Category: barcode
-

From aircraft engines to automotive assembly lines, manufacturers are under growing pressure to track every part with absolute accuracy throughout its entire lifecycle. Traditional paper labels or printed barcodes often fail in harsh industrial environments, where they are exposed to heat, abrasion, chemicals, and the passage of time. As products...
Read more › -

What Changes When Moving from 96 to 384 and 1536-Well Microplates? Laboratory automation is moving toward higher density within the same footprint. As screening and genomics workflows transition from 96-well plates to 384-well and 1536-well formats, each camera frame captures each captured image contains hundreds of small, closely spaced 2D...
Read more › -

In high-throughput laboratory automation, efficiency is rarely lost to major system failures. Instead, it declines incrementally, millisecond by millisecond. Barcode decoding latency is a common source of hidden efficiency loss. Once decoding performance is considered “acceptable,” its impact on motion control and system timing is often overlooked. Even minor delays...
Read more › -
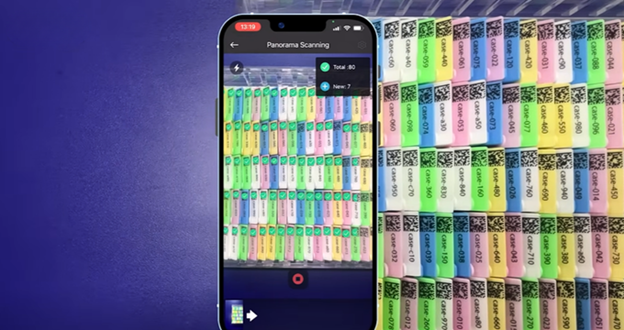
Why a 1% Read Failure Rate Creates Outsized Manual Work and Throughput Loss In high-throughput laboratory automation, most systems are built for standard scenarios, and a 99% barcode read success rate is often deemed sufficient. At scale, this assumption fails. In a facility processing 50,000 samples daily, a 1% failure...
Read more › -

As manufacturing becomes more complex, permanently marked identifiers are replacing printed labels to maintain traceability from production to service. Traditional identification methods, such as printed labels and stickers, often fail in production environments. Exposure to heat, chemicals, abrasion, sterilization, and long product lifecycles can quickly degrade labels and disrupt the...
Read more › -

Across both the EU and the US, a major shift is underway: products are beginning to carry persistent, scannable digital identities that track their history, materials, and lifecycle from manufacturing to end-of-life. The concept isn’t fully standardised worldwide yet, but momentum is accelerating - and hardware manufacturers need to prepare....
Read more › -
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into business operations is no longer a futuristic concept; it is a present-day mandate. While excitement abounds over AI’s predictive and analytical capabilities, a fundamental truth remains: AI is only as good as the data it consumes. This critical relationship is most evident in...
Read more › -

The pharmaceutical industry stands at a critical inflection point. As global supply chains grow increasingly complex and regulatory frameworks tighten, the ability to track every unit, from the research lab to the pharmacy shelf, has become non-negotiable. A single scanning error can cascade into batch rejections, compliance violations, and patient...
Read more › -

Modern organizations run on data. From retail shelves and warehouse pallets to manufacturing tools and sensitive pharmaceuticals, businesses need to know what they have, where it is, and in what condition it is. Barcodes, RFID, and IoT sensors are among the most widely used data collection methods, but each serves...
Read more › -

A library barcode scanner is essential for modern libraries looking to streamline inventory management, simplify book check-in and check-out, and improve catalog accuracy. By supporting multiple barcode symbologies such as Code 39, Code 128, ISBN, and QR codes, libraries can efficiently track books and other materials. Whether built using a...
Read more › -
For decades, the EAN/UPC barcode—a one-dimensional (1D) barcode—has been the cornerstone of price lookup functionality. However, as global commerce evolves, the limitations of 1D barcodes in meeting demands for enhanced transparency, traceability, and authentication have become apparent. To address these challenges, the supply chain is shifting to two-dimensional (2D) barcodes,...
Read more › -
Using PDF417 as Medical Barcode in Healthcare - Improve Patient Management and Prescription Tracking

As healthcare providers strive to deliver high-quality care and improve patient outcomes, accurate and efficient patient record management and prescription tracking have become increasingly important. One tool that has emerged as a key component of these efforts is the PDF417 barcode. With its ability to store large amounts of information...
Read more › -
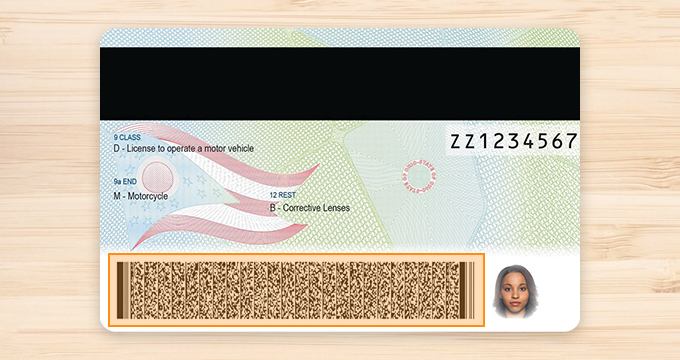
In today’s world, ID cards are an essential part of our daily lives. Whether it is for accessing secure areas, making purchases, or verifying our identities, ID cards have become an integral part of our personal and professional lives. However, with the increasing complexity of security threats and the need...
Read more › -
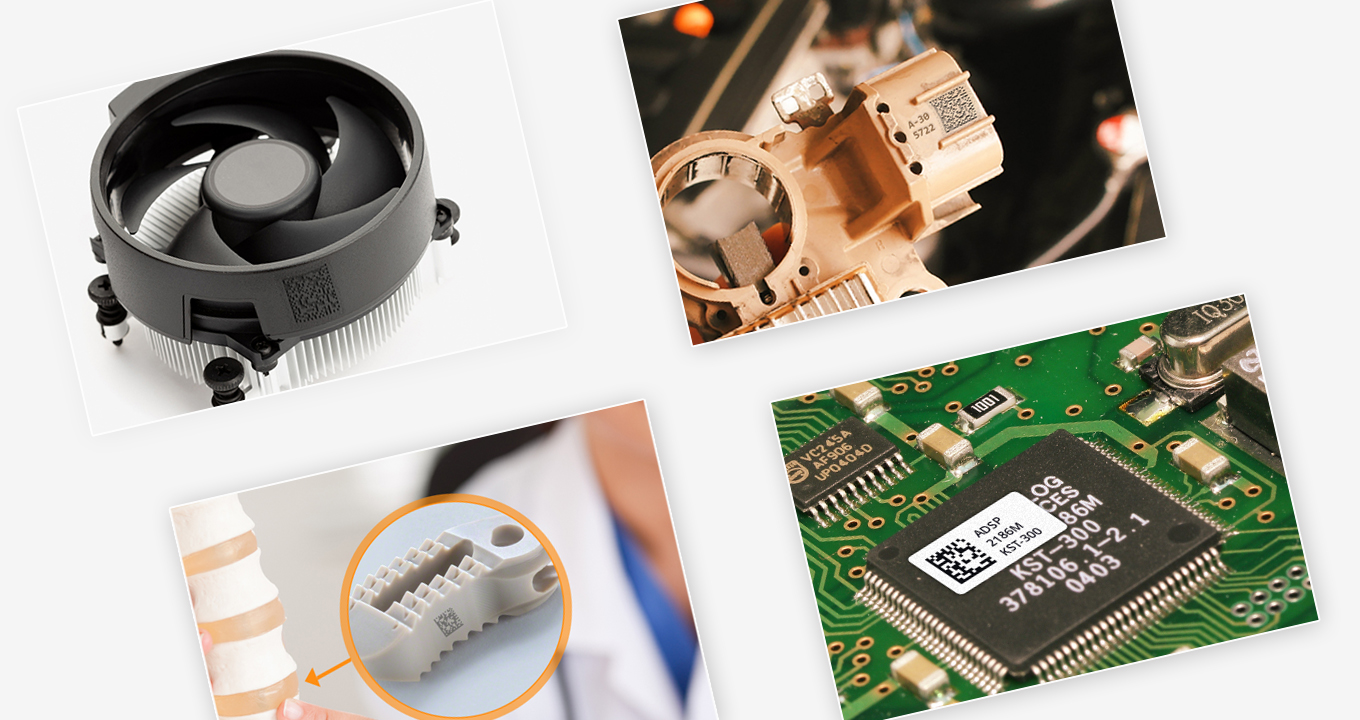
DPM codes (Direct Part Marking), are used to mark or engrave a barcode directly onto a product or part. This allows for easy identification, tracking, and traceability of the product throughout its lifecycle. In this blog, we explore the leading uses of DPM codes on plastics, difficulties encountered during the...
Read more › -
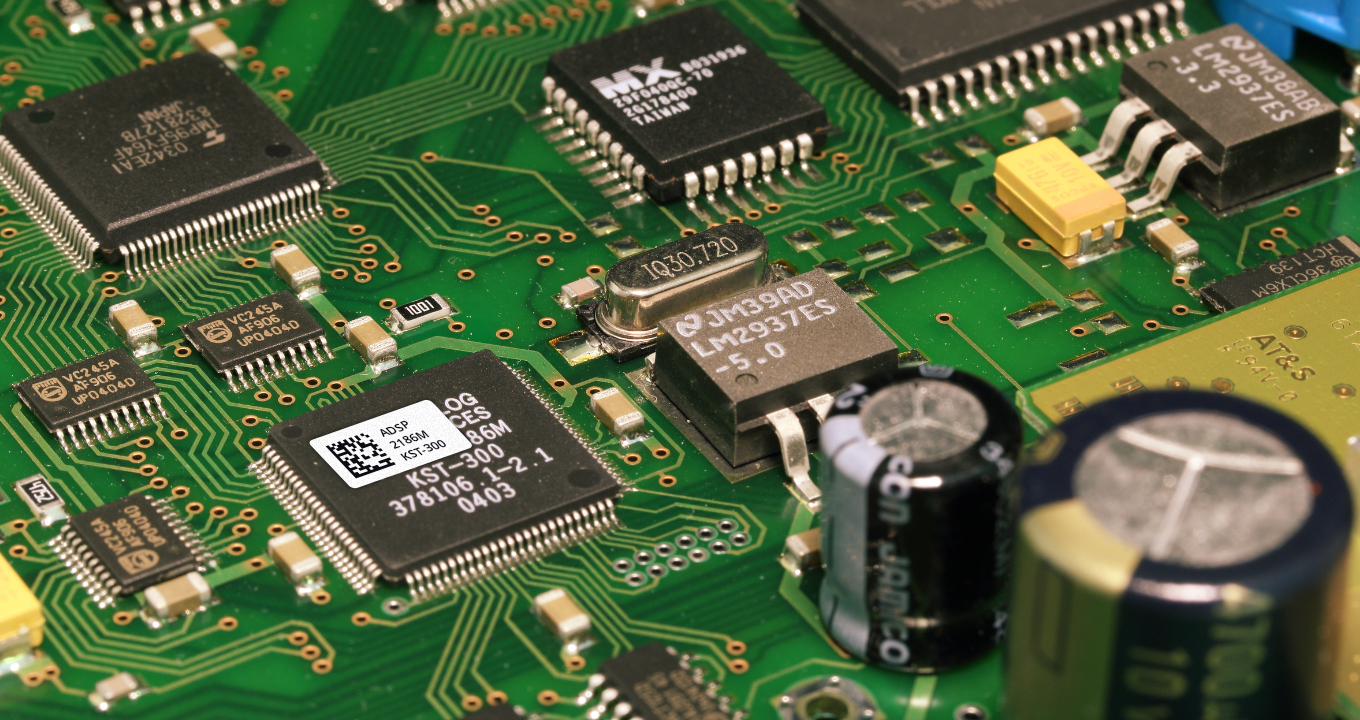

In the complicated world of Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs), exact circuit board component identification is essential for easing out troubleshooting. It ensures that the electronic devices function efficiently. This article will explore the role of Data Matrix codes for enhanced efficiency in PCB parts identification. Data Matrix codes play an...
Read more › -
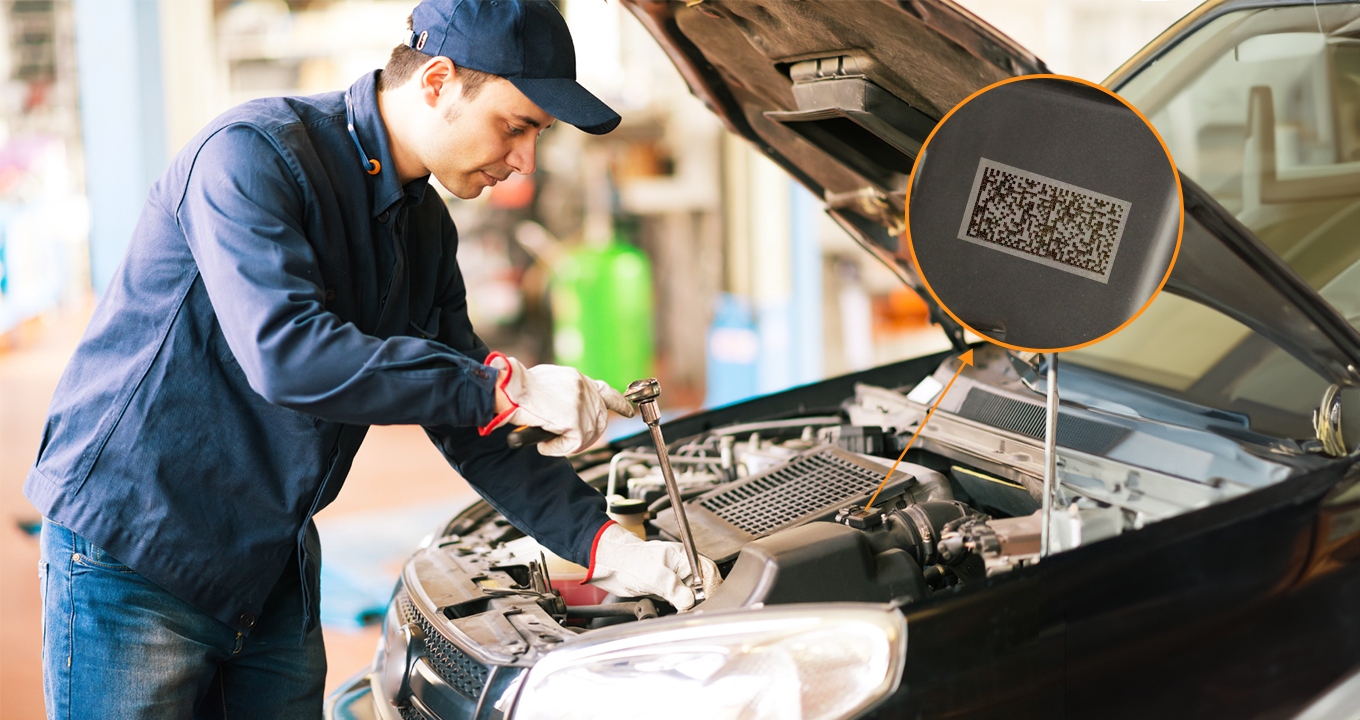

The automotive industry has fully adopted Direct Part Marking (DPM) codes, which facilitate the identification and monitoring of components during manufacturing. This blog examines the importance of DPM codes and investigates the difficulties encountered by conventional code scanning techniques within the automotive industry. Understanding DPM Codes in Automotive Manufacturing Different...
Read more › -
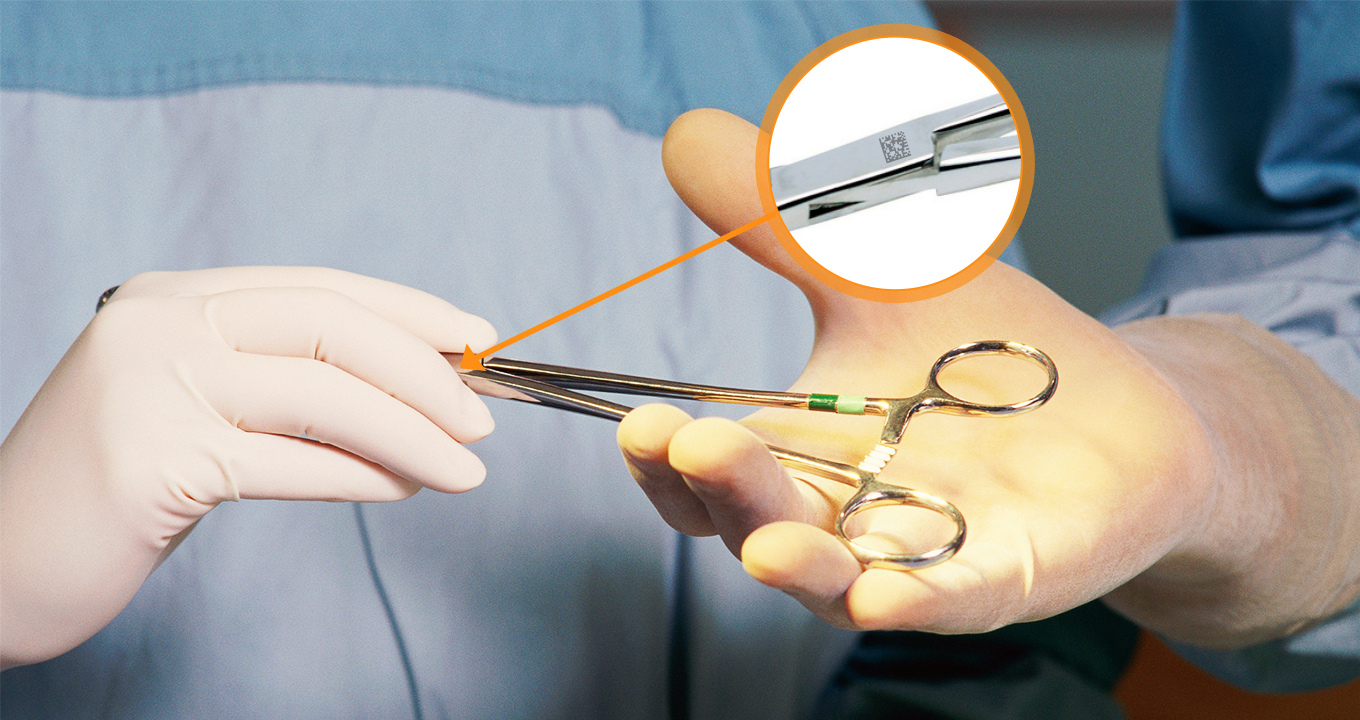
In today’s healthcare system, medical device traceability has become more critical than ever. To enhance traceability and safety in the modern healthcare landscape, UDI barcodes function as the standard for Unique Device Identification, providing a unique identifier for medical devices. DataMatrix codes are frequently used for UDI and store a...
Read more › -

Within the ever-evolving realm of consumer goods, particularly the beverage industry, organizations constantly seek creative ways to amplify customer engagement, strengthen brand loyalty, and negate counterfeit products. An emerging method garnering recognition is the implementation of DataMatrix barcode scanning on bottle caps and lids. This innovative methodology offers many benefits,...
Read more › -

With the rapid advancement of technology, it is evident that the proliferation of GS1-128 barcodes is revolutionizing the barcode utilization landscape. GS1-128 barcodes are progressively replacing conventional 1-dimensional barcodes because of their greater storage capacity, interoperability with modern identifying technologies, and global standardization. Overview of 1-Dimensional Barcodes: Limitations and Challenges...
Read more › -

Dynamsoft Barcode Scanner Demo es una aplicación gratuita de escaneo que transforma los dispositivos móviles en herramientas de reconocimiento de códigos de barras. Esta aplicación de lectura de códigos identifica códigos de barras lineales, códigos de barras de dos dimensiones y códigos QR de alta densidad en vídeos, imágenes y...
Read more ›


