Retail stores are extremely demanding environments. Barcodes need to be read instantly and accurately, every time, regardless of the glare of in-store lighting or awkward packaging. Customers want fast self-serve options on their smartphones to make informed in-store purchases. Store reps need to be savvy sales associates ready to help and advise customers with rapid access to product information, inventory and promotions.
Enable Fast In-Store Self-Service
Enable shoppers to self-scan products to check pricing, find details and purchase - all without waiting in line.
Equip Store Associates to Sell
Give store reps the knowledge to advise customers with product and promo lookups from a smartphone or tablet.
Check Inventory on the Spot
Enable real-time inventory checks to help shoppers find the product they need and ways to buy it - without leaving the shop floor.
Dynamsoft Barcode Reader is a software development kit that enables developers to efficiently embed 1D and 2D barcode reading into web, desktop, or mobile applications. It takes just a few lines of code and has a vast range of customization options to fit your retail environment.
Download 30-Day Free Trial
Resist Wrinkles and Deformation on Packagings
Read product barcode on soft packagings and deformed round bottles accurately and quickly for accurate information lookup and faster self-checkout.
Deformation Resistance >
Remove Glares on Reflective Cans
Grocery stores have a wide variety of products and often face issues like light glare from reflective surfaces such as from soda pop cans, condensation build up from frozen foods, and curved barcodes on canned goods.

Verify via Accompanying Text
To ensure 100% accuracy, and eliminate manual verification, automatically verify barcode result with the accompanying text that usually appears below the product barcode.
Get the Accompanying Text Bytes >
Any Phone or Browser
A consumer could use any brand or any mobile phone model. Dynamsoft Barcode Reader SDK supports all mainstream iOS and Android devices and modern browsers.

Any Built-in Camera
Mobile phones are equipped with different cameras from low-end to high-end. Dynamsoft barcode reader SDK auto-selects the most appropriate camera resolution and it's optimized for low-resolution cameras.

Scan Barcodes in Any Size or Angle
Barcodes can be rotated or have a perspective angle depending on how it's held in hand and some barcodes are tiny. With Dynamsoft Barcode Reader, you can grab and scan a barcode without having to rotate it upright or move it closer.
JavaScript
Android, iOS, React Native, Flutter, Xamarin, Cordova
C,C++,.NET, Python, Java
- just a few lines of code to implement
- to fit all retail business scenarios
- Sales Support to discuss your POC
in computer vision
- ISO27001 certified to keep your data secure
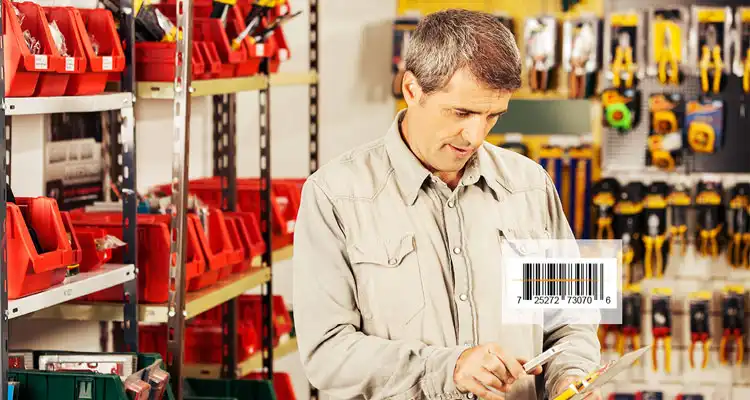

Multi-Billion Dollar Retailer Switched to Dynamsoft Barcode Reader SDK to Realize Consumer-Grade Barcode App Performance
Read More >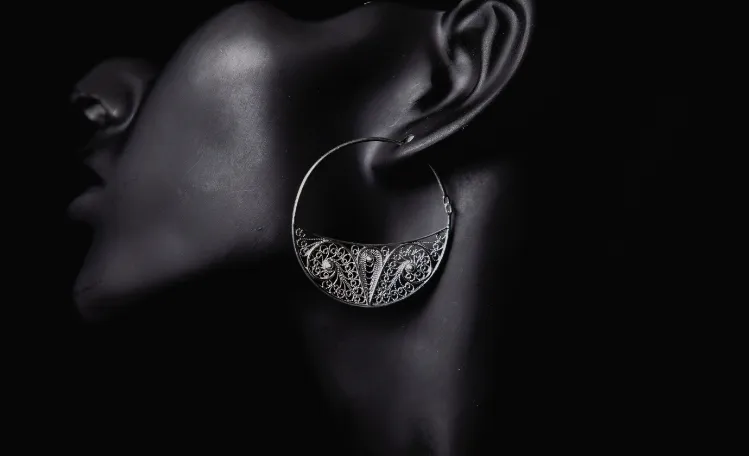
World Renowned Luxury Fashion Brand Lands on Dynamsoft Barcode Reader to Upgrade its Boutique Inventory Management
Read the Case Study >
Ralph Lauren Japan hires Virtualshop.me to build a stock management app with accurate and fast barcode scanning with Dynamsoft Barcode Reader SDK
Read More >
UPC-A
1D Barcode
UPC-E
1D Barcode
EAN-8
1D Barcode
EAN-13
1D Barcode
Industrial 2 of 5
1D Barcode
Code 93
1D Barcode
QR Codes
2D Barcodes
DataMatrix
2D Barcodes
GS1 Composite Code
Composite Code