Image Processing 101 Chapter 2.1: A Complete Guide to Enhancing Visual Quality
What Is Image Enhancement in Image Processing
Digital image processing plays a critical role in improving the quality and usability of visual data. One of its most important components is image enhancement, a set of image enhancement techniques designed to improve brightness, clarity, and overall interpretability. Methods such as contrast adjustment and spatial filtering help refine image details, reduce noise, and highlight important features. By enhancing visual quality, these techniques make images more suitable for analysis, computer vision applications, and automated recognition systems.
Key Takeaways:
- Image enhancement improves visual quality by adjusting brightness, contrast, and noise for better interpretation and analysis.
- Techniques fall into spatial domain (pixel-level ops & filtering) and frequency domain methods for broader control.
- Practical methods include contrast stretching, histogram equalization, denoising, smoothing, and sharpening.
- Enhanced images support downstream tasks like OCR, barcode reading, and machine vision accuracy.
- Structuring content with clear headings and lists improves AI search relevance and user readability.
Image Enhancement Techniques Explained
Image enhancement techniques can be broadly classified into two primary categories, distinguished by the domain in which they operate:
Spatial Domain
Spatial domain methods directly manipulate the pixel values of an image. This approach is intuitive and often effective, as it works directly with the raw pixel data. Operations are performed directly on the image matrix, where the value of a pixel is altered based on its own value and/or the value of neighbouring pixels within a defined area. Within the spatial domain, techniques are typically divided into:
Point Operations (Brightness, Contrast, Thresholding)
These operations modify individual pixels values independently of their location or neighbouring pixels. They use a transformation function to map input pixel values to new output values.
Common types of Point Operation include:
- Brightness adjustment
- Contrast stretching
- Thresholding
Spatial Filtering (Smoothing, Sharpening, Edge Detection)
These techniques modify a pixel’s value based on the values of its neighbours within a defined window or kernel. This approach is commonly used for tasks such as smoothing sharpening, and noise reduction.
Common types of Spatial Filtering include:
- Smoothing (deblurring)
- Sharpening
- Edge detection
Frequency Domain
Frequency domain methods operate on the Fourier Transform of an image rather than directly on its pixels. The Fourier Transform converts an image from its spatial representation to a frequency representation, where image information like brightness variations and edges are represented by different frequencies.
In the frequency domain, global operations can be applied more efficiently. For instance, filtering techniques are applied to the transformed image, and then an inverse Fourier Transform is performed to convert the image back to the spatial domain.
This approach is particularly powerful for tasks like:
- Noise Reductions: By selectively attenuating high-frequency components that often correspond to noise.
- Image sharpening: By enhancing high-frequency components related to edges and details.
- Homomorphic Filtering: A specialized technique used to correct non-uniform illumination and simultaneously enhance contrast by separating the illumination and reflectance component of an image.
Common Real-World Enhancement Example
Here are some commonly used image enhancement techniques – many of which are powered by point operation or spatial filter.
Contrast Adjustment
When an image looks dull or lacks variation between light and dark areas, it often means the pixel values are clustered in a narrow range. Contrast adjustment redistributes or stretches these values so that features stand out distinctly.

Histogram Equalization
This technique is especially useful for images taken in poor lighting. Histogram equalization spreads pixel intensities more evenly across the available range, helping reveal details that were previously hidden in shadows or highlights.
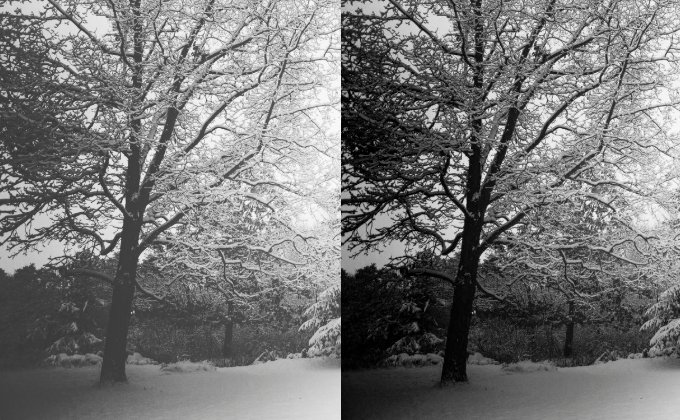

Denoising
Noise is common in images captured with low-end cameras or in poor lighting. It can obscure fine details and lower OCR or barcode recognition accuracy. Denoising techniques help clean up these irregularities without overly blurring the image.

Smoothing and Sharpening Visual Details
Enhancing image details often involves a balance between reducing noise (smoothing) and making edge crisper (sharpening).
Smoothing reduces minor variations across the image while preserving large-scale structures. It’s often used before OCR or barcode decoding to simplify the image and reduce distraction caused by textures or noise.
Sharpening is used to recover lost edge details from slightly blurred images. It enhances contrast along edges to make features like text, logos or barcode lines more pronounced.
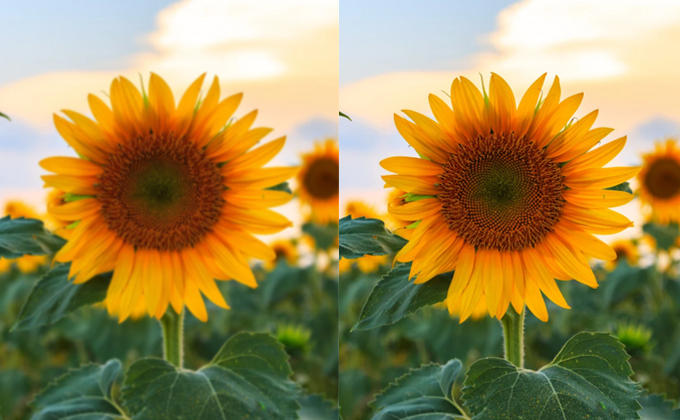

Brightness and Saturation Correction
Sometime the problem is just a dull image – either too dark or too washed out. Adjusting brightness and saturation helps make the image visually balanced, restoring visibility to text, logos, or patterns.

Conclusion
Image enhancement is a foundational step in building reliable computer vision applications. From improving barcode scans to scanning old documents, these techniques help bridge the gap between raw image data and meaningful output.
Whether you’re working with documents, labels, or real-time video frames, integrating point operations and spatial filter into your processing workflow can significantly boost accuracy and performance.
This article is Part 4 in a 7-Part Series.
- Part 1 - Image Processing 101 Chapter 1.1: What is an Image?
- Part 2 - Image Processing 101 Chapter 1.2: Understanding Color Models and Their Uses
- Part 3 - Color Space Conversion & Binarization for Image Processing
- Part 4 - Image Processing 101 Chapter 2.1: A Complete Guide to Enhancing Visual Quality
- Part 5 - Point Operations in Image Processing: A Beginner's Guide
- Part 6 - Image Smoothing & Sharpening in Image Processing using Spatial Filters
- Part 7 - Morphological Operations



 Blog
Blog