Mastering Barcode Recognition Advanced Techniques for Accurate Results
Role of Accurate Barcode Recognition in Operational Efficiency
Operational efficiency is critical in today’s fast-paced business world. Hence, companies always seek methods to streamline workflows, reduce errors, and improve productivity. Barcode recognition is one technology that has played a significant role in attaining these objectives.
Accurate barcode recognition is fundamental to operational efficiency for monitoring inventory, managing assets, and enhancing the customer experience. This blog covers the factors affecting barcode recognition, image preprocessing techniques, real-time recognition, advanced decoding algorithms, and integration- all of which contribute to accurate barcode recognition’s crucial role in enhancing operational efficiency.
Factors affecting Barcode Recognition
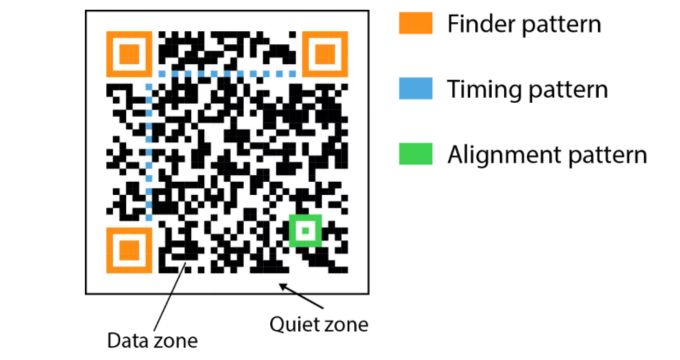
There are certain factors that must be considered to achieve optimal barcode recognition performance, as discussed in this section.
i. Reading Rate
The rate at which a barcode scanner can decode, and process barcodes is known as its barcode reading rate. It is measured in symbols or barcodes per second. The importance of a high reading rate lies in its direct impact on operational efficiency.
Check out this video for a detailed barcode reading rate benchmark and comparison.
ii. Average Runtime
The time required to identify and decode a barcode can affect operational efficacy. The quality and comprehensiveness of barcode libraries and datasets utilized by recognition systems impacts accuracy.
iii. Libraries and Dataset
The quality and comprehensiveness of barcode libraries and datasets utilized by barcode recognition systems impacts accuracy. An extensive library of diverse barcode samples improves recognition capabilities.
A comprehensive and representative collection of barcode types, image characteristics, and environmental conditions helps the scanner generalize and improve its accuracy in real-world scenarios. In contrast, a small or skewed dataset may hinder barcode recognition in challenging situations.
iv. Multiple Barcodes Reading Capability
In certain applications, such as inventory management and package tracking, the ability to read multiple barcodes in a single scan is essential. It enables barcode scanners to simultaneously capture data from multiple items or shipments, significantly enhancing operational efficiency. This feature reduces the time and effort required for data capture in scenarios where a large number of items must be processed rapidly.
In a warehouse, for instance, a single scan can record data from multiple barcoded items on a pallet, helping to expedite the inventory process. Similarly, in logistics and shipping, the ability to read multiple package barcodes simultaneously accelerates sorting and tracing operations, which increases productivity.
Shipments with multiple barcodes can be tracked faster with the multiple barcode scanning feature. This feature helps streamline the process by capturing all barcodes on a single shipment rather than scanning each barcode individually, saving time and assuring accuracy. It acts as a valuable tool for organizations that handle complex shipments, as it simplifies logistics and inventory management.
Image Preprocessing Techniques for Enhanced Accuracy
Before a barcode can be scanned and decoded, it often undergoes several image preprocessing procedures to improve its quality and clarity. This section delves into image preprocessing techniques, which are critical in boosting recognition accuracy.
i. Image Enhancement Methods
Image enhancement is the process of drawing attention to relevant aspects of an image while minimizing or erasing irrelevant ones. Some examples are unveiling previously hidden details, noise reduction, and selectively changing image brightness.
Image-enhancing methods can be broken down into two broad classes:
Spatial Domain: Enhancing an image in the spatial domain involves adjusting individual pixels according to their coordinates in space.
Frequency Domain: The image is improved by performing a Fourier Transform to the spatial domain and then altering pixels in groups.
For more information on image enhancement techniques, go through this blog- Image Processing 101 Chapter 2.1: Image Enhancement
ii. Binarization for Better Contrast
Barcode recognition relies heavily on binarization, a technique used in image preprocessing to increase contrast. The process includes changing a grayscale image to a binary one consisting of only two colors (often black and white). By enhancing the contrast between the dark lines of the barcode and the surrounding white areas, this simplification improves barcode identification accuracy.
The barcode scanner can better differentiate between the barcode elements when the image is reduced to only two colors, allowing for more accurate decoding and data extraction. Simply put, binarization enhances the readability of barcodes by increasing the contrast between the code and its background.
iii. Perspective Correction for Distorted Barcodes
Perspective correction for distorted barcodes is a critical image preprocessing method used in barcode recognition. Barcodes on curved or irregular surfaces require this image preprocessing technique. This method aligns and modifies the image such that the barcode seems like it was on a flat surface and corrects any perspective distortions.
Hence, it becomes simpler for barcode recognition software to read and decode the barcode since it conforms the barcode to the expected layout. In challenging situations where the barcode’s appearance has been altered due to surface curvature or distortion, this correction helps ensure accurate data extraction.
Advanced Decoding Algorithms

To attain the highest levels of accuracy, sophisticated decoding algorithms are critical. This section examines two important aspects of advanced decoding techniques.
i. Localizing Barcodes Using Edge Detection
Edge detection algorithms highlight the exact edges and borders of barcodes within an image, emphasizing the transition points between the barcode and its background. This information is critical because it provides decoding algorithms with a distinct reference frame, making it much simpler to accurately extract and process the encoded data from the barcode. Hence, edge detection improves the recognition process by identifying the beginning and conclusion of the barcode within the image, thereby facilitating decoding.
ii. Error Correction Strategies
An error correction strategy is essential for accurate recognition when a barcode is broken or partially hidden. These methods are made to decode barcodes with minor flaws like scratches, smudges, or printing mistakes.
The decoding method can recover the original information even when errors are present, thanks to error correction strategies that employ redundancy in the barcode data to detect and remedy faults. This feature ensures that crucial information may be reliably recovered from faulty barcodes, which is essential in situations where data integrity is paramount, such as supply chain management and inventory tracking.
Real-time Recognition and Integration

Barcode recognition has many uses, but its full potential is achieved when seamlessly integrated into systems and processes. This section covers some important real-time recognition and integration in applications and scalability options to ensure efficiency, precision, and speed as companies grow.
i. Implementing Barcode Recognition in Applications
Barcode recognition technology streamlines procedures and improves data accuracy when integrated into different applications.
Read this blog to learn how to integrate barcode scanning into your applications seamlessly. Essential Tips for Seamless Barcode Integration in Your Applications
ii. Performance Considerations for Real-Time Processing
To ensure smooth integration, it’s crucial to optimize performance for real-time barcode recognition. This involves minimizing latency and resource usage to maintain operational efficiency.
Latency Reduction: Every millisecond matters in real-time processing. The time lag between scanning and interpreting the data must be kept to a minimum. Fast recognition guarantees that critical data, like stock levels or product prices, are always up to date, streamlining decision-making.
Resource Optimization: Making optimal use of available resources is critical. The hardware and network requirements of barcode recognition systems must be kept to a minimum. This not only helps reduce energy consumption but also ensures that the system will function normally under heavy loads.
iii. Scalability Options
As businesses expand, meeting the increasing demands on barcode recognition systems is essential. Scalability options play a crucial role in this regard. Cloud-based solutions offer a scalable approach by providing resources on demand. This ensures that barcode recognition capabilities can be expanded without compromising the system’s accuracy or speed while optimizing resource allocation and maintaining cost efficiency. Additionally, scalable systems minimize downtime during expansion, ensuring uninterrupted operations, and provide a competitive edge by adapting to changing needs and technologies.
Conclusion
Accurate barcode recognition is critical to operational efficiency in a variety of businesses. Understanding the fundamentals of barcode technology, including the elements that influence recognition, image preprocessing techniques, advanced decoding algorithms, and real-time integration possibilities, enables businesses to expedite operations, decrease errors, and achieve higher productivity levels. Organizations can stay competitive in today’s fast-paced business market by investing in the correct barcode recognition technologies and processes.
Download Dynamsoft Barcode Reader SDK
Download Barcode Testing Sheet and Test Our Barcode SDK Now
Explore Our Developer Hub for Guides, API References, and More.