Scanning DPM Codes on Plastics
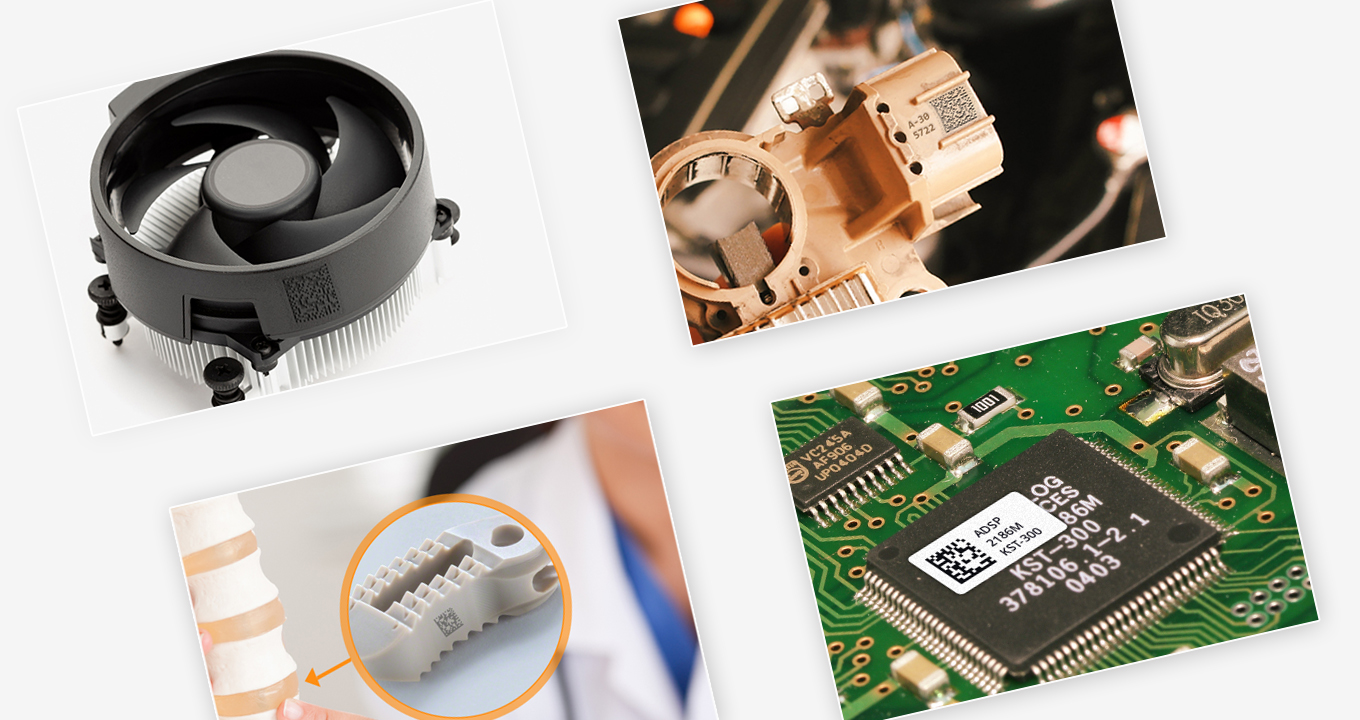
DPM codes (Direct Part Marking), are used to mark or engrave a barcode directly onto a product or part. This allows for easy identification, tracking, and traceability of the product throughout its lifecycle. In this blog, we explore the leading uses of DPM codes on plastics, difficulties encountered during the scanning process, and state-of-the-art technologies that help streamline multiple processes.
Different Types of Laser Marking Techniques for DPM Codes on Plastics
Laser marking has gained widespread usage in the plastics industry as a persistent code and marking method, providing exceptional accuracy, adaptability, and durability.

The table below compares different laser marking techniques used for marking DPM codes on plastics, and their uses.
| Laser Marking Technique | Description | Durability | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Ablation for High-Contrast DPM Codes | Laser ablation removes material layers to produce high-contrast DPM codes to provide durability in challenging environments | Very high - material removal creates lasting marks | Automotive Parts, Aerospace Components |
| Engraving for Permanent Barcodes | This method carves out materials to form long-lasting barcodes, which are commonly utilized in industrial settings due to their durability | Very high - physically alters material | Heavy Machinery, Industrial Tools |
| UV Laser Marking for Fine Detail Barcodes | UV laser marking is mainly used for small items and fragile materials to create fine-detail, precise barcodes using ultraviolet light | Moderate – Depends on material and exposure | Electronic Components, Medical Devices |
| Dynamic Laser Marking for Continuous Production Lines | Dynamic laser marking is a rapid and seamless process employed in continuous production settings, facilitating instantaneous marking integration into high-speed production lines | High - adaptable to various materials in industrial settings | Packaging, Automotive, Pharmaceuticals |
| Color Change for Visual Distinction | This technique modifies material color using chemical or physical methods, improving barcode visibility and aesthetic appeal | Variable - Depends on material and method of color change | Branding, Consumer Goods, Security |
Challenges in Scanning DPM Codes on Plastics
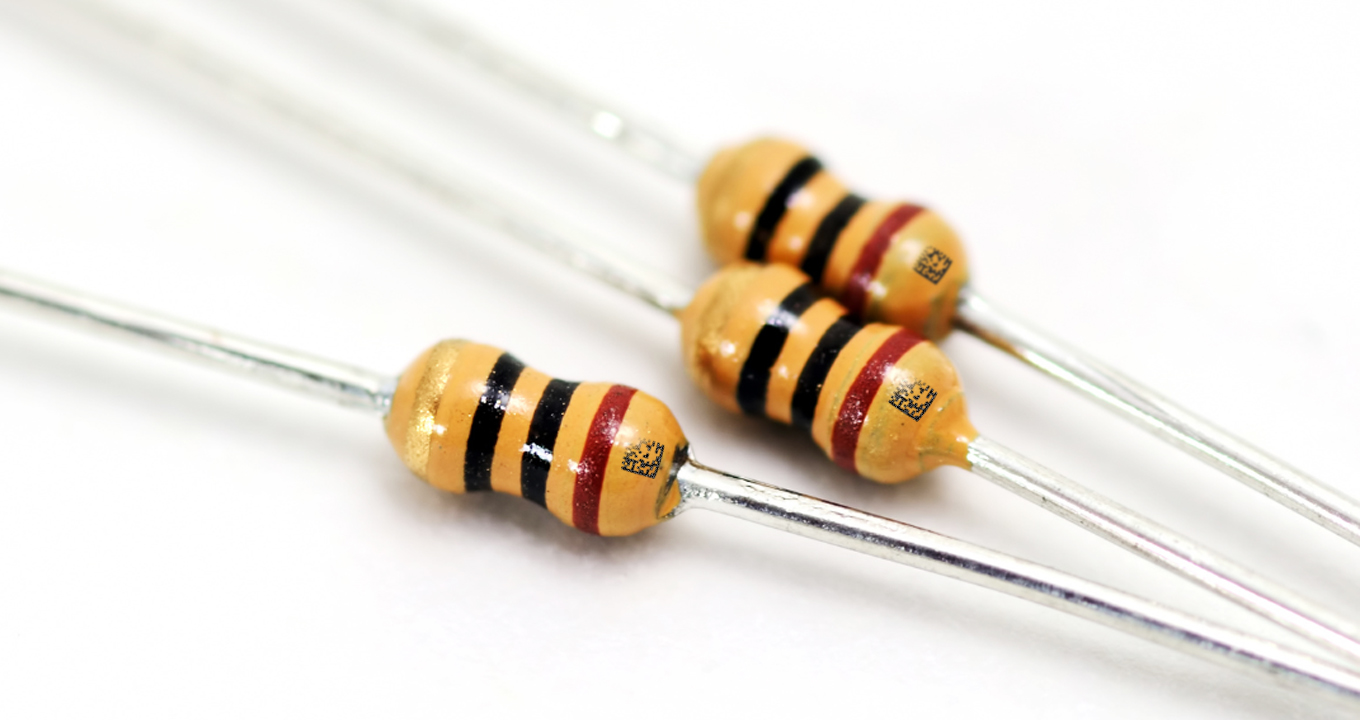

Common challenges encountered with DPM marking on plastics include reflective surfaces, barcodes with low contrast, environmental variables that influence accuracy, and surface irregularities.
- Reflective Surfaces and Low-Contrast Issues: Barcode scanners may encounter difficulties when dealing with reflective surfaces, which can cause reflections and impede accuracy. Code misinterpretation caused by glare can result in misidentification and monitoring errors. Also, low-contrast barcodes can negatively impact traceability and quality control procedures, compromising accuracy.
- Environmental Factors: Severe environmental conditions, including high humidity or extreme temperature, may adversely affect barcode scanning. The decreased precision and reliability of barcode scanning may result in data acquisition and processing errors.
- Surface Irregularities: The readability and visibility of DPM codes can be compromised by surface irregularities, such as varying textures or defects, on plastics. Reduced code readability impacts the efficiency of tracking systems and overall operations.
Technologies for Scanning DPM Codes on Plastics
In this section, we explore the wide range of scanning technologies designed for scanning DPM codes on plastic, including laser technology, 2D imagers, and other innovative techniques.
Overview of Different Scanning Technologies
Laser Technology: Laser-based scanners leverage laser beams to read and interpret the DPM codes on plastic surfaces. Laser technology is widely used in industrial environments and is renowned for its accuracy and dependability in barcode reading. However, laser scanners might encounter difficulties with reflective surfaces and low-contrast codes.
2D Imagers: By employing sophisticated imaging technology, 2D imagers are capable of reading both 1D and 2D codes, thereby providing a more adaptable scanning method. 2D image scanners are smart devices used in numerous sectors requiring adaptability in code comprehension, including the automotive, healthcare, and electronics industries.
As smart devices such as mobile phones and tablets are used as 2D imagers, they can be adjusted to different orientations to read codes on complex surfaces.
Benefits of using 2D Imagers over Laser Scanners
2D Imagers offer multiple benefits over traditional laser scanners.

-
High-Resolution Scanning: By capturing detailed images, 2D imagers improve the readability of barcodes on plastics, even with surface irregularities.
-
Good Performance in Challenging Conditions: 2D Imagers work well in challenging conditions, such as reflective surfaces or low-contrast codes. They can easily read tough barcodes- tiny, damaged, or poorly printed.
-
Improved Traceability: 2D imagers improve traceability by collecting detailed images of DPM) codes, allowing for accurate data extraction. Their ability to read both 1D and 2D codes enables enhanced traceability across a wide range of industries.
-
Cost-Effectiveness and ROI: Smartphones or tablets with a good camera can be used as effective 2D imagers, dramatically reducing hardware costs. Increased traceability, decreased downtime, and improved quality control all contribute to the economic viability of 2D imagers.
Industry Applications of DPM Codes on Plastics
DPM codes on plastics can be used in a variety of ways such as:
Automotive Industry: DPM codes can be used on plastic components in cars, such as airbag covers, to ensure traceability and quality control.
Medical Devices: DPM codes can be used on plastic medical devices to ensure their authenticity, track their usage, and monitor their performance.
Consumer Electronics: DPM codes can be used on plastic components in electronic devices to ensure traceability and quality control.
Aerospace industry: DPM codes can be used on plastic components in airplanes to ensure traceability and quality control.
Packaging industry: DPM codes can be used on plastic packaging to ensure traceability, prevent counterfeiting, and improve inventory management.
Best Practices for Scanning DPM Codes on Plastics
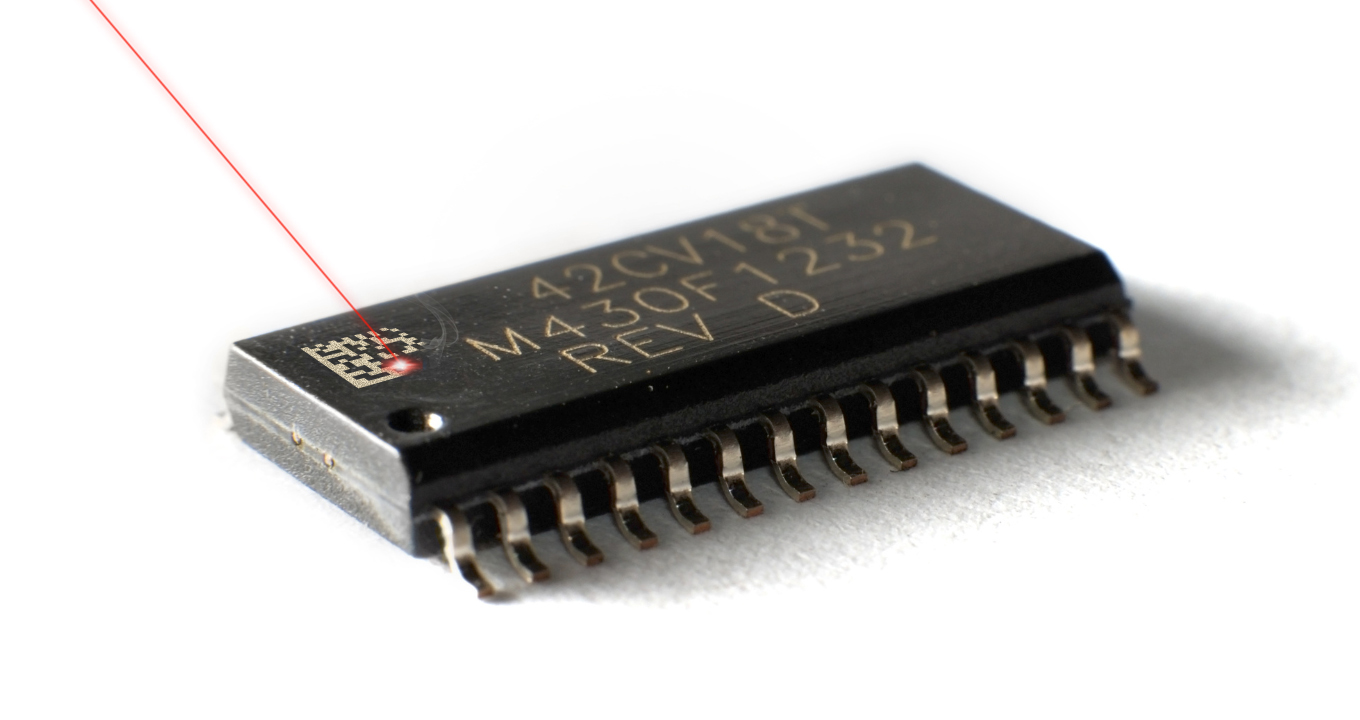
This section explores crucial techniques for achieving optimal scanning of DPM codes on plastic materials to improve the efficiency for seamless operations.

-
Proper Lighting and Positioning for Optimal Scanning: Optimal results on plastic surfaces require proper lighting and accurate positioning of the barcode scanning equipment. Optimal lighting reduces glare, enhancing barcode readability, while strategic placement guarantees precise barcode scanning, hence decreasing errors.
-
Regular Maintenance and Calibration of Scanning Equipment: Consistent maintenance and scanning equipment calibration are crucial for optimal performance and precision. Regular inspections and fine-tuning prevent equipment deterioration, guaranteeing that scanners function effectively. Calibration ensures the accuracy needed for precise barcode reading on plastics, which leads to consistent and uninterrupted scanning operations over an extended period.
-
Training for Operators to Improve Scanning Efficiency: Improving scanning efficiency relies heavily on operator proficiency. Operators are prepared to operate scanning equipment, diagnose problems, and read DPM codes on plastics with the highest degree of precision when thorough training programs are provided. Scanner operations run more smoothly, with less downtime and more efficiency.
Why Choose Dynamsoft?
Choose Dynamsoft Barcode Reader SDK for DPM code scanning on plastics for fast and accurate barcode detection. Its comprehensive features and easy integration make it a reliable tool for achieving precise and consistent DPM code readings. Contact us to learn more.


 Blog
Blog