Why GS1 Standards Are Transforming Healthcare Supply Chains
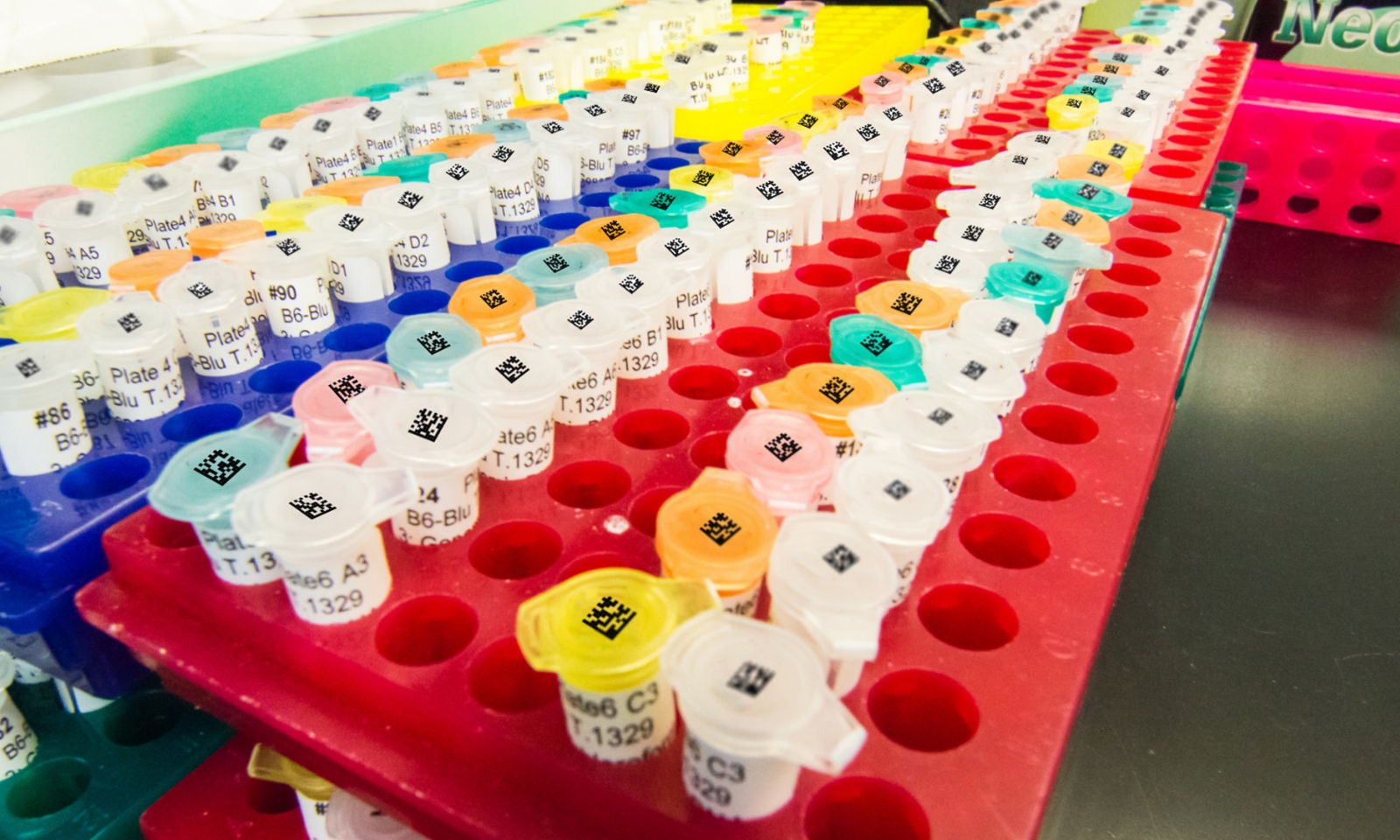

Behind every medical device, vial, or pharmaceutical package that’s scanned in a hospital or lab, there’s a global standard quietly enabling safety and efficiency - GS1.
GS1 standards define how healthcare products are identified, barcoded, and tracked across the supply chain. They underpin everything from patient safety to recall traceability. As healthcare becomes more digital and interconnected, GS1 is emerging as the foundation for safe, compliant, and data-driven operations worldwide.
This article explains why GS1 is vital in healthcare, how its standards are used across the industry, the main barcode formats, and the regional changes shaping what’s next.
Why GS1 Matters in Healthcare
Healthcare supply chains are uniquely complex. A single hospital can handle tens of thousands of products daily - from surgical instruments and implants to pharmaceuticals and consumables. Misidentification or inconsistent labeling can lead to delays, waste, or worse - patient harm.
GS1 standards create a common language for data that ensures consistency and interoperability across the global supply chain. They help organizations answer critical questions:
- Is this the right product?
- Is it authentic?
- Is it within its expiry date?
- Where did it come from, and where has it been used?
Let’s look at the main reasons GS1 is so important in healthcare today.
1. Patient Safety
Barcode scanning based on GS1 identifiers helps ensure the “five rights”: the right patient, product, dose, time, and route. At the point of care, nurses can verify a product instantly before administration. Hospitals using GS1 DataMatrix codes report dramatic reductions in medication and implant errors.
2. Traceability and Anti-Counterfeiting
Each item’s Global Trade Item Number (GTIN), along with batch/lot, serial number, and expiry date, enables traceability across every step of the supply chain. If a product recall is issued, affected lots can be identified and removed immediately. The same serialization supports anti-counterfeiting - a growing global concern in pharmaceuticals and medical devices.
3. Operational Efficiency
GS1 streamlines warehouse, inventory, and procurement operations. Standardized identifiers reduce manual entry errors, automate replenishment, and simplify data exchange between systems. Hospitals can track expiry dates automatically and avoid waste due to overstocking or unnoticed product expiration.
4. Interoperability
Perhaps most importantly, GS1 enables interoperability across systems, vendors, and borders. When all stakeholders use the same identifiers (GTINs for products, GLNs for locations, SSCCs for shipments), data can flow freely and accurately from manufacturers to regulators to hospitals.
Where GS1 Standards are Used in Healthcare
| Application Area | Typical Users | GS1 Components | Use Case Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical packaging | Manufacturers, distributors, pharmacies | GTIN, batch/lot, expiry (GS1 DataMatrix) | Ensures full drug traceability under FMD or DSCSA |
| Medical devices | Device manufacturers, hospitals | GTIN (UDI-DI), serial (UDI-PI) | Implant tracking, recall management |
| Laboratory samples | Diagnostic labs, biobanks | GTIN, serial (GS1 DataMatrix) | Sample traceability and automation |
| Hospital supply chain | Hospitals, logistics providers | GLN, GTIN, SSCC | Goods receipt, inventory management |
| Point of care | Clinicians, nurses | GTIN + UDI | Verifying devices and medication before use |
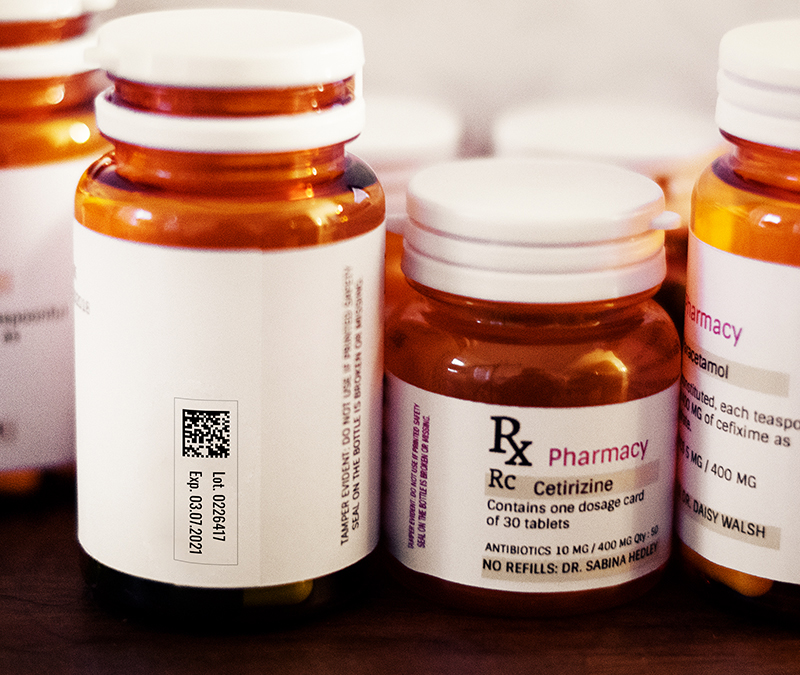
Understanding Barcode Formats in Healthcare
Healthcare uses a mix of barcode formats to serve different operational needs - from outer-case logistics labels to unit-dose vials. GS1 defines which symbology is appropriate for which application.
| Barcode Type | Description | Where It’s Used | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| GS1-128 (1D) | High-density linear barcode that encodes GTIN, batch, expiry, serial. | Cartons, outer cases, logistics units. | Ideal for scanning on conveyors or in warehouses. |
| GS1 DataMatrix (2D) | Compact symbol encoding multiple data elements. | Individual medical devices, pharma, vials. | The standard for regulated healthcare packaging. |
| GS1 DataBar | Compact linear format for small retail items. | Small pharma or healthcare consumables. | Less common in regulated healthcare. |
| GS1 QR Code | Links product to digital data (e.g. electronic leaflets). | OTC products, patient information access. | Part of GS1’s Digital Link initiative. |
| SSCC (Serial Shipping Container Code) | Unique ID for logistics units like pallets. | Distribution and warehousing. | Typically encoded in GS1-128. |
The industry trend is clear: 2D barcodes (especially GS1 DataMatrix) are becoming the universal standard for healthcare products. They carry more information in less space, can be scanned even on curved or small surfaces, and support traceability requirements.
-
GS1-128

-
GS1-Data Matrix -

-
GS1-Databar -

-
GS1-QR Code -

-
SSCC -

Regional Standards and What’s Changing
United States
- Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) mandated end-to-end serialization in 2024. GS1 identifiers (GTIN, batch, serial, expiry) form the backbone of compliance.
- FDA Unique Device Identification (UDI) system requires all medical devices to have standardized identifiers; GS1 is one of the approved issuing agencies.
- Increasing adoption of EPCIS 1.3 for digital traceability across supply chain events.
European Union
- The Falsified Medicines Directive (FMD) requires GS1 DataMatrix codes on all prescription drugs.
- EU MDR/IVDR mandates UDIs for medical devices, including a new “Master UDI” definition effective in 2025.
- The region is rapidly moving toward full 2D barcode adoption at all packaging levels.
Canada
- GS1 Canada’s Healthcare Ready Initiative targets full 2D barcode readiness across suppliers and hospitals by end of 2025.
- Aim: interoperability between manufacturers, distributors, and care providers using GS1 standards.
Asia Pacific
- Countries such as Australia, Japan, Singapore, and China are aligning their UDI systems with GS1 global standards.
- Several are introducing serialization and digital traceability mandates similar to DSCSA and MDR.
Global Updates
- Starting January 1, 2025, all regulated healthcare products using GS1 barcodes must include a real day in the expiry date (no “00” placeholders).
- GS1’s Digital Link and 2D barcode convergence projects are merging supply chain and patient-facing barcodes — one code that works for both logistics and consumer data.
- New updates in the GS1 General Specifications 2025 introduce terminology and structures to support next-generation medical device identification.
What It Means for Healthcare Technology Providers
For software developers, integrators, and solution providers, GS1’s growing role means data capture tools must be more intelligent, interoperable, and compliant than ever.
- Scanners and SDKs must support all major GS1 formats — including GS1 DataMatrix and GS1-128.
- Applications should parse and validate AI (Application Identifier) data such as expiry dates, batch numbers, and serials.
- Capture systems must handle mixed barcode environments (1D + 2D) in warehouses and hospitals.
- Solutions that can read hundreds of barcodes at once — such as batch barcode scanning — can significantly speed up inventory and verification workflows.
- Integration with hospital, manufacturing, or logistics systems (ERP, MES, WMS, LIMS) must preserve GS1-compliant data structures.
By building on GS1 standards, healthcare technology companies not only ensure compliance but also position themselves for interoperability across global supply chains.
GS1 as the Foundation for Connected Healthcare
From production to patient care, GS1 is becoming the global language of healthcare logistics and safety. It ensures that every item — from a surgical implant to a vial in the lab — can be accurately identified, tracked, and verified.
As the industry transitions to full 2D barcode adoption and more granular traceability standards, healthcare organizations and developers alike must prepare their data capture systems to keep pace.
Dynamsoft’s data capture SDKs — including our new Batch Barcode Scanner — are designed to decode GS1 barcodes at scale, enabling faster, precision capture across healthcare workflows. Whether scanning medical devices, lab samples or medications, we help healthcare providers and software providers stay compliant and ready for the next wave of GS1 innovation.
Start Scanning GS1 Barcodes in Minutes
Dynamsoft Barcode Reader is a barcode scanning software developer kit (SDK) that provides exceptional accuracy, even with challenging barcodes. Using advanced algorithms, it can read damaged, distorted, or poorly barcodes reliably at industry leading speeds, reducing the need for manual data entry and minimizing errors. Dynamsoft Barcode Reader is designed to integrate seamlessly with existing systems, making it easy to deploy and use in existing healthcare systems.
Integrate Dynamsoft Barcode Reader into your application with just a few lines of code.
Try the online demo
Read the tech tutorial: https://www.dynamsoft.com/codepool/scan-and-parse-gs1-barcode.html
Download the SDK, explore our samples, and start decoding GS1 barcodes today.
Contact Sales for enterprise licensing



 Blog
Blog