How to Build a macOS Barcode Scanner App Using SwiftUI and C++ Barcode SDK from Scratch
Developing a barcode scanner app for macOS comes with unique challenges, particularly due to the limited availability of barcode SDKs specifically designed for the platform. Fortunately, the Dynamsoft Capture Vision SDK provides a powerful and reliable solution, enabling developers to easily build barcode, MRZ, and document scanners using Python (powered by C++ under the hood). In this tutorial, we’ll leverage the C++ shared libraries wrapped in the Python SDK to build a macOS barcode scanner app step by step, transitioning from C++ to Objective-C and finally to Swift.
This article is Part 3 in a 6-Part Series.
- Part 1 - Creating an iOS Barcode and QR Code Scanner with SwiftUI on M1 Mac
- Part 2 - How to Build an iOS MRZ Scanner with SwiftUI and Dynamsoft Capture Vision
- Part 3 - How to Build a macOS Barcode Scanner App Using SwiftUI and C++ Barcode SDK from Scratch
- Part 4 - How to Create an iOS Barcode Scanner Project for macOS and iOS in SwiftUI
- Part 5 - How to Build a Document Scanner App with SwiftUI for Both macOS and iOS
- Part 6 - Building a macOS Framework with Objective-C++ and C++ for Swift Barcode Detection
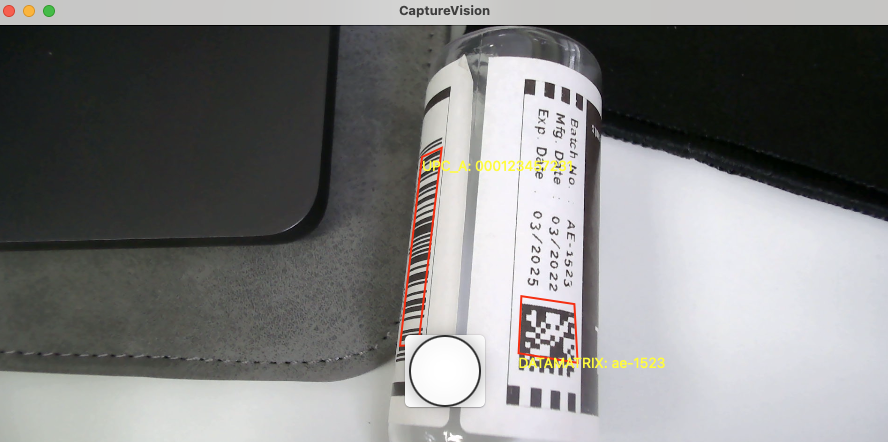
macOS 1D/2D Barcode Scanner Demo Video
Prerequisites
- Obtain a license key for the Dynamsoft Capture Vision SDK.
- Download the
.tar.tzpackage of the Dynamsoft Capture Vision SDK from pypi. This package contains header files, shared libraries and parameter templates for Windows, Linux, and macOS. Extract the*.h,*.dyliband*.jsonfiles from the package.
Setting Up a macOS Barcode Scanner Project
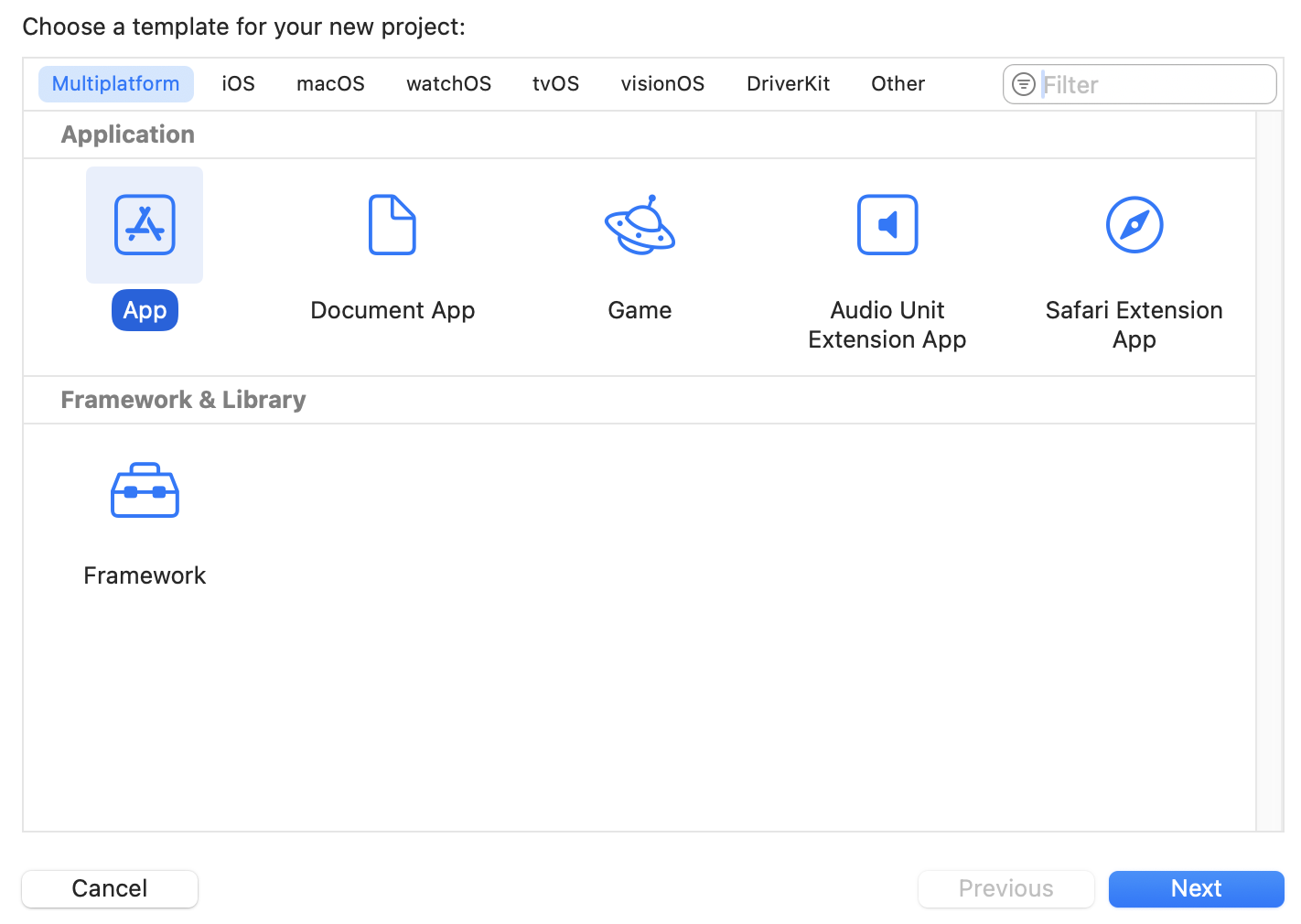
Since the current target of the project is macOS, with potential future extension to iOS, we’ll select the Multiplatform template when creating the project in Xcode.
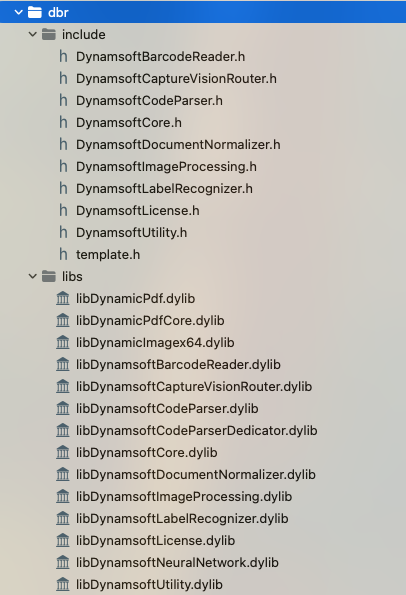
Next, copy the.h and .dylib files to a new folder named dbr and drag the folder into the project.
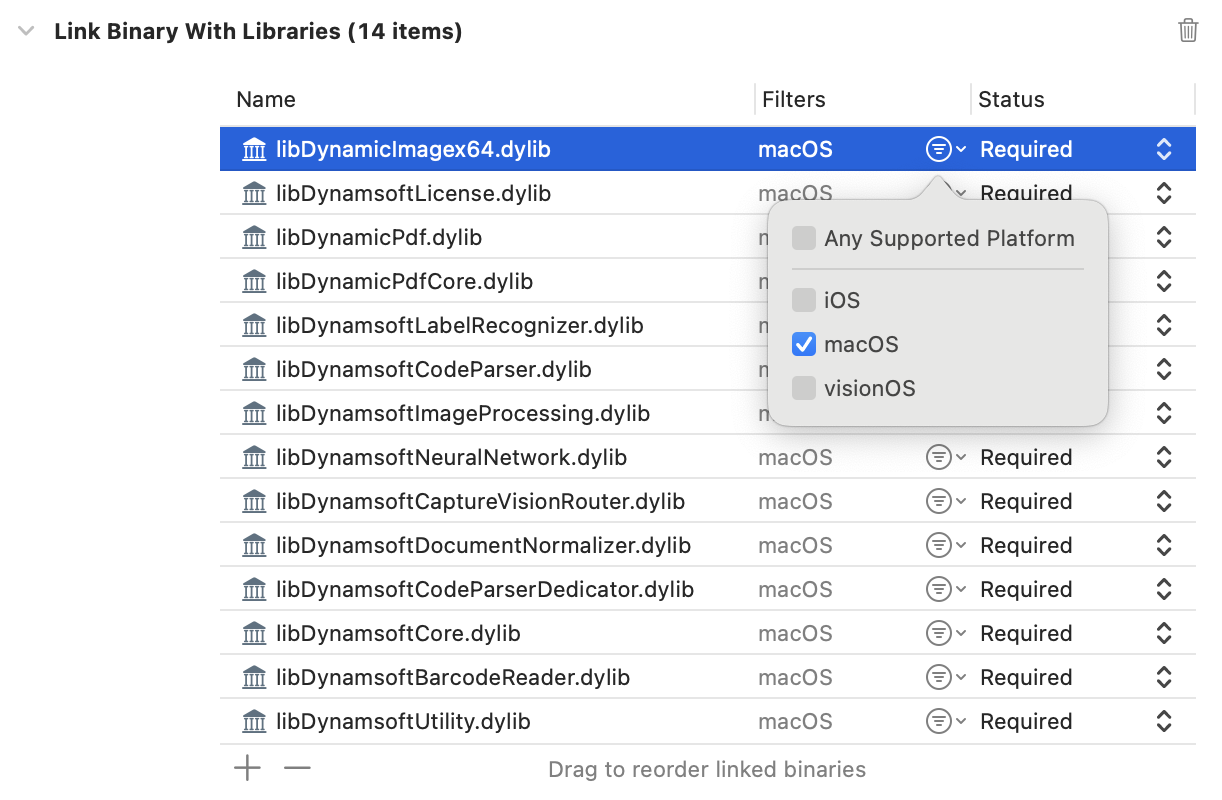
Navigate to Build Phases -> Link Binary With Libraries and add the *.dylib files. Ensure that the supported platform is set to macOS only.
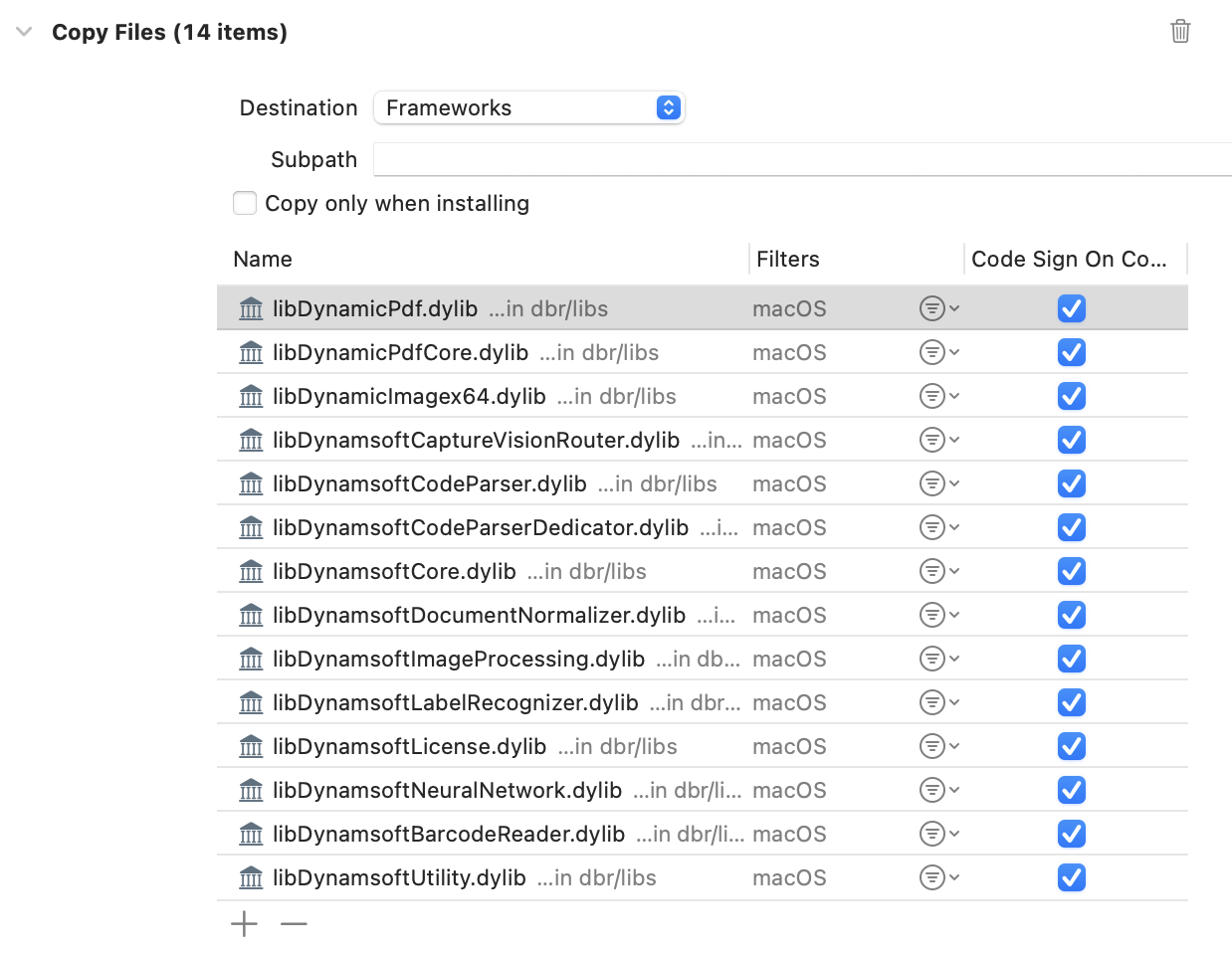
Click the + button and select New Copy Files Phase. Set the destination to Frameworks and add the *.dylib files. This step bundles the *.dylib files with the app.
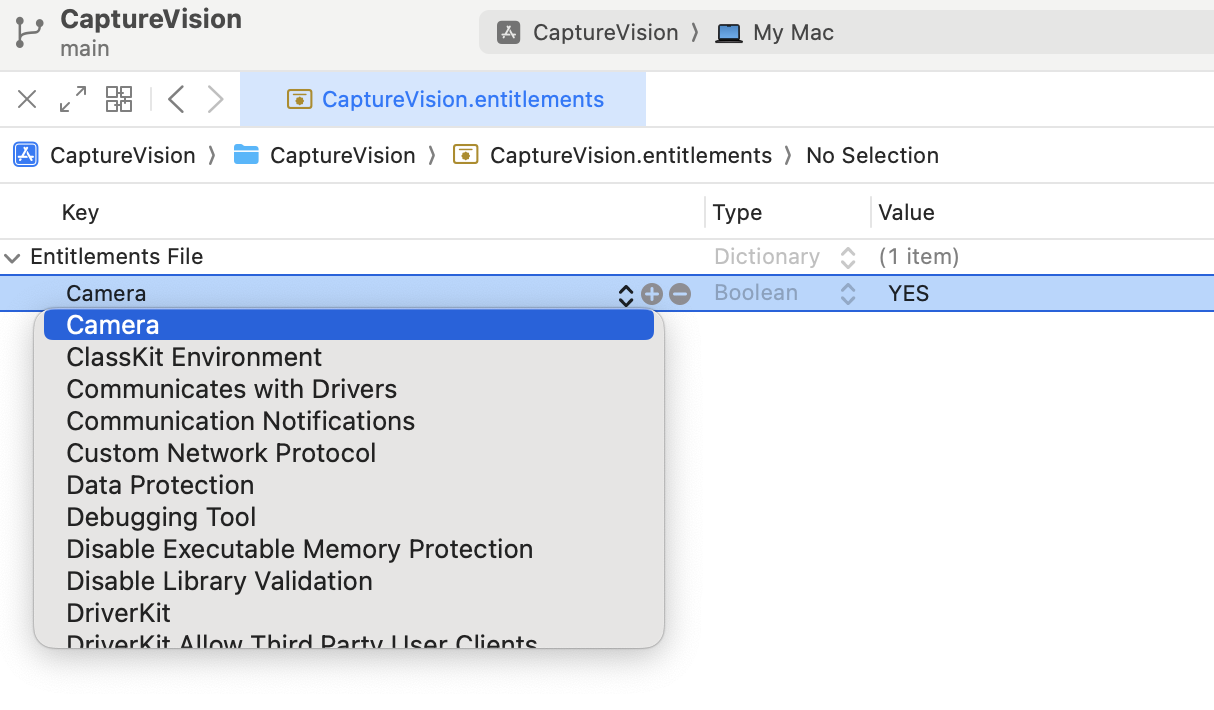
Finally, open the .entitlements file and add the camera permission for the macOS app.
Bridging C++ Barcode Detection API to Objective-C
To invoke C++ functions in Swift, we need to create an Objective-C++ wrapper.
-
Create an Objective-C bridging header file named
DCV-Bridging-Header.hand add the following code:#ifndef DCV_Bridging_Header_h #define DCV_Bridging_Header_h #ifdef __cplusplus #include "DynamsoftCaptureVisionRouter.h" #include "DynamsoftUtility.h" #include "template.h" using namespace dynamsoft::license; using namespace dynamsoft::cvr; using namespace dynamsoft::dbr; using namespace dynamsoft::utility; using namespace dynamsoft::basic_structures; #endif #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> @interface CaptureVisionWrapper : NSObject + (int)initializeLicense:(NSString *)licenseKey; - (NSArray *)captureImageWithData:(NSData *)imageData width:(int)width height:(int)height stride:(int)stride pixelFormat:(OSType)pixelFormat; @end #endifExplanation
- The code inside the
#ifdef __cplusplusblock includes headers (DynamsoftCaptureVisionRouter.h, DynamsoftUtility.h, and template.h) and uses C++ features like namespaces. These features are not compatible with plain C or Objective-C. Objective-C does not support C++ syntax directly. To allow this bridging header to be included in both Objective-C and C++ files, the C++-specific parts are guarded by#ifdef __cplusplus. - The
template.hfile contains a string of JSON settings for barcode detection. You can find the settings in the Dynamsoft Capture Vision bundle package.
- The code inside the
-
In
Build Settings, set theObjective-C Bridging Headerto the created header file.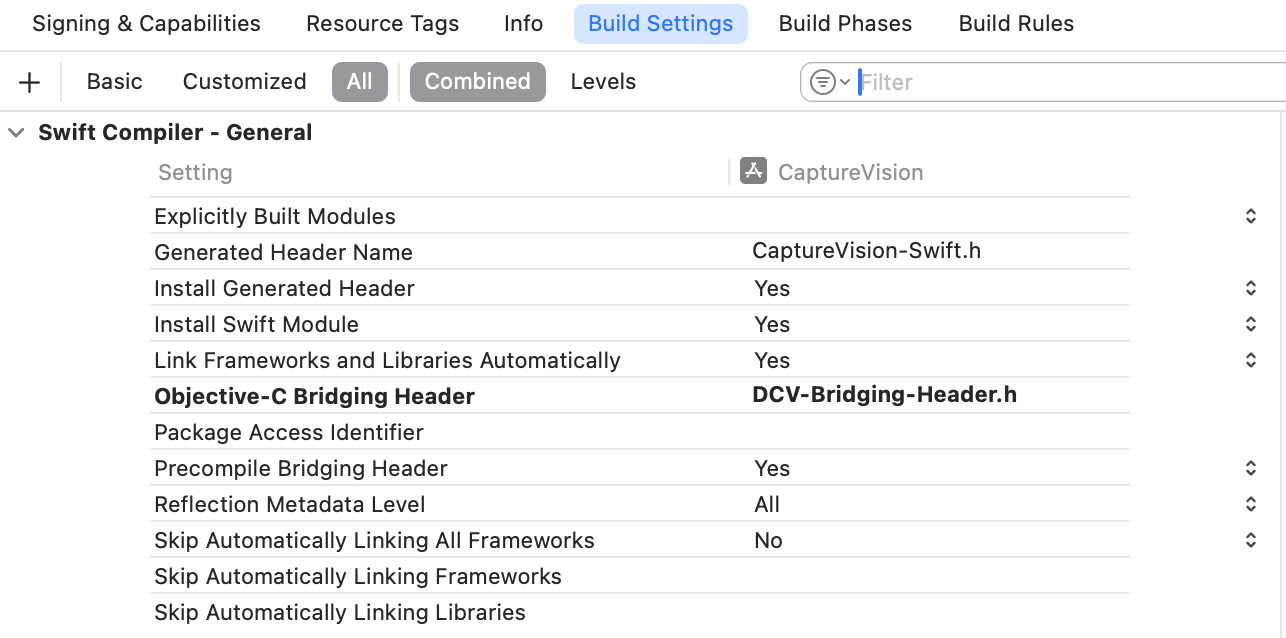
-
Create a
dcv.mmfile, which allows calling C++ functions, using C++ libraries, and interacting with C++ objects within Objective-C methods.-
Import the bridging header file:
#import <CoreVideo/CoreVideo.h> #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> #import "DCV-Bridging-Header.h" -
Initialize the license key:
@implementation CaptureVisionWrapper { CCaptureVisionRouter *cvr; } + (int)initializeLicense:(NSString *)licenseKey { char errorMsgBuffer[512]; const char *licenseCString = [licenseKey UTF8String]; int ret = CLicenseManager::InitLicense(licenseCString, errorMsgBuffer, sizeof(errorMsgBuffer)); if (ret != 0) { NSString *errorMessage = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:errorMsgBuffer]; NSLog(@"License initialization failed: %@", errorMessage); } else { NSLog(@"License initialized successfully"); } return ret; } -
Manage the lifecycle of the
CCaptureVisionRouterobject:- (instancetype)init { self = [super init]; if (self) { cvr = new CCaptureVisionRouter(); } char errorMsgBuffer[512]; int ret = cvr->InitSettings(jsonString.c_str(), errorMsgBuffer, sizeof(errorMsgBuffer)); if (ret != 0) { NSString *errorMessage = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:errorMsgBuffer]; NSLog(@"Init setting failed: %@", errorMessage); } return self; } - (void)dealloc { if (cvr) { delete cvr; cvr = nullptr; } } -
Convert the frame image format from
OSTypetoImagePixelFormat:- (ImagePixelFormat)mapPixelFormat:(OSType)pixelFormat { switch (pixelFormat) { case kCVPixelFormatType_32ARGB: return IPF_ARGB_8888; case kCVPixelFormatType_32BGRA: return IPF_ABGR_8888; default: return IPF_NV21; } } -
Decode barcodes from an image and return an array of barcode results:
- (NSArray *)captureImageWithData:(NSData *)imageData width:(int)width height:(int)height stride:(int)stride pixelFormat:(OSType)pixelFormat { ImagePixelFormat sdkPixelFormat = [self mapPixelFormat:pixelFormat]; CImageData *imageStruct = new CImageData(stride * height, (unsigned char *)[imageData bytes], width, height, stride, sdkPixelFormat); CCapturedResult *result = cvr->Capture(imageStruct, ""); if (result->GetErrorCode() != 0) { NSLog(@"Error code: %d", result->GetErrorCode()); } CDecodedBarcodesResult *barcodeResult = result->GetDecodedBarcodesResult(); if (barcodeResult == nullptr || barcodeResult->GetItemsCount() == 0) { NSLog(@"No barcode found"); delete imageStruct; return nil; } int barcodeResultItemCount = barcodeResult->GetItemsCount(); NSLog(@"Total barcode(s) found: %d", barcodeResultItemCount); NSMutableArray *barcodeArray = [NSMutableArray array]; for (int j = 0; j < barcodeResultItemCount; j++) { const CBarcodeResultItem *barcodeResultItem = barcodeResult->GetItem(j); const char *format = barcodeResultItem->GetFormatString(); const char *text = barcodeResultItem->GetText(); CPoint *points = barcodeResultItem->GetLocation().points; NSLog(@"Result %d", j + 1); NSLog(@"Barcode Format: %s", barcodeResultItem->GetFormatString()); NSLog(@"Barcode Text: %s", barcodeResultItem->GetText()); NSDictionary *barcodeData = @{ @"format" : [NSString stringWithUTF8String:format], @"text" : [NSString stringWithUTF8String:text], @"points" : @[ @{@"x" : @(points[0][0]), @"y" : @(points[0][1])}, @{@"x" : @(points[1][0]), @"y" : @(points[1][1])}, @{@"x" : @(points[2][0]), @"y" : @(points[2][1])}, @{@"x" : @(points[3][0]), @"y" : @(points[3][1])} ] }; [barcodeArray addObject:barcodeData]; } if (barcodeResult) barcodeResult->Release(); result->Release(); delete imageStruct; return [barcodeArray copy]; }
-
Creating a Camera View Controller in Swift
Create a CameraViewController.swift file and add the following code to set up a camera view:
import AVFoundation
import Accelerate
import SwiftUI
import Cocoa
typealias ViewController = NSViewController
typealias ImageType = NSImage
class CameraViewController: ViewController,
AVCaptureVideoDataOutputSampleBufferDelegate
{
var captureSession: AVCaptureSession!
var previewLayer: AVCaptureVideoPreviewLayer!
let cv = CaptureVisionWrapper()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
setupCamera()
}
func setupCamera() {
captureSession = AVCaptureSession()
guard let camera = AVCaptureDevice.default(for: .video) else {
print("Unable to access the camera!")
return
}
do {
let input = try AVCaptureDeviceInput(device: camera)
let videoOutput = AVCaptureVideoDataOutput()
videoOutput.videoSettings = [
kCVPixelBufferPixelFormatTypeKey as String: kCVPixelFormatType_32ARGB
]
videoOutput.setSampleBufferDelegate(self, queue: DispatchQueue(label: "videoQueue"))
if captureSession.canAddInput(input) && captureSession.canAddOutput(photoOutput) {
captureSession.addInput(input)
captureSession.addOutput(videoOutput)
previewLayer = AVCaptureVideoPreviewLayer(session: captureSession)
previewLayer.videoGravity = .resizeAspectFill
previewLayer.frame = view.bounds
view.layer = CALayer()
view.wantsLayer = true
view.layer?.insertSublayer(previewLayer, at: 0)
DispatchQueue.global(qos: .userInitiated).async {
self.captureSession.startRunning()
}
}
} catch {
print("Error Unable to initialize camera: \(error.localizedDescription)")
}
}
func captureOutput(
_ output: AVCaptureOutput,
didOutput sampleBuffer: CMSampleBuffer,
from connection: AVCaptureConnection
) {
guard let pixelBuffer = CMSampleBufferGetImageBuffer(sampleBuffer) else {
return
}
processCameraFrame(pixelBuffer)
}
func processCameraFrame(_ pixelBuffer: CVPixelBuffer) {
...
}
override func viewDidLayout() {
super.viewDidLayout()
if previewLayer != nil {
previewLayer.frame = view.bounds
}
}
}
Explanation
- The
CameraViewControllerclass subclassesNSViewControllerand conforms to theAVCaptureVideoDataOutputSampleBufferDelegateprotocol. - The
setupCameramethod initializes the camera and sets up video output for capturing frames. - The
captureOutputmethod processes video frames for further image handling.
Creating a SwiftUI Camera View
Create a CameraView.swift file to integrate the CameraViewController into a SwiftUI view hierarchy:
import AVFoundation
import SwiftUI
struct CameraView: NSViewControllerRepresentable {
func makeCoordinator() -> Coordinator {
Coordinator(self)
}
func makeNSViewController(context: Context) -> CameraViewController {
let cameraViewController = CameraViewController()
context.coordinator.cameraViewController = cameraViewController
return cameraViewController
}
func updateNSViewController(_ nsViewController: CameraViewController, context: Context) {
}
class Coordinator: NSObject {
var parent: CameraView
var cameraViewController: CameraViewController?
init(_ parent: CameraView) {
self.parent = parent
}
}
}
Explanation
makeCoordinatorcreates aCoordinatorinstance to facilitate communication betweenCameraViewandCameraViewController.makeNSViewControllerinitializes theCameraViewControllerto be embedded in the SwiftUI view.updateNSViewControllerallows dynamic updates toCameraViewControllerwhen theCameraViewstate changes.
Detecting Barcodes in Swift
Swift and Objective-C can interoperate seamlessly. In the processCameraFrame function,
we call the Objective-C++ wrapper to process the captured frames.
func processCameraFrame(_ pixelBuffer: CVPixelBuffer) {
CVPixelBufferLockBaseAddress(pixelBuffer, .readOnly)
let baseAddress = CVPixelBufferGetBaseAddress(pixelBuffer)
let width = CVPixelBufferGetWidth(pixelBuffer)
let height = CVPixelBufferGetHeight(pixelBuffer)
let bytesPerRow = CVPixelBufferGetBytesPerRow(pixelBuffer)
let pixelFormat = CVPixelBufferGetPixelFormatType(pixelBuffer)
if let baseAddress = baseAddress {
let buffer = Data(bytes: baseAddress, count: bytesPerRow * height)
let barcodeArray =
cv.captureImage(
with: buffer, width: Int32(width), height: Int32(Int(height)),
stride: Int32(Int(bytesPerRow)), pixelFormat: pixelFormat)
as? [[String: Any]] ?? []
...
}
CVPixelBufferUnlockBaseAddress(pixelBuffer, .readOnly)
}
Drawing Barcode Results with an Overlay View
To display barcode detection results in real-time, we overlay the bounding boxes on the camera preview.
-
Create a
BarcodeOverlayView.swiftfile and add the following code:import SwiftUI import Cocoa typealias OverlayView = NSView typealias OverlayColor = NSColor class BarcodeOverlayView: OverlayView { var barcodeData: [[String: Any]] = [] var cameraPreviewSize: CGSize = .zero override func draw(_ rect: CGRect) { guard cameraPreviewSize != .zero else { return } guard let context = NSGraphicsContext.current?.cgContext else { return } let overlaySize = bounds.size for barcode in barcodeData { guard let points = barcode["points"] as? [[String: NSNumber]], let format = barcode["format"] as? String, let text = barcode["text"] as? String else { continue } let convertedPoints = points.map { point -> CGPoint in let x = CGFloat(point["x"]!.doubleValue) let y = CGFloat(point["y"]!.doubleValue) return convertToOverlayCoordinates( cameraPoint: CGPoint(x: x, y: y), overlaySize: overlaySize) } context.setStrokeColor(OverlayColor.red.cgColor) context.setLineWidth(2.0) if let firstPoint = convertedPoints.first { context.beginPath() context.move(to: firstPoint) for point in convertedPoints.dropFirst() { context.addLine(to: point) } context.closePath() context.strokePath() } let labelRect = CGRect( x: convertedPoints[0].x, y: convertedPoints[0].y - 20, width: 200, height: 20 ) let paragraphStyle = NSMutableParagraphStyle() paragraphStyle.alignment = .left let attributes: [NSAttributedString.Key: Any] = [ .font: NSFont.systemFont(ofSize: 14), .foregroundColor: OverlayColor.yellow, .paragraphStyle: paragraphStyle, ] let attributedText = NSAttributedString( string: "\(format): \(text)", attributes: attributes) attributedText.draw(in: labelRect) } } private func convertToOverlayCoordinates(cameraPoint: CGPoint, overlaySize: CGSize) -> CGPoint { let cameraSize = cameraPreviewSize let scaleX = overlaySize.width / cameraSize.width let scaleY = overlaySize.height / cameraSize.height if scaleX < scaleY { let deltaX = CGFloat((cameraSize.width * scaleY - overlaySize.width) / 2) return CGPoint(x: cameraPoint.x * scaleY - deltaX, y: cameraPoint.y * scaleY) } else { let deltaY = CGFloat((cameraSize.height * scaleX - overlaySize.height) / 2) return CGPoint(x: cameraPoint.x * scaleX, y: cameraPoint.y * scaleX - deltaY) } } }Explanation
- The
drawmethod draws the barcode bounding boxes and text labels on the overlay view. - The
convertToOverlayCoordinatesconverts camera space coordinates to overlay space coordinates.
- The
-
In the
CameraViewControllerclass, add the following code to create an overlay view:var overlayView: BarcodeOverlayView! override func viewDidLoad() { super.viewDidLoad() overlayView = BarcodeOverlayView() overlayView.wantsLayer = true overlayView.layer?.backgroundColor = NSColor.clear.cgColor overlayView.frame = view.bounds view.addSubview(overlayView, positioned: .above, relativeTo: nil) setupCamera() } override func viewDidLayout() { super.viewDidLayout() if previewLayer != nil { previewLayer.frame = view.bounds } if overlayView != nil { overlayView.frame = view.bounds } } func processCameraFrame(_ pixelBuffer: CVPixelBuffer) { let previewWidth = CVPixelBufferGetWidth(pixelBuffer) let previewHeight = CVPixelBufferGetHeight(pixelBuffer) DispatchQueue.main.async { [weak self] in guard let self = self else { return } self.overlayView.cameraPreviewSize = CGSize(width: previewWidth, height: previewHeight) } let flippedPixelBuffer = flipVertically(pixelBuffer: pixelBuffer) ?? pixelBuffer CVPixelBufferLockBaseAddress(flippedPixelBuffer, .readOnly) let baseAddress = CVPixelBufferGetBaseAddress(flippedPixelBuffer) let width = CVPixelBufferGetWidth(flippedPixelBuffer) let height = CVPixelBufferGetHeight(flippedPixelBuffer) let bytesPerRow = CVPixelBufferGetBytesPerRow(flippedPixelBuffer) let pixelFormat = CVPixelBufferGetPixelFormatType(flippedPixelBuffer) if let baseAddress = baseAddress { let buffer = Data(bytes: baseAddress, count: bytesPerRow * height) let barcodeArray = cv.captureImage( with: buffer, width: Int32(width), height: Int32(Int(height)), stride: Int32(Int(bytesPerRow)), pixelFormat: pixelFormat) as? [[String: Any]] ?? [] DispatchQueue.main.async { [weak self] in guard let self = self else { return } self.overlayView.barcodeData = barcodeArray self.overlayView.setNeedsDisplay(self.overlayView.bounds) } } CVPixelBufferUnlockBaseAddress(flippedPixelBuffer, .readOnly) } func flipVertically(pixelBuffer: CVPixelBuffer) -> CVPixelBuffer? { CVPixelBufferLockBaseAddress(pixelBuffer, .readOnly) guard let srcBaseAddress = CVPixelBufferGetBaseAddress(pixelBuffer) else { CVPixelBufferUnlockBaseAddress(pixelBuffer, .readOnly) return nil } let width = CVPixelBufferGetWidth(pixelBuffer) let height = CVPixelBufferGetHeight(pixelBuffer) let bytesPerRow = CVPixelBufferGetBytesPerRow(pixelBuffer) var srcBuffer = vImage_Buffer( data: srcBaseAddress, height: vImagePixelCount(height), width: vImagePixelCount(width), rowBytes: bytesPerRow ) guard let dstData = malloc(bytesPerRow * height) else { CVPixelBufferUnlockBaseAddress(pixelBuffer, .readOnly) return nil } var dstBuffer = vImage_Buffer( data: dstData, height: vImagePixelCount(height), width: vImagePixelCount(width), rowBytes: bytesPerRow ) vImageVerticalReflect_ARGB8888(&srcBuffer, &dstBuffer, 0) CVPixelBufferUnlockBaseAddress(pixelBuffer, .readOnly) var flippedPixelBuffer: CVPixelBuffer? CVPixelBufferCreate( nil, width, height, CVPixelBufferGetPixelFormatType(pixelBuffer), nil, &flippedPixelBuffer ) if let flippedPixelBuffer = flippedPixelBuffer { CVPixelBufferLockBaseAddress(flippedPixelBuffer, .readOnly) memcpy( CVPixelBufferGetBaseAddress(flippedPixelBuffer), dstBuffer.data, bytesPerRow * height) CVPixelBufferUnlockBaseAddress(flippedPixelBuffer, .readOnly) } free(dstData) return flippedPixelBuffer }Explanation
- The
flipVerticallyfunction flips the camera frame vertically before passing it to the C++ barcode detection function, ensuring that the barcode detection results are displayed accurately.
- The
Running the macOS Barcode Scanner App
Run the macOS barcode scanner app in Xcode to see the results:



