Building an MCP Server for Dynamsoft SDKs: Enabling AI-Assisted Barcode and Document Scanning Development
Large Language Models (LLMs) like Claude and GitHub Copilot are revolutionizing how developers write code. However, they face a critical limitation: they’re trained on data with knowledge cutoffs, meaning they lack information about:
- Latest SDK versions and their breaking changes
- Actual working code examples from official repositories
- Platform-specific implementations (Android vs iOS, high-level vs low-level APIs)
- Real license keys and configuration needed for testing
When developers ask AI assistants to generate code for specialized SDKs like barcode scanners or document imaging libraries, the results are often:
- Outdated or using deprecated APIs
- Syntactically correct but functionally broken
- Missing critical configuration steps
- Unable to run without extensive modifications
Demo Video: Vibe Coding with Dynamsoft MCP Server
The Solution: Model Context Protocol (MCP)
The Model Context Protocol bridges this gap. MCP is an open standard that allows AI assistants to access external data sources and tools in real-time. Think of it as an API that lets AI models fetch up-to-date information during conversations.
Why Build an MCP Server for Dynamsoft SDKs?
Dynamsoft provides enterprise-grade SDKs for:
- Barcode Reading (mobile, web, desktop, server)
- Document Scanning (TWAIN/WIA/ICA/SANE scanners)
- Document Processing (PDF conversion, OCR, image enhancement)
These SDKs span multiple platforms (Android/iOS/Web/Python), API levels (high-level/low-level), and programming languages (Java/Kotlin/Swift/JavaScript/Python). An MCP server can provide:
- Real, working code snippets from official sample repositories
- Latest SDK versions and documentation links
- Trial license keys for immediate testing
- Platform-specific configuration (Gradle, Podfile, npm)
- API usage patterns for complex scenarios
Architecture Overview
MCP Server Components
Our MCP server consists of four key layers:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ AI Clients (Claude, Copilot) │
└─────────────────┬───────────────────────────────┘
│ JSON-RPC over stdio
┌─────────────────▼───────────────────────────────┐
│ MCP Server (Node.js) │
│ ┌───────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Tools (14 endpoints) │ │
│ │ - list_sdks, get_code_snippet, etc. │ │
│ └───────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ┌───────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Resources (Dynamic registration) │ │
│ │ - SDK info, code samples by platform │ │
│ └───────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ┌───────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Registry (dynamsoft_sdks.json) │ │
│ │ - Version info, docs, platforms │ │
│ └───────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
└─────────────────┬───────────────────────────────┘
│ File System Access
┌─────────────────▼───────────────────────────────┐
│ Code Snippets Directory │
│ - Android/iOS samples (Java/Kotlin/Swift) │
│ - Python samples │
│ - Web samples (JavaScript/TypeScript) │
│ - Dynamic Web TWAIN samples (HTML/JS) │
└──────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Technology Stack
- Runtime: Node.js 18+ (ES Modules)
- MCP SDK:
@modelcontextprotocol/sdk(official TypeScript SDK) - Schema Validation: Zod (for input validation)
- Transport: stdio (standard input/output for JSON-RPC)
- Data Format: JSON for registry, source code files for samples
Implementation Guide
1. Project Setup and Dependencies
First, initialize the project with proper Node.js configuration:
package.json
{
"name": "simple-dynamsoft-mcp",
"version": "2.0.2",
"type": "module",
"engines": {
"node": ">=18"
},
"bin": {
"simple-dynamsoft-mcp": "./src/index.js"
},
"dependencies": {
"@modelcontextprotocol/sdk": "^1.25.2",
"zod": "~3.24.0"
}
}
Key decisions:
"type": "module"enables ES modules (required by MCP SDK)"engines": {"node": ">=18"}enforces minimum Node.js version"bin"entry allowsnpxexecution- Zod pinned to
~3.24.0to avoid breaking changes in v4
2. SDK Registry Design
The registry (data/dynamsoft_sdks.json) is the single source of truth:
{
"trial_license": "DLS2eyJoYW5kc2hha2VDb2RlIjoiMjAwMDAxLTE2NDk4Mjk3OTI2MzUi...",
"license_request_url": "https://www.dynamsoft.com/customer/license/trialLicense/?product=dcv&package=cross-platform",
"maven_url": "https://download2.dynamsoft.com/maven/aar",
"sdks": {
"dbr-mobile": {
"name": "Dynamsoft Barcode Reader Mobile SDK",
"version": "11.2.5000",
"platforms": {
"android": {
"languages": ["Kotlin", "Java"],
"docs": {
"high-level": {
"user-guide": "https://...",
"api-reference": "https://..."
},
"low-level": { /* ... */ }
},
"samples": {
"high-level": "https://github.com/...",
"low-level": "https://github.com/..."
}
},
"ios": { /* ... */ }
}
},
"dbr-python": { /* Python SDK config */ },
"dbr-web": { /* Web SDK config */ },
"dwt": { /* Dynamic Web TWAIN config */ }
}
}
Design principles:
- Hierarchical structure: SDK → Platform → API Level → Docs/Samples
- Separation of concerns: global settings vs SDK-specific settings
- Extensibility: easy to add new SDKs or platforms
- Documentation-first: every platform includes links to official docs
3. MCP Server Initialization
The entry point (src/index.js) sets up the server with stdio transport:
#!/usr/bin/env node
import { Server } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/index.js";
import { StdioServerTransport } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/stdio.js";
import { z } from "zod";
import { readFileSync, existsSync, readdirSync, statSync } from "fs";
import { join, dirname } from "path";
import { fileURLToPath } from "url";
// ES module path resolution
const __filename = fileURLToPath(import.meta.url);
const __dirname = dirname(__filename);
const projectRoot = join(__dirname, "..");
// Load SDK registry
const registryPath = join(projectRoot, "data", "dynamsoft_sdks.json");
const registry = JSON.parse(readFileSync(registryPath, "utf-8"));
// Initialize MCP server
const server = new Server(
{
name: "simple-dynamsoft-mcp",
version: "2.0.2"
},
{
capabilities: {
tools: {},
resources: {}
}
}
);
// Tool and resource registration will follow...
// Start server with stdio transport
const transport = new StdioServerTransport();
await server.connect(transport);
Critical details:
- Shebang
#!/usr/bin/env nodeenablesnpxexecution - ES module
__dirnameemulation usingfileURLToPath - Server declares capabilities for both tools and resources
- Stdio transport for JSON-RPC communication
4. Implementing Tools
Tools are the primary interface for AI assistants. The new registerTool() API requires:
- Name: unique identifier
- Options:
{ title, description, inputSchema } - Handler: async function returning result
Example: list_sdks Tool
server.registerTool(
"list_sdks",
{
title: "List SDKs",
description: "List all available Dynamsoft SDKs with versions and platforms",
inputSchema: {}
},
async () => {
const lines = ["# Available Dynamsoft SDKs\n"];
for (const [id, sdk] of Object.entries(registry.sdks)) {
lines.push(`## ${sdk.name} (v${sdk.version})`);
lines.push(`**SDK ID:** \`${id}\``);
lines.push(`**Platforms:** ${Object.keys(sdk.platforms).join(", ")}`);
// Add documentation links
const firstPlatform = Object.values(sdk.platforms)[0];
if (firstPlatform.docs) {
lines.push(`**Docs:** ${firstPlatform.docs["user-guide"] || firstPlatform.docs["high-level"]?.["user-guide"]}`);
}
lines.push("");
}
return {
content: [{
type: "text",
text: lines.join("\n")
}]
};
}
);
Example: get_code_snippet Tool (Complex Logic)
This tool demonstrates file system interaction and fallback logic:
server.registerTool(
"get_code_snippet",
{
title: "Get Code Snippet",
description: "Get actual source code from mobile sample projects",
inputSchema: {
platform: z.enum(["android", "ios"]).describe("Platform: android or ios"),
sample_name: z.string().describe("Sample name, e.g. ScanSingleBarcode"),
api_level: z.string().optional().describe("API level: high-level or low-level"),
language: z.string().optional().describe("Language: java, kotlin, swift"),
file_name: z.string().optional().describe("Specific file to retrieve")
}
},
async ({ platform, sample_name, api_level, language, file_name }) => {
// Normalize and locate sample
const level = normalizeApiLevel(api_level);
let samplePath = getMobileSamplePath(platform, level, sample_name);
// Auto-fallback: try opposite API level if not found
if (!existsSync(samplePath)) {
const otherLevel = level === "high-level" ? "low-level" : "high-level";
samplePath = getMobileSamplePath(platform, otherLevel, sample_name);
if (!existsSync(samplePath)) {
return {
content: [{
type: "text",
text: `Sample "${sample_name}" not found. Use list_samples to see available.`
}]
};
}
}
// Find code files
const codeFiles = findCodeFilesInSample(samplePath);
// Filter by language if specified
if (language) {
const langExts = {
java: [".java"],
kotlin: [".kt"],
swift: [".swift"]
};
codeFiles = codeFiles.filter(f =>
langExts[language]?.some(ext => f.filename.endsWith(ext))
);
}
// Return main file or all files
const mainFile = getMainCodeFile(platform, samplePath);
const filesToReturn = mainFile ? [mainFile] : codeFiles.slice(0, 3);
// Format response with metadata
const output = [
`# ${sample_name} - ${platform} (${level})`,
`**SDK Version:** ${registry.sdks["dbr-mobile"].version}`,
`**Trial License:** \`${registry.trial_license}\``,
""
];
for (const file of filesToReturn) {
const content = readFileSync(file.path, "utf-8");
output.push(`## ${file.relativePath}`);
output.push("```" + getFileExtension(file.filename));
output.push(content);
output.push("```");
output.push("");
}
return {
content: [{ type: "text", text: output.join("\n") }]
};
}
);
Key patterns demonstrated:
- Zod schema validation for inputs
- Intelligent fallback logic (try alternate API levels)
- Language filtering
- Automatic main file detection
- Markdown-formatted output with code blocks
- Inclusion of SDK version and license in response
5. Dynamic Resource Registration
Resources provide structured access to data. We dynamically register resources based on discovered samples:
// Discover samples from file system
function discoverMobileSamples(platform) {
const samples = { "high-level": [], "low-level": [] };
const basePath = join(projectRoot, "code-snippet", "dynamsoft-barcode-reader", platform);
const highLevelPath = join(basePath, "BarcodeScannerAPISamples");
const lowLevelPath = join(basePath, "FoundationalAPISamples");
if (existsSync(highLevelPath)) {
samples["high-level"] = readdirSync(highLevelPath)
.filter(name => statSync(join(highLevelPath, name)).isDirectory());
}
if (existsSync(lowLevelPath)) {
samples["low-level"] = readdirSync(lowLevelPath)
.filter(name => statSync(join(lowLevelPath, name)).isDirectory());
}
return samples;
}
// Register resources dynamically
for (const platform of ["android", "ios"]) {
const samples = discoverMobileSamples(platform);
for (const level of ["high-level", "low-level"]) {
for (const sampleName of samples[level]) {
const resourceUri = `dynamsoft://samples/mobile/${platform}/${level}/${sampleName}`;
const resourceName = `mobile-${platform}-${level}-${sampleName}`
.toLowerCase()
.replace(/[^a-z0-9-]/g, "-");
server.registerResource(
resourceName,
resourceUri,
{
title: `${sampleName} (${platform})`,
description: `${sampleName} for ${platform} (${level})`,
mimeType: "text/plain"
},
async (uri) => {
const samplePath = getMobileSamplePath(platform, level, sampleName);
const mainFile = getMainCodeFile(platform, samplePath);
if (!mainFile) {
return {
contents: [{
uri: uri.href,
text: "Sample not found",
mimeType: "text/plain"
}]
};
}
const content = readFileSync(mainFile.path, "utf-8");
const mimeType = getMimeType(mainFile.filename);
return {
contents: [{
uri: uri.href,
text: content,
mimeType
}]
};
}
);
}
}
}
Design highlights:
- Discovery-driven: resources are created based on actual file system contents
- URI scheme:
dynamsoft://samples/{sdk}/{platform}/{level}/{sample} - Sanitized names: convert to lowercase kebab-case for consistency
- Lazy loading: content read only when requested
- MIME type detection: appropriate content-type for different languages
6. Helper Functions and Utilities
The server includes several utility functions that follow consistent patterns:
// Normalize user input
function normalizeApiLevel(level) {
if (!level) return "high-level";
const l = level.toLowerCase();
if (l.includes("high") || l.includes("scanner")) return "high-level";
if (l.includes("low") || l.includes("foundation") || l.includes("router")) return "low-level";
return "high-level";
}
function normalizeLanguage(lang) {
if (!lang) return null;
const l = lang.toLowerCase();
if (l.includes("java") && !l.includes("script")) return "java";
if (l.includes("kotlin") || l === "kt") return "kotlin";
if (l.includes("swift")) return "swift";
return null;
}
// Path construction
function getMobileSamplePath(platform, level, sampleName) {
const apiFolder = level === "high-level"
? "BarcodeScannerAPISamples"
: "FoundationalAPISamples";
return join(
projectRoot,
"code-snippet",
"dynamsoft-barcode-reader",
platform,
apiFolder,
sampleName
);
}
// File discovery
function findCodeFilesInSample(samplePath) {
const codeFiles = [];
const extensions = [".java", ".kt", ".swift", ".m", ".h"];
function traverse(dir) {
const entries = readdirSync(dir);
for (const entry of entries) {
const fullPath = join(dir, entry);
const stat = statSync(fullPath);
if (stat.isDirectory() && !entry.startsWith(".")) {
traverse(fullPath);
} else if (stat.isFile() && extensions.some(ext => entry.endsWith(ext))) {
codeFiles.push({
path: fullPath,
filename: entry,
relativePath: fullPath.replace(samplePath + "/", "")
});
}
}
}
traverse(samplePath);
return codeFiles;
}
// Smart main file detection
function getMainCodeFile(platform, samplePath) {
const files = findCodeFilesInSample(samplePath);
// Platform-specific patterns
const mainPatterns = platform === "android"
? ["MainActivity", "ScanActivity", "Application"]
: ["ViewController", "AppDelegate"];
// Priority 1: Match pattern
for (const pattern of mainPatterns) {
const match = files.find(f => f.filename.includes(pattern));
if (match) return match;
}
// Priority 2: Shortest path (likely in main source dir)
files.sort((a, b) => a.relativePath.length - b.relativePath.length);
return files[0];
}
Pattern observations:
- Defensive programming: always provide defaults
- Fuzzy matching: accept various input formats
- Platform-aware logic: different conventions for Android vs iOS
- Prioritized search: use heuristics to find the most relevant file
Configuration and Usage
Setting Up MCP Clients
The server can be used with any MCP-compatible client. Here are the most common configurations:
OpenCode
Location:
- macOS:
~/.config/opencode/opencode.json - Windows:
%USERPROFILE%\.config\opencode\opencode.json
Configuration:
{
"$schema": "https://opencode.ai/config.json",
"mcp": {
"dynamsoft": {
"type": "local",
"command": [
"npx",
"simple-dynamsoft-mcp"
]
}
}
}
Claude Desktop
Location:
- macOS:
~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json - Windows:
%APPDATA%\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json
Configuration:
{
"mcpServers": {
"dynamsoft": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "simple-dynamsoft-mcp"]
}
}
}
VS Code with GitHub Copilot
Global Location:
- macOS:
~/Library/Application Support/Code/User/mcp.json - Windows:
%APPDATA%\Code\User\mcp.json
{
"servers": {
"dynamsoft": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "simple-dynamsoft-mcp"]
}
}
}
Or create workspace-specific .vscode/mcp.json:
{
"servers": {
"dynamsoft": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "simple-dynamsoft-mcp"]
}
}
}
Cursor
Location:
- macOS:
~/.cursor/mcp.json - Windows:
%USERPROFILE%\.cursor\mcp.json
Configuration:
{
"mcpServers": {
"dynamsoft": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "simple-dynamsoft-mcp"]
}
}
}
Windsurf
Location:
- macOS:
~/.codeium/windsurf/mcp_config.json - Windows:
%USERPROFILE%\.codeium\windsurf\mcp_config.json
{
"mcpServers": {
"dynamsoft": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "simple-dynamsoft-mcp"]
}
}
}
Real-World Usage Examples
Example 1: Android Barcode Scanner (High-Level API)
User prompt:
"Create an Android barcode scanner app using Dynamsoft's high-level API"
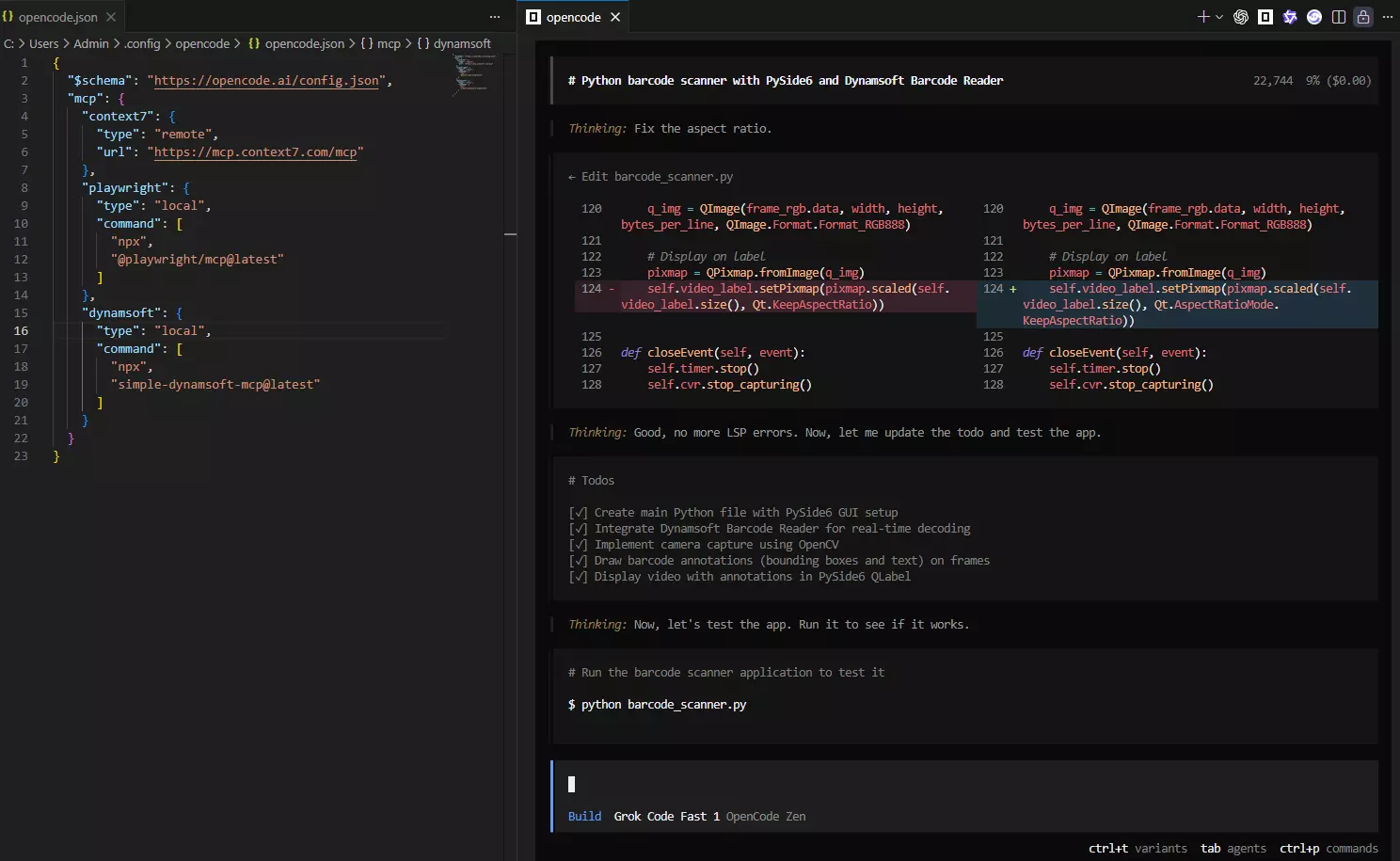
Example 2: Python Video Decoding
User prompt:
"Create a Python barcode scanner with PySide6 and Dynamsoft Barcode Reader. Display barcode annotations on video frames."
Example 3: Web Document Scanner
User prompt:
"Create a web page that scans documents from a TWAIN scanner using Dynamic Web TWAIN"
Testing the Server
Manual Testing via stdio
Test the server without an MCP client. Note that tools/call requires an arguments field:
-
List all tools:
echo '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"tools/list"}' | node src/index.js -
Call a specific tool (list_sdks):
echo '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"tools/call","params":{"name":"list_sdks","arguments":{}}}' | node src/index.js -
Call tool with arguments (get_code_snippet):
echo '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"tools/call","params":{"name":"get_code_snippet","arguments":{"platform":"android","sample_name":"ScanSingleBarcode"}}}' | node src/index.js -
List resources:
echo '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"resources/list"}' | node src/index.js -
Read a specific resource:
echo '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"resources/read","params":{"uri":"dynamsoft://sdk-info"}}' | node src/index.js
Automated Testing
Create test scripts:
import { spawn } from "child_process";
async function testMCPServer() {
const server = spawn("node", ["src/index.js"]);
const tests = [
{ method: "tools/list" },
{ method: "tools/call", params: { name: "list_sdks" } },
{ method: "resources/list" }
];
for (const test of tests) {
const request = JSON.stringify({
jsonrpc: "2.0",
id: Date.now(),
...test
});
server.stdin.write(request + "\n");
// Wait for response
await new Promise((resolve) => {
server.stdout.once("data", (data) => {
const response = JSON.parse(data.toString());
console.log(`✓ ${test.method}:`, response.result ? "OK" : "FAIL");
resolve();
});
});
}
server.kill();
}
testMCPServer();
Publishing and Distribution
# Test package contents
npm pack --dry-run
# Publish to npm
npm publish
# Verify installation
npx -y simple-dynamsoft-mcp@latest


