefully deliberating the implementation of GS1-128 barcodes is of utmost importance for enterprises. It requires the formulation of effective transition strategies. Adopting a gradual and incremental strategy is better than opting for an abrupt and absolute substitution of 1-dimensional barcodes. This strategy may entail a phased implementation of GS1-128 barcodes into the current systems and workflows while concurrently maintaining support for and leveraging 1-dimensional barcodes when deemed essential.
Transition Strategies for Businesses
-
Conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the distinct needs and prerequisites of the enterprise to ascertain the optimal barcode format that aligns with each application or product.
-
Find the critical areas where GS1-128 barcodes may be more beneficial than 1-dimensional barcodes, such as compliance with global standards or enhanced data capacity.
-
Equipment, system, and software must be upgraded or updated to handle both barcode types, ensuring seamless integration and compatibility.
-
Provide proper training to the staff and partners involved in data management and barcode scanning to guarantee a seamless transition and successful usage of both barcode symbologies.
-
Work and collaborate with industry partners to standardize data sharing, barcode usage, and supply chain integration approaches.
Future Outlook: Potential for GS1-128 Barcode Dominance

GS1-128 barcodes have the potential to establish supremacy in some industries. Businesses may increasingly leverage GS1-128 barcodes as they grasp the benefits of increased data capacity, worldwide standards, and interoperability with modern identifying systems. The widespread use of GS1-128 barcodes across businesses may result in a move away from traditional 1-dimensional barcodes.
Evolving Technologies and Barcoding Solutions
With the evolution of technologies, new barcoding solutions may be developed to meet developing requirements and tackle challenges. Combining barcodes with future technologies such as blockchain, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, or artificial intelligence may open new avenues for product monitoring, data management, and supply chain optimization.
How Dynamsoft Can Help You Transition?
If you are willing to implement GS1-128 barcodes into your business workflow, you’ll require a barcode scanner that supports the symbology. Choosing Dynamsoft Barcode Reader SDK will help you build a robust GS1-128 barcode scanner using a few lines of code. You can also add the GS1-128 barcode scanning functionality to your existing system.
Leveraging the flexible APIs of our SDK, you can build a barcode scanning solution that supports multiple symbologies, from 1D barcodes to GS1 barcodes and 2-dimensional barcodes.
Try the online barcode scanner demo


 Blog
Blog