How to Build an iOS MRZ Scanner with SwiftUI and Dynamsoft Capture Vision
Machine-readable zones (MRZ) are an essential feature for processing passports, IDs, and other travel documents. In this tutorial, we’ll demonstrate how to build an iOS MRZ scanner app using SwiftUI and Dynamsoft Capture Vision SDK.
This article is Part 2 in a 6-Part Series.
- Part 1 - Creating an iOS Barcode and QR Code Scanner with SwiftUI on M1 Mac
- Part 2 - How to Build an iOS MRZ Scanner with SwiftUI and Dynamsoft Capture Vision
- Part 3 - How to Build a macOS Barcode Scanner App Using SwiftUI and C++ Barcode SDK from Scratch
- Part 4 - How to Create an iOS Barcode Scanner Project for macOS and iOS in SwiftUI
- Part 5 - How to Build a Document Scanner App with SwiftUI for Both macOS and iOS
- Part 6 - Building a macOS Framework with Objective-C++ and C++ for Swift Barcode Detection
iOS SwiftUI MRZ Scanner Demo Video
Prerequisites
- Obtain a license key for the Dynamsoft Capture Vision SDK.
Learning the Sample Code Provided by Dynamsoft
Dynamsoft has released a sample project: an iOS MRZ scanner app built with Storyboard. You can find the source code on GitHub: https://github.com/Dynamsoft/mrz-scanner-mobile/tree/main/ios
By studying the API usage, you’ll be equipped to build an iOS MRZ scanner app using SwiftUI.
Setting Up a New SwiftUI Project
- In Xcode, select the
Multiplatformtab and clickApp. - Click
Nextto create a new project scaffolded with SwiftUI. -
Navigate to
File > Add Package Dependenciesto add the Dynamsoft Capture Vision SDK. Ensure all packages are added to the target.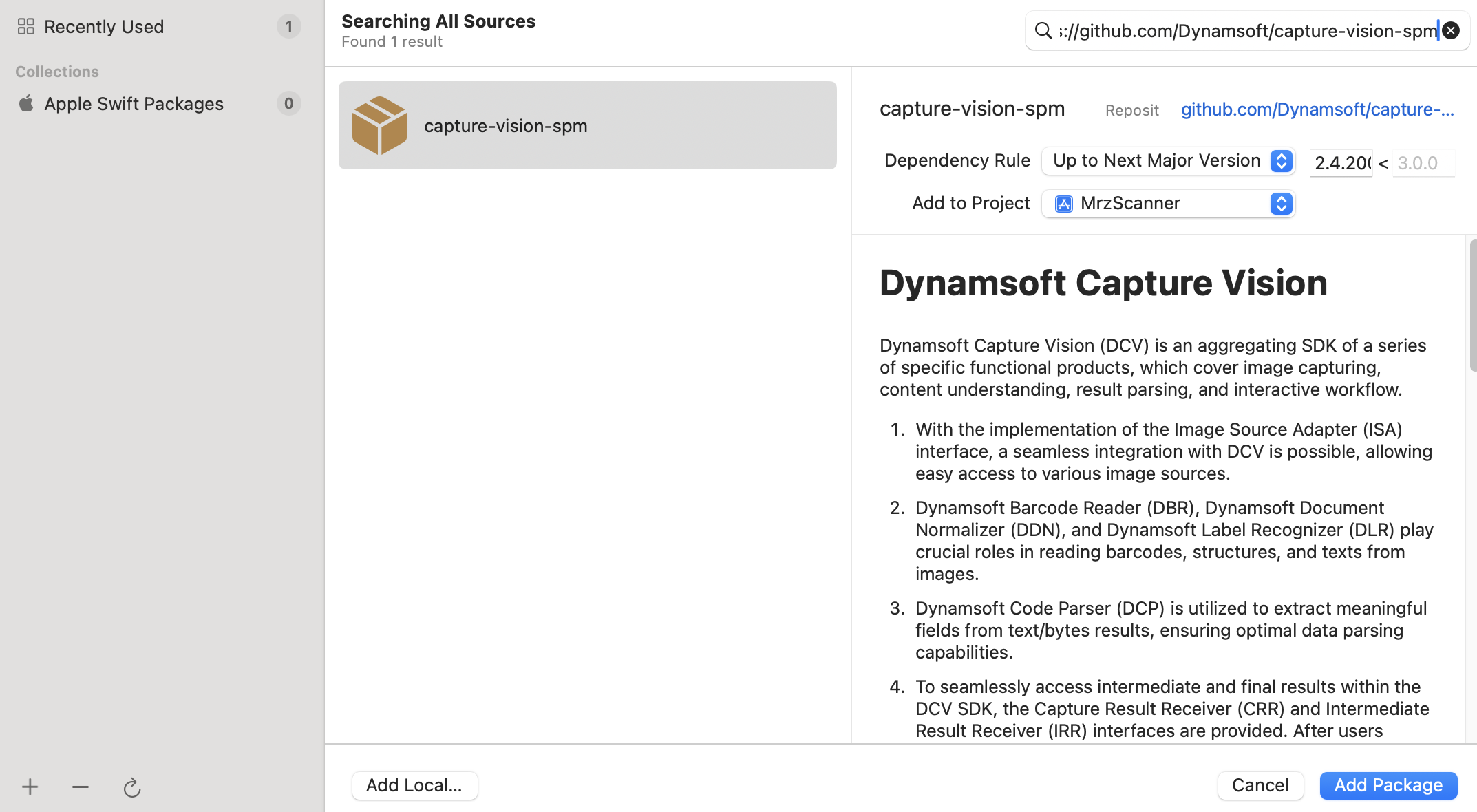
-
Go to
Project > Infoand add a new row with the keyNSCameraUsageDescription, along with a description to request camera permission.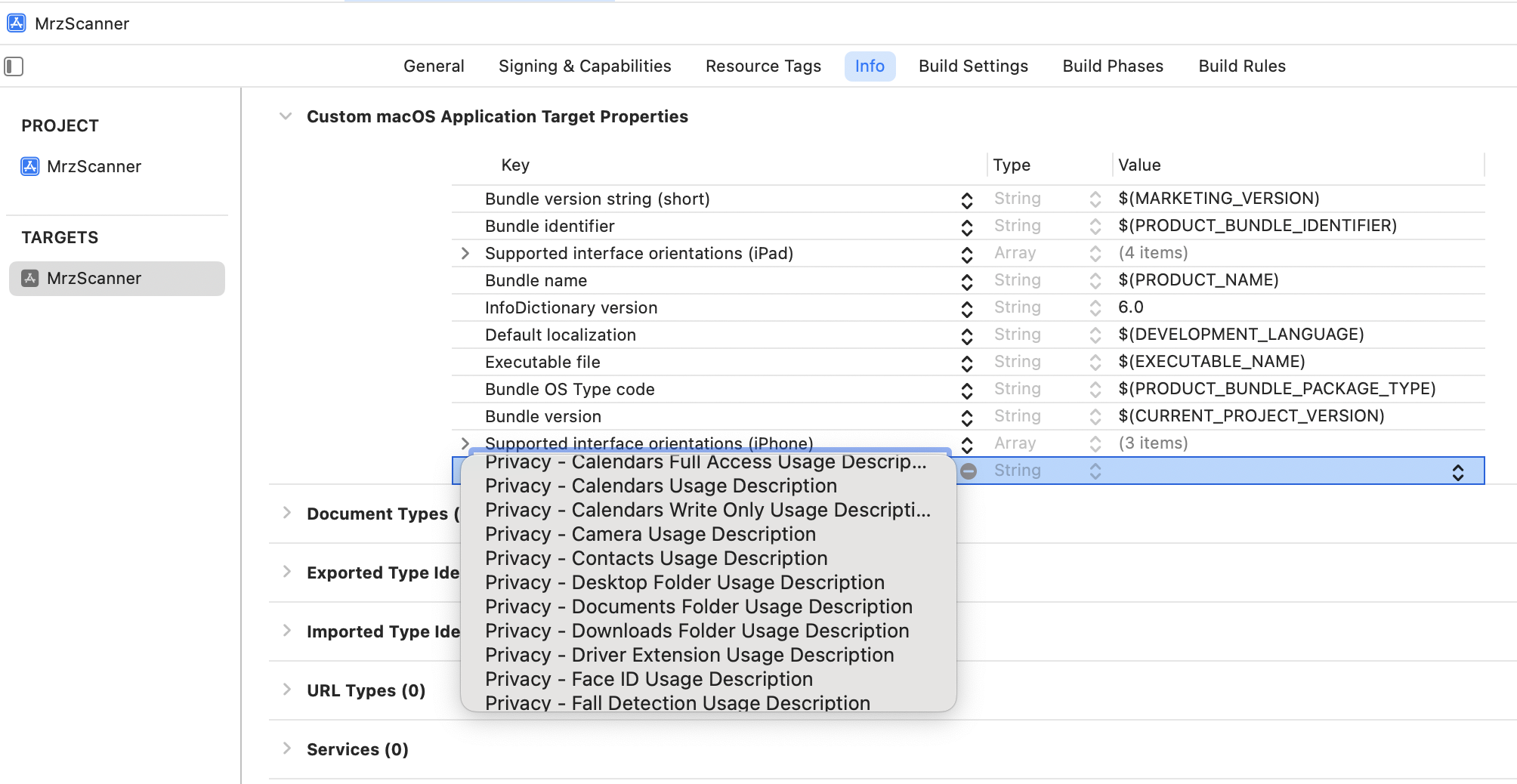
Implementing iOS MRZ Scanner with SwiftUI
The code snippets for opening the camera and scanning MRZ in the Storyboard project can be reused in the SwiftUI project. To begin, copy MRZScannerViewController.swift into the SwiftUI project and rename it to CameraViewController.swft. Remember to replace the license key with your own in MRZScannerViewController.
func setLicense() {
LicenseManager.initLicense("LICENSE-KEY", verificationDelegate: self)
}
Next, adapt the UI components to SwiftUI.
Camera Capture View
Create a new file named CaptureView.swift and include the following code:
import SwiftUI
struct CaptureView: View {
var title:String
var body: some View {
VStack {
CameraViewControllerRepresentable()
}
.navigationTitle(title)
.padding()
}
}
struct CameraViewControllerRepresentable: UIViewControllerRepresentable {
func makeUIViewController(context: Context) -> CameraViewController {
let vc = CameraViewController()
return vc
}
func updateUIViewController(_ viewController: CameraViewController, context: Context) {
}
}
Explanation
CaptureViewis a SwiftUI view that wraps and displays theCameraViewControllerRepresentable. It shows the camera preview.CameraViewControllerRepresentableconforms to theUIViewControllerRepresentableprotocol, bridgingCameraViewControllerinto the SwiftUI framework.
Content View
The ContentView serves as the main view of the app. Replace its content with the following code to include a navigation button leading to CaptureView:
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
NavigationView {
VStack(spacing: 20) {
NavigationLink(destination:CaptureView(title: "Scan MRZ")) {
Text("Scan MRZ")
.font(.title2)
.padding()
.background(Color.red)
.foregroundColor(.white)
.cornerRadius(10)
}
}
.navigationTitle("Home")
}
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}
Displaying MRZ Results in a Popup Dialog
In the existing CameraViewController code, the MRZ result is displayed in a new view controller taking the full screen:
let vc = MRZResultViewController()
self.navigationController?.pushViewController(vc, animated: true)
Let’s make some changes to display the MRZ result in a popup dialog.
-
Use
presentinstead ofpushViewControllerfor modal presentation:let vc = MRZResultViewController() vc.modalPresentationStyle = .overCurrentContext vc.view.backgroundColor = UIColor.black.withAlphaComponent(0.3) vc.preferredContentSize = CGSize(width: self.view.bounds.width * 0.8, height: self.view.bounds.height * 0.6) self.present(vc, animated: true, completion: nil) -
Resize the MRZ result view:
override func viewDidLoad() { super.viewDidLoad() self.title = "MRZ Result" view.backgroundColor = UIColor.black.withAlphaComponent(0.5) let contentView = UIView() contentView.backgroundColor = .white contentView.layer.cornerRadius = 10 contentView.clipsToBounds = true contentView.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false view.addSubview(contentView) NSLayoutConstraint.activate([ contentView.centerXAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.centerXAnchor), contentView.centerYAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.centerYAnchor), contentView.widthAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.widthAnchor, multiplier: 0.8), contentView.heightAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.heightAnchor, multiplier: 0.6) ]) analyzeData() setupUI(in: contentView) } -
Add a
backbutton to dismiss the view controller:func setupUI(in contentView: UIView) { let safeArea = contentView.safeAreaLayoutGuide let tableView = UITableView() tableView.flashScrollIndicators() tableView.delegate = self tableView.dataSource = self tableView.separatorStyle = .none tableView.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false contentView.addSubview(tableView) NSLayoutConstraint.activate([ tableView.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: safeArea.leadingAnchor), tableView.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: safeArea.trailingAnchor), tableView.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: safeArea.topAnchor), tableView.bottomAnchor.constraint(equalTo: safeArea.bottomAnchor) ]) let dismissButton = UIButton(type: .system) dismissButton.setTitle("Back", for: .normal) dismissButton.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false dismissButton.addTarget(self, action: #selector(dismissViewController), for: .touchUpInside) contentView.addSubview(dismissButton) NSLayoutConstraint.activate([ dismissButton.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: contentView.topAnchor, constant: 20), dismissButton.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: contentView.trailingAnchor, constant: -20) ]) } @objc func dismissViewController() { self.dismiss(animated: true, completion: nil) }
Restarting MRZ Scanning After Dismissing the Popup
To ensure MRZ scanning resumes after the popup dialog is dismissed:
-
In the
MRZResultViewController, define a protocol that will notify theCameraViewControllerto start capturing again when the modal is dismissed.protocol MRZResultViewControllerDelegate: AnyObject { func restartCapturing() } class MRZResultViewController: UIViewController { weak var delegate: MRZResultViewControllerDelegate? override func viewDidLoad() { super.viewDidLoad() ... } @objc func dismissViewController() { delegate?.restartCapturing() self.dismiss(animated: true, completion: nil) } } -
In
CameraViewController, conform to the protocol and implement therestartCapturing()method to start the capturing process when the modal is dismissed.extension CameraViewController: MRZResultViewControllerDelegate { func restartCapturing() { cvr.startCapturing(currentTemplateName) { isSuccess, error in if !isSuccess, let error = error { self.showResult("Error", error.localizedDescription) } } } } -
When presenting
MRZResultViewController, set theCameraViewControlleras the delegate of theMRZResultViewController.extension CameraViewController: CapturedResultReceiver { func onCapturedResultReceived(_ result: CapturedResult) { if let item = result.parsedResult?.items?.first, model.isLegalMRZ(item) { DispatchQueue.main.async { self.cvr.stopCapturing() self.dce.clearBuffer() let vc = MRZResultViewController() vc.mrzResultModel = self.model vc.delegate = self vc.modalPresentationStyle = .overCurrentContext vc.view.backgroundColor = UIColor.black.withAlphaComponent(0.3) vc.preferredContentSize = CGSize(width: self.view.bounds.width * 0.8, height: self.view.bounds.height * 0.6) self.present(vc, animated: true, completion: nil) } } } }
Running the iOS MRZ Scanner App
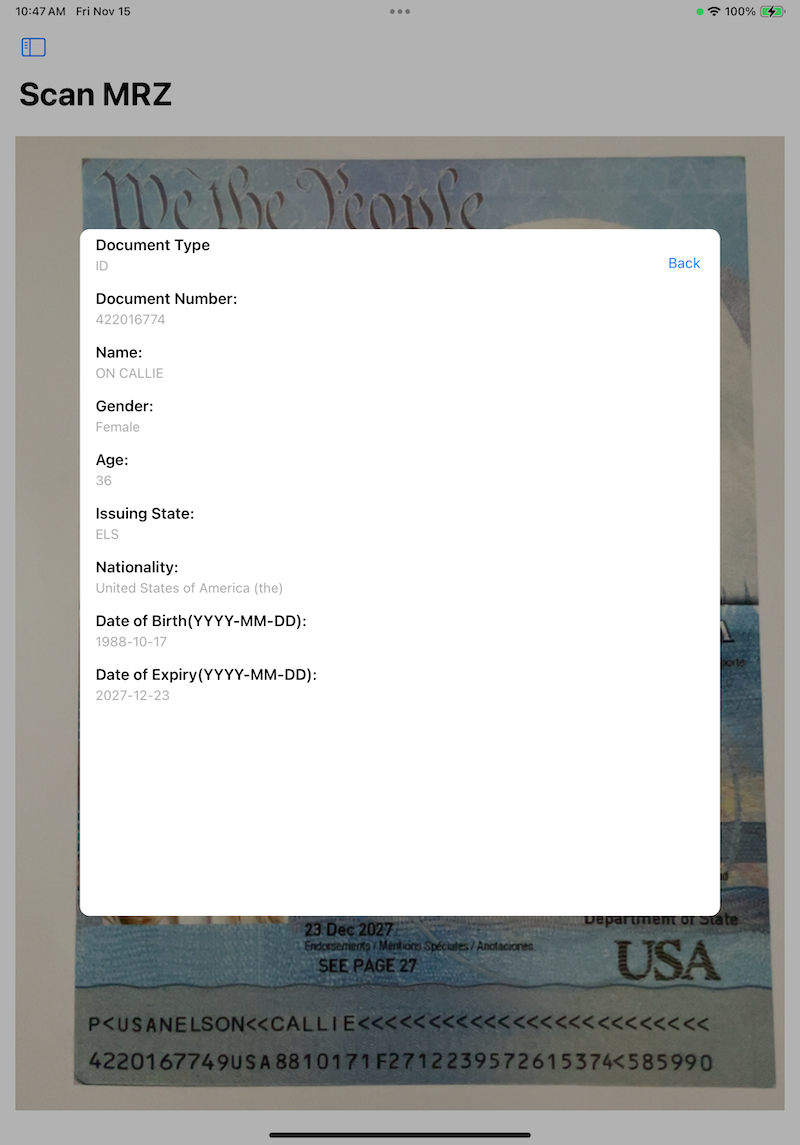
Connect your iOS device and run the app. You will see a button labeled Scan MRZ. Tap the button to open the camera and scan the MRZ on a passport or ID card. The scanned MRZ result will be displayed in a popup dialog.
Source Code
https://github.com/yushulx/ios-swiftui-barcode-mrz-document-scanner/tree/main/examples/mrz