Building an Auto-Scan Document Processing Solution: Automatic Image Cropping and Barcode Extraction
Modern enterprises process thousands of documents daily—from shipping labels and invoices to medical records and ID cards. Manual document processing is slow, error-prone, and doesn’t scale. This comprehensive guide demonstrates how to build a production-ready auto-scan document processing solution that automatically detects documents, crops them with perspective correction, and extracts barcode data—all in real-time.
Demo Video: Document Detection and Barcode Extraction
Online Demo
https://yushulx.me/javascript-barcode-qr-code-scanner/examples/document_barcode/
Business Case
The Problem
Manual document processing creates bottlenecks:
- Slow processing: Employees spend hours cropping, rotating, and extracting data
- Human error: Incorrect data entry, missed barcodes, poor image quality
- No scalability: Can’t handle volume spikes (50,000+ documents/month)
- High costs: Labor-intensive workflows require continuous staffing
The Solution
An auto-scan system that:
- Detects documents automatically using AI edge detection
- Crops & straightens documents with perspective correction
- Extracts barcode data from 1D/2D barcodes instantly
- Processes at scale - handle millions of documents/month
Technical Architecture
System Components
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Web Application Interface │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Camera Input │─────▶│ Document Detector │ │
│ │ (Live Stream) │ │ (DDN Module) │ │
│ └─────────────────┘ └──────┬─────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ Quad Detected │
│ │ │
│ ┌────────▼─────────────┐ │
│ │ Stability Tracker │ │
│ │ (Auto-Capture) │ │
│ └────────┬─────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ Stable Document │
│ │ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────▼──────────────┐ │
│ │ Document Normalizer (DDN) │ │
│ │ • Perspective correction │ │
│ │ • Image cropping │ │
│ │ • Quality enhancement │ │
│ └────────────────────────┬──────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ Cropped Image │
│ │ │
│ ┌────────────────────────▼──────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Barcode Reader (DBR) │ │
│ │ • 1D/2D barcode detection │ │
│ │ • Multi-format support │ │
│ │ • Data extraction │ │
│ └────────────────────────┬──────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ┌──────▼────────┐ │
│ │ Result Data │ │
│ │ • Image │ │
│ │ • Barcodes │ │
│ └───────────────┘ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Key Technologies
- Document Detection & Normalization (DDN): AI-powered edge detection and perspective correction
- Barcode Reader (DBR): Reads 40+ barcode formats (QR, Code 39, Code 128, PDF417, etc.)
- Camera Enhancer (DCE): Real-time video streaming with auto-focus optimization
- Capture Vision Router (CVR): Orchestrates multi-module workflows
Get Your Trial License
-
Register for a free trial license
-
Receive license key via email
-
Use in your web application:
// Initialize the SDK with your license key await Dynamsoft.License.LicenseManager.initLicense("YOUR-LICENSE-KEY", true);
Step-by-Step Implementation
Let’s build the auto-scan document processing system from scratch using JavaScript for a web-based solution that runs in any modern browser.
Step 1: Project Setup
Create your project structure:
auto-document-scanner/
├── index.html # Main HTML page
├── app.js # Application logic
├── styles.css # Styling
└── README.md # Documentation
index.html - Basic HTML structure:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Auto Document Scanner</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">
<!-- Load Dynamsoft Capture Vision Bundle -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/dynamsoft-capture-vision-bundle@3.2.5000/dist/dcv.bundle.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- License activation screen -->
<div id="license-screen" class="screen">
<h1>📱 Auto Document Scanner</h1>
<input type="text" id="license-input" placeholder="Enter license key">
<button id="activate-btn">Activate & Start</button>
</div>
<!-- Camera view (initially hidden) -->
<div id="camera-screen" class="screen hidden">
<div id="camera-view"></div>
<div id="status">Looking for document...</div>
<button id="capture-btn">Capture</button>
</div>
<!-- Results screen -->
<div id="result-screen" class="screen hidden">
<h2>Scan Result</h2>
<img id="cropped-image" alt="Cropped document">
<div id="barcode-results"></div>
<button id="scan-next-btn">Scan Next</button>
</div>
</div>
<script src="app.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Step 2: SDK Initialization & License Activation
app.js - Initialize the SDK:
let cvr = null;
let cameraEnhancer = null;
let cameraView = null;
let isSDKReady = false;
const licenseInput = document.getElementById('license-input');
const activateBtn = document.getElementById('activate-btn');
const cameraScreen = document.getElementById('camera-screen');
const resultScreen = document.getElementById('result-screen');
activateBtn.addEventListener('click', async () => {
const licenseKey = licenseInput.value.trim();
if (!licenseKey) {
alert('Please enter a license key');
return;
}
try {
console.log('Activating license...');
await Dynamsoft.License.LicenseManager.initLicense(licenseKey, true);
console.log('Loading modules...');
await Dynamsoft.Core.CoreModule.loadWasm(["DBR", "DDN"]);
console.log('Initializing camera...');
await initCamera();
console.log('Setting up scanner...');
cvr = await Dynamsoft.CVR.CaptureVisionRouter.createInstance();
cvr.addResultReceiver({
onCapturedResultReceived: handleCapturedResult
});
isSDKReady = true;
document.getElementById('license-screen').classList.add('hidden');
cameraScreen.classList.remove('hidden');
await startScanning();
} catch (error) {
console.error('Initialization failed:', error);
alert(`Error: ${error.message}`);
}
});
Step 3: Camera Setup
async function initCamera() {
cameraView = await Dynamsoft.DCE.CameraView.createInstance();
cameraEnhancer = await Dynamsoft.DCE.CameraEnhancer.createInstance(cameraView);
const container = document.getElementById('camera-view');
container.appendChild(cameraView.getUIElement());
const cameras = await cameraEnhancer.getAllCameras();
console.log('Available cameras:', cameras);
if (cameras.length > 0) {
await cameraEnhancer.selectCamera(cameras[0]);
cameraEnhancer.setPixelFormat(10);
await cameraEnhancer.open();
} else {
throw new Error('No cameras found');
}
}
Step 4: Document Detection with Auto-Capture
This is where the magic happens—automatic document detection with stability tracking:
async function startScanning() {
if (!isSDKReady) return;
try {
let settings = await cvr.getSimplifiedSettings("DetectDocumentBoundaries_Default");
await cvr.updateSettings("DetectDocumentBoundaries_Default", settings);
cvr.setInput(cameraEnhancer);
await cvr.startCapturing("DetectDocumentBoundaries_Default");
updateStatus('Looking for document...');
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to start scanning:', error);
}
}
let stabilityThreshold = 12;
let movementTolerance = 15;
let stabilityCounter = 0;
let lastQuadPoints = null;
let latestDetectedQuad = null;
let isCaptureInProgress = false;
async function handleCapturedResult(result) {
if (isCaptureInProgress) return;
const items = result.items;
if (!items || items.length === 0) {
resetStabilityTracking();
updateStatus('Looking for document...');
return;
}
for (const item of items) {
if (item.type === Dynamsoft.Core.EnumCapturedResultItemType.CRIT_DETECTED_QUAD) {
latestDetectedQuad = item;
checkStability(item.location.points);
}
}
if (stabilityCounter >= stabilityThreshold && !isCaptureInProgress) {
await performCapture();
}
}
function checkStability(currentPoints) {
if (!lastQuadPoints) {
lastQuadPoints = currentPoints;
stabilityCounter = 1;
updateStatus('Document detected, hold steady...');
return;
}
const isStable = isQuadStable(currentPoints, lastQuadPoints);
if (isStable) {
stabilityCounter++;
const progress = Math.min(stabilityCounter / stabilityThreshold * 100, 100);
if (stabilityCounter >= stabilityThreshold) {
updateStatus('Ready to capture!');
} else {
updateStatus(`Hold steady... ${Math.round(progress)}%`);
}
} else {
resetStabilityTracking();
stabilityCounter = 1;
updateStatus('Movement detected, hold steady...');
}
lastQuadPoints = currentPoints;
}
function isQuadStable(current, last) {
if (current.length !== 4 || last.length !== 4) return false;
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
const dx = Math.abs(current[i].x - last[i].x);
const dy = Math.abs(current[i].y - last[i].y);
if (dx > movementTolerance || dy > movementTolerance) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
function resetStabilityTracking() {
stabilityCounter = 0;
lastQuadPoints = null;
}
function updateStatus(message) {
document.getElementById('status').textContent = message;
}
Step 5: Document Cropping & Normalization
When the document is stable, capture and normalize it:
async function performCapture() {
isCaptureInProgress = true;
updateStatus('Capturing...');
try {
await cvr.stopCapturing();
let normalizeSettings = await cvr.getSimplifiedSettings("NormalizeDocument_Default");
normalizeSettings.roiMeasuredInPercentage = false;
normalizeSettings.roi = latestDetectedQuad.location;
await cvr.updateSettings("NormalizeDocument_Default", normalizeSettings);
const image = cameraEnhancer.fetchImage();
const normalizeResult = await cvr.capture(image, "NormalizeDocument_Default");
let normalizedImage = null;
for (const item of normalizeResult.items) {
if (item.type === Dynamsoft.Core.EnumCapturedResultItemType.CRIT_NORMALIZED_IMAGE) {
normalizedImage = item;
break;
}
}
if (!normalizedImage) {
throw new Error('Failed to normalize document');
}
await readBarcodesFromDocument(normalizedImage);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Capture failed:', error);
alert('Failed to capture document');
isCaptureInProgress = false;
resetStabilityTracking();
await startScanning();
}
}
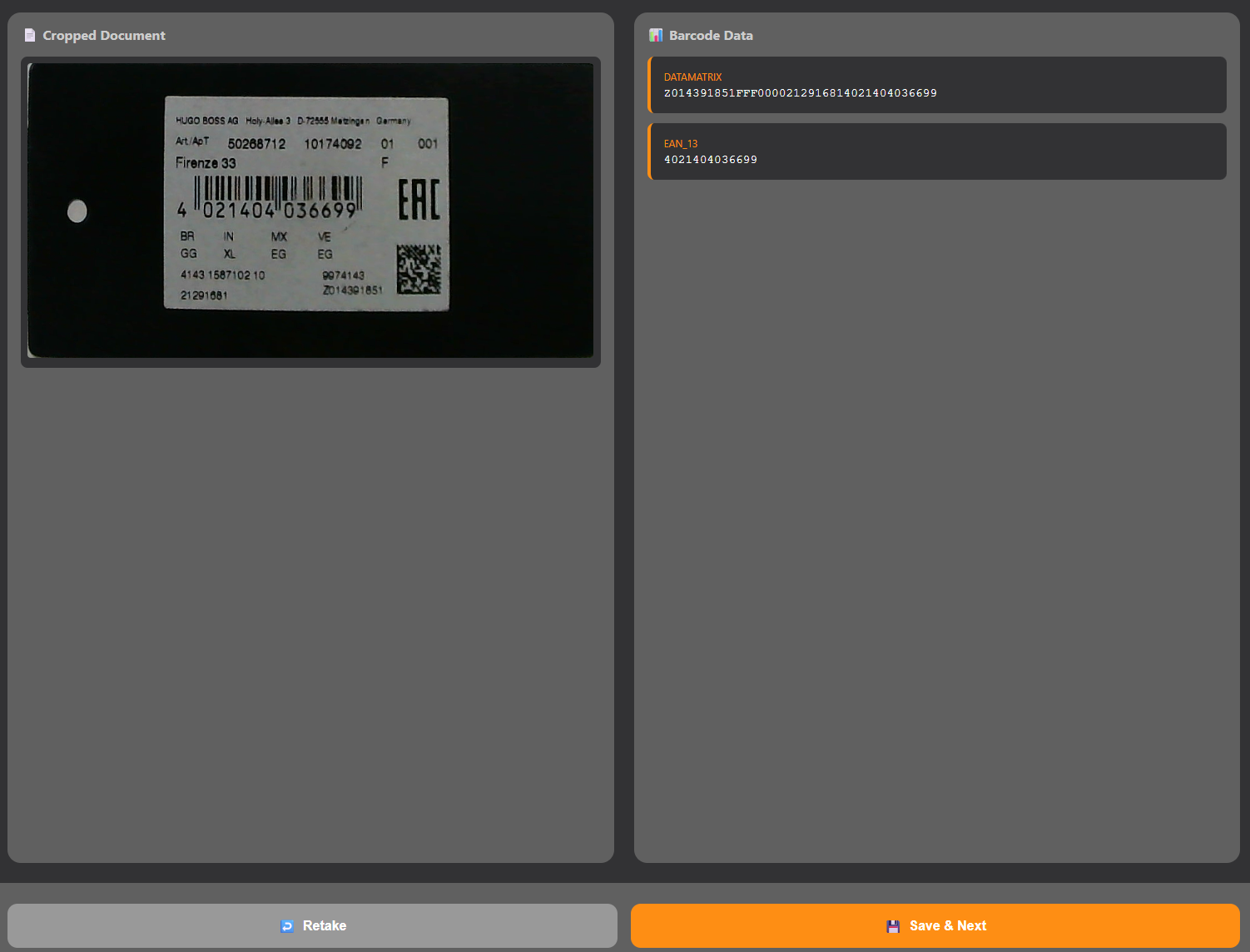
Step 6: Barcode Extraction
After cropping and normalizing the document, extract barcodes from it:
async function readBarcodesFromDocument(normalizedImageItem) {
try {
updateStatus('Reading barcodes...');
const imageData = normalizedImageItem.toCanvas().toDataURL();
let barcodeSettings = await cvr.getSimplifiedSettings("ReadBarcodes_Balance");
await cvr.updateSettings("ReadBarcodes_Balance", barcodeSettings);
const barcodeResult = await cvr.capture(normalizedImageItem.imageData, "ReadBarcodes_Balance");
const barcodes = [];
for (const item of barcodeResult.items) {
if (item.type === Dynamsoft.Core.EnumCapturedResultItemType.CRIT_BARCODE) {
barcodes.push({
text: item.text,
format: item.formatString,
type: item.formatString
});
}
}
displayResults(imageData, barcodes);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Barcode reading failed:', error);
displayResults(normalizedImageItem.toCanvas().toDataURL(), []);
}
}
function displayResults(croppedImageData, barcodes) {
cameraScreen.classList.add('hidden');
resultScreen.classList.remove('hidden');
const croppedImage = document.getElementById('cropped-image');
croppedImage.src = croppedImageData;
const barcodeResults = document.getElementById('barcode-results');
barcodeResults.innerHTML = '';
if (barcodes.length === 0) {
barcodeResults.innerHTML = '<p>No barcodes detected</p>';
} else {
barcodeResults.innerHTML = '<h3>Detected Barcodes:</h3>';
barcodes.forEach((barcode, index) => {
barcodeResults.innerHTML += `
<div class="barcode-item">
<strong>Barcode ${index + 1}:</strong> ${barcode.text}<br>
<em>Format:</em> ${barcode.format}
</div>
`;
});
}
currentScanResult = {
imageDataUrl: croppedImageData,
barcodes: barcodes,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString()
};
}
Step 7: IndexedDB History Storage
The captured documents and barcode results will be saved to a history using IndexedDB for later review.
const DB_NAME = 'DocumentScannerDB';
const DB_VERSION = 1;
const STORE_NAME = 'scanHistory';
function openDB() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const request = indexedDB.open(DB_NAME, DB_VERSION);
request.onerror = (event) => reject('Database error: ' + event.target.error);
request.onsuccess = (event) => resolve(event.target.result);
request.onupgradeneeded = (event) => {
const db = event.target.result;
if (!db.objectStoreNames.contains(STORE_NAME)) {
db.createObjectStore(STORE_NAME, { keyPath: 'timestamp' });
}
};
});
}
async function saveScanToDB(scanResult) {
const db = await openDB();
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const transaction = db.transaction([STORE_NAME], 'readwrite');
const store = transaction.objectStore(STORE_NAME);
const request = store.add(scanResult);
request.onsuccess = () => resolve();
request.onerror = (event) => reject('Save error: ' + event.target.error);
});
}
async function saveToHistory() {
if (!currentScanResult) return;
try {
await saveScanToDB(currentScanResult);
scanHistory.unshift(currentScanResult);
if (scanHistory.length > 50) {
scanHistory = scanHistory.slice(0, 50);
}
updateHistoryCount();
currentScanResult = null;
} catch (e) {
console.warn('Failed to save history to DB:', e);
showToast('Failed to save history');
}
}
Step 8: Adjustable Stability Settings
To give users control over the auto-capture sensitivity, add a settings UI that allows real-time adjustment of stability parameters:
HTML (Settings Modal):
<!-- Add to your index.html -->
<div id="settings-overlay" class="overlay hidden">
<div class="settings-modal">
<div class="settings-header">
<h2>Settings</h2>
<button id="close-settings-btn" class="close-btn">×</button>
</div>
<div class="settings-body">
<div class="setting-group">
<label for="stability-threshold">
Stability Threshold: <span id="stability-threshold-value">12</span>
<span class="tooltip">Number of stable frames required before capture</span>
</label>
<input type="range" id="stability-threshold"
min="5" max="30" value="12" step="1">
</div>
<div class="setting-group">
<label for="movement-tolerance">
Movement Tolerance: <span id="movement-tolerance-value">15</span>
<span class="tooltip">Allowed pixel movement to be considered stable</span>
</label>
<input type="range" id="movement-tolerance"
min="5" max="50" value="15" step="1">
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Add Settings button to your status bar -->
<button id="settings-btn" class="icon-button" title="Settings">⚙️</button>
JavaScript (Settings Logic):
// Settings UI Management
const settingsBtn = document.getElementById('settings-btn');
const settingsOverlay = document.getElementById('settings-overlay');
const closeSettingsBtn = document.getElementById('close-settings-btn');
const stabilityInput = document.getElementById('stability-threshold');
const stabilityValue = document.getElementById('stability-threshold-value');
const movementInput = document.getElementById('movement-tolerance');
const movementValue = document.getElementById('movement-tolerance-value');
function initSettings() {
// Open settings modal
settingsBtn.addEventListener('click', () => {
// Sync inputs with current values
stabilityInput.value = stabilityThreshold;
stabilityValue.textContent = stabilityThreshold;
movementInput.value = movementTolerance;
movementValue.textContent = movementTolerance;
settingsOverlay.classList.remove('hidden');
});
// Close settings
const closeSettings = () => {
settingsOverlay.classList.add('hidden');
};
closeSettingsBtn.addEventListener('click', closeSettings);
// Close on click outside modal
settingsOverlay.addEventListener('click', (e) => {
if (e.target === settingsOverlay) {
closeSettings();
}
});
// Real-time parameter updates
stabilityInput.addEventListener('input', (e) => {
stabilityThreshold = parseInt(e.target.value);
stabilityValue.textContent = stabilityThreshold;
});
movementInput.addEventListener('input', (e) => {
movementTolerance = parseInt(e.target.value);
movementValue.textContent = movementTolerance;
});
}
initSettings();
CSS (Settings Modal Styling):
.settings-modal {
position: fixed;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
background: white;
border-radius: 12px;
padding: 24px;
min-width: 400px;
max-width: 90%;
box-shadow: 0 8px 32px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
z-index: 10001;
}
.setting-group {
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.setting-group label {
display: block;
margin-bottom: 8px;
font-weight: 600;
}
.setting-group input[type="range"] {
width: 100%;
height: 6px;
border-radius: 3px;
background: #e0e0e0;
outline: none;
}
.tooltip {
display: block;
font-size: 12px;
color: #666;
font-weight: normal;
margin-top: 4px;
}
This feature is particularly valuable for:
- Production environments - optimize for speed vs. quality
- Different document types - small cards vs. large posters
- Various lighting conditions - adjust sensitivity for low-light scenarios
- User preferences - let end-users customize their experience
Testing Your Implementation
# Option 1: Using Python
python -m http.server 8000 --bind localhost
# Option 2: Using Node.js (http-server)
npx http-server -p 8000
Source Code
https://github.com/yushulx/javascript-barcode-qr-code-scanner/tree/main/examples/document_barcode


