How DPM Barcode Scanning Is Powering Traceability in Manufacturing

As manufacturing becomes more complex, permanently marked identifiers are replacing printed labels to maintain traceability from production to service. Traditional identification methods, such as printed labels and stickers, often fail in production environments. Exposure to heat, chemicals, abrasion, sterilization, and long product lifecycles can quickly degrade labels and disrupt the data chain.
Direct Part Marking (DPM) barcode scanning addresses these challenges by marking a code directly on the part’s surface. To learn more about the technical foundations of this technology, check out our detailed guide on DPM code scanning.
Why DPM Codes Matter in Manufacturing
Recognizing the fundamental role of DPM is essential for optimizing your production line for long-term success.
Direct Part Marking engraves, etches, or indents a barcode or 2D symbol into the material. Common methods include laser marking, dot peen, and chemical etching. Data Matrix is the most widely used symbology due to its high data density and error-correction capabilities.
Industry standards organizations recognize DPM as a core identification method. GS1, for example, explicitly supports Data Matrix symbols applied using direct marking techniques such as laser and dot peen for part identification in manufacturing environments.
DPM matters because it delivers:
- Permanent Traceability: Codes remain readable throughout the product’s lifetime, even under environmental conditions.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting global standards increasingly depends on initiatives such as Digital Product Passports, which use DPM to ensure hardware transparency.
- Anti-Counterfeiting: DPM codes are difficult to remove, providing an auditable digital record.
- High-Density Data: DataMatrix codes store substantial information in minimal space.
Challenges with Scanning DPM Codes in Manufacturing Setups
While DPM offers superior durability, the physical characteristics of the marks present unique challenges for standard scanning hardware.
Parts often move through high-speed production lines and oily environments, which can directly affect scanner performance.
Common DPM Scanning Challenges
| Challenge | Why It Happens | Typical Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Low contrast | Laser marks often have minimal tonal difference from metal surfaces | High-dynamic-range (HDR) imaging, adaptive exposure, specialized DPM algorithms |
| Reflective and shiny materials | Glare on stainless steel, aluminum, or oiled parts obscures modules | Diffuse or angled lighting, polarizing filters |
| Curved or uneven surfaces | Perspective distortion affects symbol geometry | Higher-resolution sensors, fixed working distance, multiple-angle reads |
| Small symbol size | Electronics and micro-components may use very small codes | Optics matched to module size (X-dimension), precise focus |
| Environmental contamination | Oil, dust, coolant, vibration, and inconsistent lighting | Ruggedized scanners, real-time image enhancement |
| Mark degradation over time | Abrasion, coatings, or blasting reduce readability | Redundant encoding and robust marking processes |
To address these challenges, manufacturers are adopting industrial barcode scanner SDKs with dedicated DPM modes, advanced image processing, and AI-assisted decoding. To address these challenges, manufacturers are adopting industrial barcode scanner SDKs that leverage AI-assisted decoding to handle the most challenging factory-floor scenarios.
Benefits of DPM for Traceability
Once scanning challenges are resolved, DPM becomes one of the most robust tools for manufacturing traceability.
Key Traceability Advantages
By associating each part with its complete production and quality history, manufacturers can eliminate reliance on labels or paperwork and achieve the following:
- Gain end-to-end visibility from raw material intake through production, assembly, and field service, enabling true production traceability across the value chain.
- Reduce data entry errors by replacing manual recording with automated identification.
- Ensure regulatory compliance with UDI, aerospace, and defense identification requirements.
- Improve quality management by linking parts to inspection data, test results, and process parameters within MES traceability systems.
- Accelerate and target recall containment more effectively.
- Strengthen supply chain security by authenticating genuine components.
Studies in industrial automation show that manual data entry results in about one error per 300 characters, while barcode scanning reduces this to one error per 3 million characters. This demonstrates why automated identification is fundamental to modern quality systems.
Industry Applications of DPM Barcode Scanning

DPM implementation varies significantly across sectors based on their specific demands and regulatory requirements.
Automotive Manufacturing
Automotive plants permanently mark engine blocks, transmissions, chassis parts, and safety-critical components. Standards such as AIAG B-17 specify how direct part marking should be applied for durability and readability. DPM enables full traceability from supplier through assembly and after-sales service, allowing manufacturers to isolate defects to specific batches or individual components.
Aerospace and Defense
Aerospace components may remain in service for 20 to 30 years and undergo multiple maintenance, repair, and overhaul cycles. Standards such as SAE AS9132 specify requirements for Data Matrix quality and application on aerospace parts. DPM ensures that each component’s identity, maintenance history, and compliance data remain accessible throughout its operational life. For more information on these systems in demanding environments, see our post on parts tracking in aviation operations.
Electronics Manufacturing
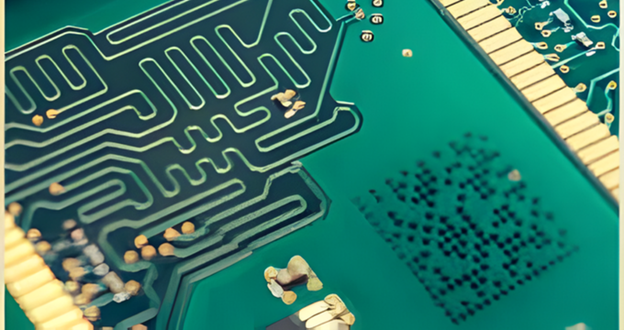
Printed circuit boards, connectors, and miniature housings often lack space for labels. DPM enables manufacturers to apply small, high-density Data Matrix codes directly onto components, supporting traceability across assembly, testing, and supply-chain distribution. This is especially valuable for combating counterfeit electronic parts.
Medical Devices
Surgical instruments, implants, and reusable devices must withstand repeated sterilization. Under FDA UDI rules, many reusable devices require direct marking. DPM ensures that identifiers survive autoclaving, chemical cleaning, and long-term clinical use, supporting device history records, inventory management, and patient safety.
The Role of Advanced Scanner SDKs in DPM
DPM traceability depends on the quality of the scanning technology. Modern manufacturing systems increasingly use barcode scanning SDKs rather than standalone hardware. These SDKs offer:
- DPM-specific decoding algorithms optimized for low contrast and damaged marks
- AI-driven image enhancement to improve readability on reflective or curved surfaces
- Flexible deployment across mobile devices, fixed industrial cameras, and robotic inspection systems
- Seamless integration with MES, ERP, and quality-management systems
These integrations are essential to Industry 4.0 strategies, where machine vision, robotics, and IoT systems require reliable, automated identification at every production step.
Looking Ahead: The Future of DPM in Manufacturing
Several trends are shaping the next phase of DPM adoption:
- AI-Enhanced Decoding: Machine-learning models are improving read rates for low-contrast and degraded marks.
- Robotic and Vision Integration: DPM scanning is increasingly embedded in robotic cells for automated inspection and in-line quality control.
- Digital Thread and Industry 4.0: As manufacturers connect design, production, and service data, DPM provides the persistent identifier that links the entire digital lifecycle of a part.
- Tighter Compliance and Security: Growing focus on supply-chain security and counterfeit prevention will further elevate the importance of permanent, verifiable marking.
Powering Real-World DPM Traceability with Dynamsoft
Direct Part Marking has evolved from a niche identification method to a cornerstone of modern manufacturing traceability. By creating a permanent, machine-readable identity on each part, DPM enables accurate tracking, enhanced quality control, regulatory compliance, and supply-chain security across automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices.
While DPM scanning presents challenges such as low contrast, reflectivity, small codes, and harsh environments, advances in imaging, AI, and specialized barcode scanning SDKs now enable reliable decoding at scale.
Dynamsoft Barcode Reader SDK is designed for these conditions, offering DPM-optimized decoding, intelligent image processing, and seamless integration with mobile apps, industrial cameras, and MES or ERP systems to help manufacturers achieve reliable production traceability using a modern manufacturing barcode scanner approach.
Explore Dynamsoft Barcode Reader SDK
Speak with an expert to design your DPM scanning workflow



 Blog
Blog