AI in Barcode and Document Capture: Moving Beyond Hype to Demonstrable Value
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into business operations is no longer a futuristic concept; it is a present-day mandate. While excitement abounds over AI’s predictive and analytical capabilities, a fundamental truth remains: AI is only as good as the data it consumes. This critical relationship is most evident in the foundational processes of barcode and document capture, where data quality underpins AI success.
As interest in GenAI grows, organizations increasingly ask practical questions such as: What is AI barcode scanning? How is it different from traditional scanning? And does it actually improve accuracy in real-world conditions?
Building on this foundation, we move beyond the hype to analyze the tangible value AI brings to precision data capture and examine why accuracy is essential for any enterprise relying on intelligent automation.
What Do People Mean When They Ask About “AI Barcode Scanning”?
When teams search for “AI barcode scanning,” they are typically seeking clarity, not novelty.
What does “AI barcode scanning” actually mean?
AI barcode scanning uses machine learning and computer vision to interpret barcode images in real-world conditions such as glare, damage, skew, or poor lighting, rather than relying only on rigid, rule-based pattern matching.
How is AI different from traditional barcode scanning?
Traditional barcode scanners use deterministic algorithms that perform best in clean, controlled environments. AI-enhanced systems learn from visual variability, making them more resilient when barcodes are curved, partially obscured, or captured at challenging angles.
Is AI always better than traditional scanning?
No. The most reliable systems combine deterministic algorithms with AI, using each where it performs best.
The “Garbage In, Garbage Out” Principle in the Context of AI
It is a well-worn adage from the early days of computing, but in the age of complex machine learning models, “garbage in, garbage out” has become a high-stakes mantra. Errors introduced at the capture stage don’t just persist; they expand under AI, leading to distorted insights and misguided decisions.
Even minor capture errors, such as a misread barcode or an incorrect invoice field, can significantly affect the performance of modern AI systems. Such errors compromise the integrity of AI models and may result in erroneous decision-making when the underlying data is flawed.
Data Quality: The Deciding Factor Between AI Success and Failure
Inaccurate AI outcomes have direct financial consequences. According to Gartner, poor data quality results in an average annual loss of $12.9 million for businesses. While data quality encompasses accessibility, timeliness, and relevance, accuracy is the most critical factor for AI effectiveness.
The consequences of poor capture accuracy ripple across industries:
- Supply Chain Issues: Torn barcodes or incorrectly encoded RFID tags can cause inventory systems to lose track of goods. When AI-driven logistics models, demand forecasting systems, or computer vision pipelines ingest these errors, they propagate incorrect inventory predictions, triggering misplaced orders, unexpected stockouts or overstocking, and widespread delays throughout the supply chain.
- Retail Misreads: Retail operations rely on accurate scans from point-of-sale (POS) barcodes, RFID tags, and optical character recognition (OCR) on product labels. Inaccurate inputs can disrupt pricing systems, cause discrepancies in shelf counts, and lead to slower checkouts or unavailable products for customers. When this poor capture data feeds into AI analytics, recommendation engines, or automated replenishment models, it results in incorrect product availability predictions, faulty trend analysis, and degraded customer experience.
- Finance and Healthcare Risks: In the financial sector, minor OCR errors in identification documents or invoices can distort transaction data, prevent legitimate users from accessing systems, or facilitate fraudulent activity. For AI-powered fraud detection or automated underwriting, these bad inputs train models to misclassify risk, reject legitimate claims, or increase false positives. In healthcare, a single misread document can lead to treatment delays or billing errors. Fed into AI triage, coding, or claims automation, these inaccuracies can escalate into systemic patient care mistakes and costly compliance violations.
How Does AI Improve Barcode and Document Capture Performance?
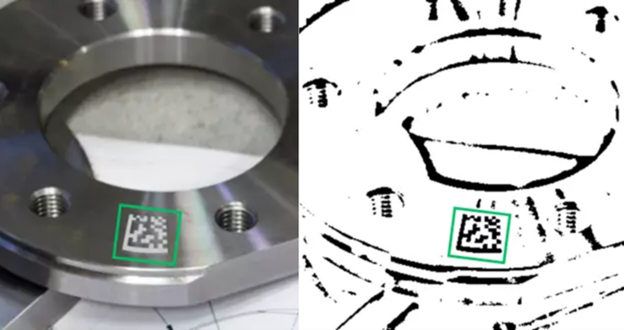
In this context, AI provides value beyond simple recognition by addressing inherent challenges in data collection and transforming data capture from an error-prone process into an intelligent, reliable system.
However, AI is not needed everywhere. Using it indiscriminately can add unnecessary complexity.
The most reliable capture systems combine deterministic algorithms with targeted machine learning enhancements, applying each where it performs best.
1. When Deterministic Algorithms Are the Right Tool
Some core capture tasks don’t need AI at all. In fact, they perform better without it:
- Barcode decoding
- Document edge detection
- Binarization and thresholding
These operations rely on optimized, rule-based algorithms that are:
- extremely fast,
- predictable,
- lightweight enough for offline or on-device use, and
- battle-tested across millions of scans.
For well-lit, clean, or standardized inputs, deterministic logic remains the gold standard.
2. When Machine Learning Makes a Meaningful Difference
AI shines when capture conditions are inconsistent, varied, or unpredictable:
- Distorted or curved barcodes
- Poor lighting, glare, or shadows
- Unstandardized documents captured in uncontrolled environments (e.g., field, warehouse, customer site)
- Handwriting OCR and complex ID verification
- *Detecting manipulated or fraudulent documents
These scenarios are common concerns, such as whether AI can read damaged barcodes or assist with low-light scanning.
In these cases, AI’s ability to learn from visual variability allows it to correct issues traditional algorithms cannot resolve on their own.
3. A Hybrid Approach: The Best of Both Worlds
Most real-world capture scenarios benefit from a blended pipeline.
AI acts as an enhancement layer that supports deterministic algorithms where they begin to struggle. Examples include:
- Adaptive thresholding tuned by Machine Learning (automatically adjusting contrast and brightness so barcodes and text remain readable even in poor lighting or uneven backgrounds)
- Automatic angle correction for skewed documents
- Retry strategies that evaluate image quality and reprocess intelligently
- Fallback pipelines that escalate to AI models for difficult cases
- Image cleanup and enhancement before OCR or barcode decoding (removing noise, improving clarity, and making text or codes easier to read)
This layered approach dramatically improves accuracy while keeping performance efficient.
Where Is AI Barcode Scanning Most Useful?
AI-enhanced capture provides the most value in environments where scanning conditions are unpredictable or prone to errors:
- Retail & POS: Faster checkouts, fewer rescans, and more reliable inventory data feeding AI-driven demand forecasting
- Logistics & Warehousing: Improved reads of damaged labels, curved surfaces, and dense multi-barcode environments
- Healthcare: Accurate scanning of patient IDs, specimen labels, and medication barcodes where errors have serious consequences
- Finance & Identity Verification: Higher OCR accuracy for IDs, invoices, and compliance documents used by downstream AI systems
Document and ID Optimization: AI for Precision and Clarity

For document and ID capture, AI ensures optimal image quality before OCR extraction even begins:
- Glare and Shadow Removal: AI identifies reflective hotspots or dark regions, then balances lighting across the image.
- Worn Documents: Models enhance contrast and restore faded or aged text, improving text extraction. Stabilization: AI smooths motion blur and corrects perspective distortions.
By addressing these issues at the point of capture, organizations minimize the need for manual data entry and review, reducing the highest source of human error.
Is AI Barcode Scanning Trustworthy?
A common concern is whether AI introduces false reads or “hallucinations.” In practice, hybrid architectures mitigate this risk:
- Deterministic decoders validate known barcode symbologies.
- AI models activate selectively when image quality degrades.
- Multi-factor validation cross-checks scans against backend records or expected formats.
This results in higher accuracy, fewer false positives, and greater trust in AI-driven workflows.
The Future: Precision as the Foundation for Transformation
While much attention focuses on AI’s generative capabilities and large language models, its most transformative impact begins with accurate capture and interpretation of real-world data.
As industries adopt richer data formats, such as QR codes embedding batch numbers, product details, and traceability metadata, the demand for precision increases.
AI is evolving toward context-aware capture, understanding not only what was scanned but also whether the data is appropriate for the workflow.
Take the Next Step in Your AI Journey with Confidence
Real AI acceleration begins with getting the foundations right, and that starts at the point of capture. Seek out flexible SDKs that provide enterprise-level barcode and document accuracy across mobile, web, and desktop workflows. Tools designed to ensure every scan, image, and data point meets the highest standards.
Solutions such as Dynamsoft’s Capture SDKs, built for reliability and cross-platform performance, can help teams achieve that level of integrity, providing AI systems with the clean, consistent inputs they need to deliver accurate results.



 Blog
Blog